Introduction
College Dropout Statistics: Leaving College before finishing a degree happens more often than many people realise, and the numbers are surprising. Each year, millions of students drop out of College, which can lead to long-term financial difficulties, limited career options, and unfulfilled personal goals. Some of the main reasons include high tuition costs, challenging coursework, and inadequate support.
These dropout rates reveal serious issues within the education system that impact not only students but also their families and the U.S. economy. In this article,” College Dropout Statistics, we’ll look at the latest college dropout stats, the most common reasons students quit, how dropout rates differ by gender and race, and how leaving College early can affect future income. Knowing these facts can help students, parents, and schools make better decisions about higher education.
Editor’s Choice
- Nearly 23.3% of first-time, full-time, first-year college students leave school during their first year.
- On average, people who don’t finish College make 35% less money than those who earn a bachelor’s degree.
- Those without a degree are 20% more likely to be unemployed than people with any college diploma.
- Each year, around 32.9% of college students drop out.
- The total number of college dropouts in the U.S. is about 43.3 million, which is a 3.6% increase from the year before.
- California has the largest share of college dropouts, with 15.27%, or roughly 6.6 million people.
- College dropouts have a jobless rate of 6.4%, while college grads face just 3.6% unemployment. Among men, it’s 4.8%, and for women, it’s 5.9%.
- People without a degree make about USD 39,900 per year, while those with a bachelor’s or higher earn around USD 91,000 —a difference of 56.15%.
- Community colleges produce the highest number of dropouts, accounting for 58.3% of the total.
- Students attending school full-time are less likely to drop out than part-time learners.
General College Dropout Statistics
- College dropouts are 25% more likely to be unemployed than degree holders.
- College dropouts have a median 35% lower than degree holders.
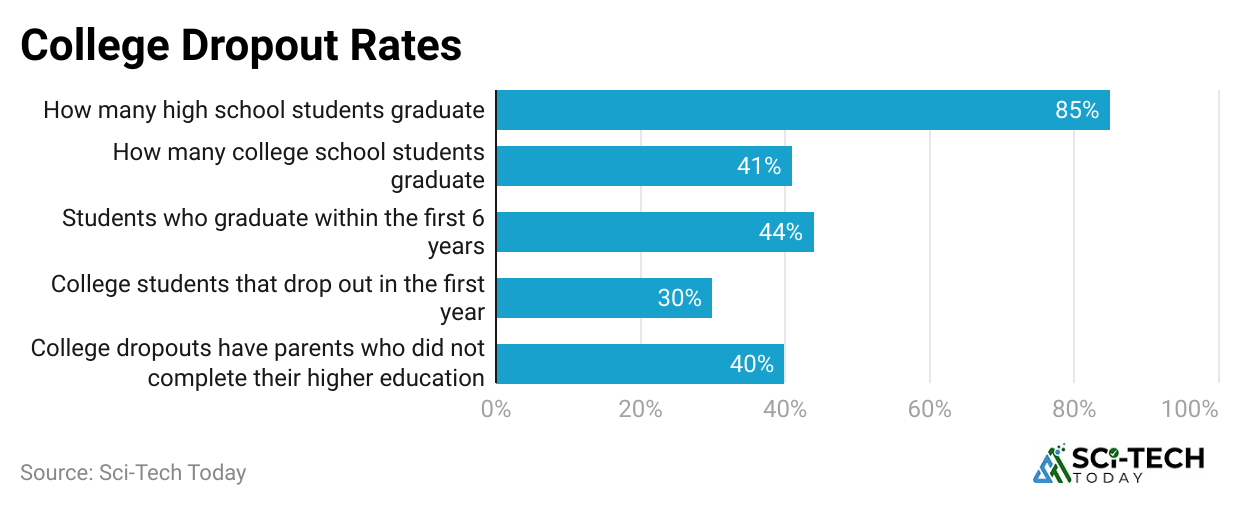
- Around 41.9 million residents of the United States were college dropouts, as per the July 2024 survey.
- First-time full-time undergraduate freshers have a 12-month dropout rate of 23.3%.
- College Dropout Statistics stated that 67% of the overall population was under 35 years old when they last attended College.
- Nearly 32% of people currently aged 35 are college dropouts.
- For the recent undergraduates, there are 2 SCNCs nationwide.
- Around 2 to 3% of all SCNCs re-enroll in their basic degree, as granted by the institute.
- Workers with college experience but no degree have an unemployment rate of 3.3%, which is almost 10 percentage points higher than the national average.
- Employees aged 25 and older with a college degree earn a median of USD992 per week, which is approximately 17.9% less than the median weekly earnings of all employees.
- Employees aged 25 and older with college experience but no degree earn almost 6.7% less than degree holders on average.
- College students aged 35 to 64 are less likely to drop out compared to those under 35. Women have higher dropout rates up to age 24, but after turning 25, more men tend to leave College.
 (Reference: thinkimpact.com)
(Reference: thinkimpact.com)
- California has the highest number of college dropouts in the country.
- In Alaska, there are nearly six dropouts for every student currently in College—the highest dropout-to-enrollment ratio in the U.S.
- In Texas, only 8% of college dropouts were last enrolled between the ages of 45 and 64. That’s the lowest rate for that age group in any state.
- Mississippi has the highest rate of dropouts under the age of 25, with 61.3% of students leaving College before reaching that age.
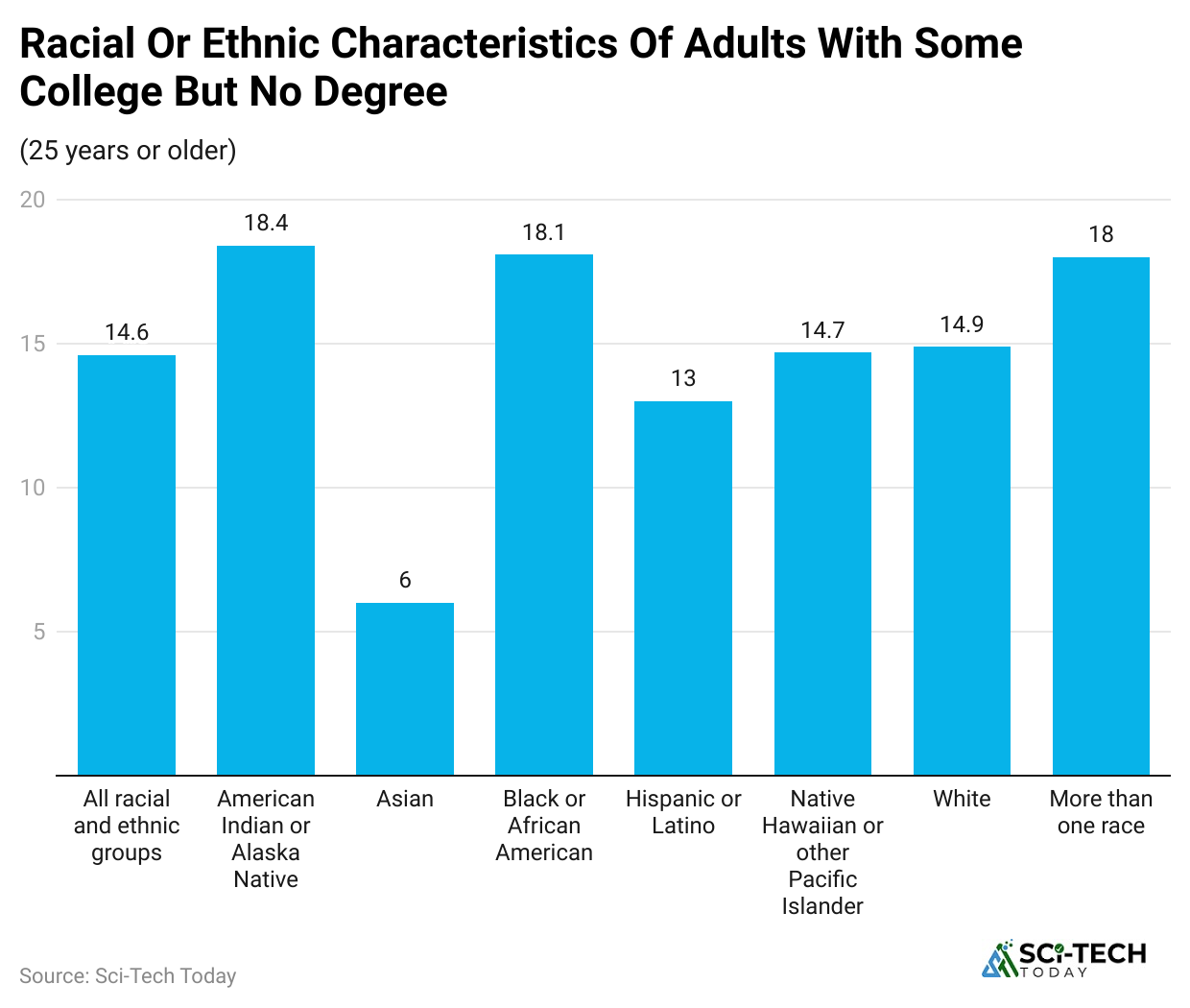
- Looking at race, Asian students make up 2.6% of all dropouts, which is the third lowest.
- Native American students account for 1.0%, the second lowest.
- Black students make up 14.1% of dropouts, while White students represent the largest group at 32.9%.
College Dropout Demographic Statistics
- Reports show that Asian students are the least likely to drop out of College, while Black students are more likely to leave school before finishing a degree.
- Below is a summary of college dropout data and graduation trends by race:
 (Reference: research.com)
(Reference: research.com)
#1. Asian Students
- 8% of Asian students earn their bachelor’s degree within 5 years—the highest of all groups. They make up just 2.6% of all college dropouts.
- A 2024 report by the American Council on Education shows that Asian adults (25 and older) have the highest education levels:
-1% have a bachelor’s degree
-3% earned a master’s degree
-9% completed a professional or doctorate
- Only 7.7% have some college but didn’t graduate.
#2. White/Caucasian Students
- 6% of White students finish College within 5 years.
- They account for 32.9% of all students who drop out of school.
- 6% of all college graduates in the U.S. are White.
- 9% of White adults (25 and older) have some college education but no degree.
#3. Hispanic/Latino Students
- 4% of Hispanic students earn their bachelor’s within 5 years.
- A 2023 Gallup poll found that 43% of Hispanic college students had thought about quitting school.
- 59% of Hispanic adults say financial aid and scholarships are very important for going to College.
- 13% of Hispanic adults (25 and older) started College but didn’t finish.
#4. American Indian/Alaska Native Students
- Just 43.4% finish a bachelor’s degree in 5 years—the lowest rate among all groups.
- They represent 1% of total dropouts.
- Only 0.5% of U.S. college graduates belong to this group.
- 4% of Native American adults (25 years and older) have some college education but no degree.
#5. Black/African American Students
- 6% of Black students complete their degree within 5 years.
- They make up 14.1% of all college dropouts.
- In the same 2023 Gallup survey, 40% of Black students reported having considered dropping out in the past six months.
- 1% of Black adul25 and older(2attended collegelege but didn’t finish.
#6. Multiracial Students
- 4% finish their bachelor’s degree in 5 years.
- People of two or more races make up 3.7% of all college graduates.
- Eighteen per cent of multiracial adults (25+) have some college experience without a degree.
#7. Graduation Rates for Men and Women by School Type
- At public universities, 66.2% of women earn their degrees, compared to 60.2% of men.
- In private nonprofit colleges, 71.9% of women graduate, while 64.6% of men finish their programs.
- In private for-profit schools, 34.5% of men graduate, compared to 32.8% of women.
#8. Enrolment and Re-enrolment Trends by Gender
- 6% of young men who recently finished high school enrolled in College.
- Out of all college dropouts who return to school, 40.4% are men.
- 3% of recent female high school grads went on to College.
- Women make up 56.6% of those who come back to College after dropping out.
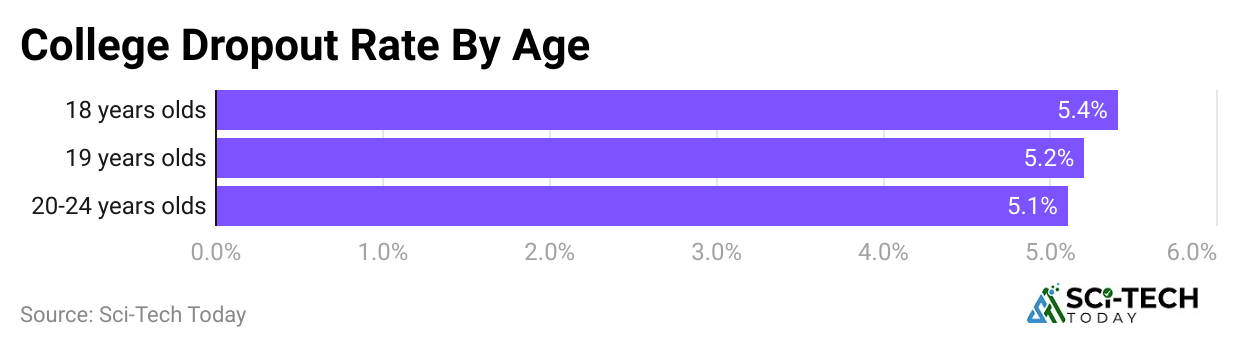 (Reference: essayhub.com)
(Reference: essayhub.com)
- Around 5.4% of 18-year-olds drop out, and the number slightly decreases to 5.2% by age 19. Moving from high school to College is more difficult than many expect.
- For students between the ages of 20 and 24, the dropout rate decreases slightly to 5.1%.
Students who are at high risk of dropping out of College
- College Dropout Statistics stated that 30% of students who seriously considered quitting school cited money issues as the main reason.
- 53% of students at risk of dropping out said they struggled to cover tuition costs, compared to 21% of students who were doing well.
- 57% of at-risk students worked at off-campus jobs, while only 38% of students on track to finish school did the same.
- Just 31% of at-risk students said their mental health was excellent or good, compared to 61% of students who were on track.
- 18% of students said mental health problems were a key reason they considered leaving College.
Let us check the college dropout risk factors in 2024:
| Students Category | On Track | At Risk | Considered Leaving |
|
No Payment Plan |
51% | 34% | 15% |
| Had a College Payment Plan | 76% | 15% |
9% |
|
High Income |
76% | 16% | 8% |
| Middle Income | 69% | 18% |
13% |
|
Low Income |
54% | 33% | 13% |
| Not First-Generation | 70% | 18% |
12% |
|
First-Generation |
45% | 41% | 14% |
| Hispanic | 56% | 31% |
13% |
|
Black |
60% | 31% | 9% |
| White | 67% | 21% |
12% |
|
Overall |
64% | 24% |
12% |
Highest Dropout Rate by State Statistics
- California has the highest number of college dropouts in the country, with approximately 5.8 million people, accounting for 15.8% of all dropouts in the U.S. Texas is second with 2.5 million (6.9%), and New York is third with 1.8 million (5.1%).
- The top 5 states together account for 36.4% of the total college dropouts in the U.S. California alone has more dropouts than the combined total of the lowest 20 states.
- The following are the top 10 states with the highest college dropout rate:
| Rank | State | Total Dropouts | % of U.S TOTAL |
|
10 |
Washington | 951,263 | 2.6% |
| 9 | North Carolina | 981,707 |
2.7% |
|
8 |
Pennsylvania | 1,023,642 | 2.8% |
| 7 | Michigan | 1,067,715 |
2.9% |
|
6 |
Ohio | 1,256,009 | 3.4% |
| 5 | Florida | 1,561,133 |
4.2% |
|
4 |
Illinois | 1,631,475 | 4.4% |
| 3 | New York | 1,893,457 |
5.1% |
|
2 |
Texas | 2,556,544 | 6.9% |
| 1 | California | 5,830,613 |
15.8% |
- C. has the lowest dropout rate worldwide, with just 35,515 dropouts.
- The Northeastern states generally exhibit lower-than-median rates, whereas the Southern states display a mixed range of results, with some high numbers but a lower rate relative to their population.
Common reasons for dropout Statistics
 (Reference: essayhub.com)
(Reference: essayhub.com)
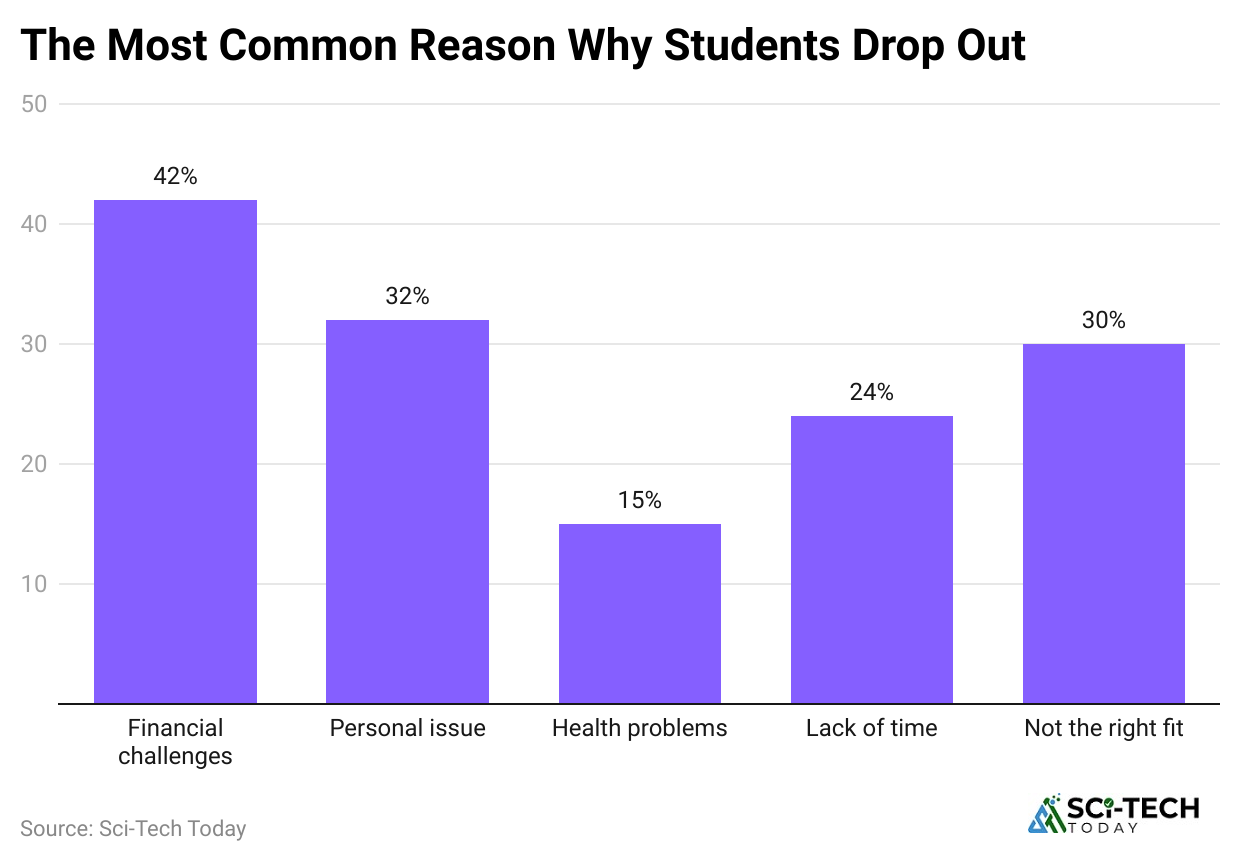
- Financial Struggles: About 42% of students in the U.S. say they left College because it was too expensive. This shows just how high the cost of College can be—almost unbelievably so.
- Personal and Family Problems: Approximately 32% of students drop out because issues at home or in their personal lives make it too difficult to continue attending school.
- Health Problems: College life can take a toll on your body and mind. Roughly 15% of students leave school due to health issues, often from stress, poor sleep, or unhealthy habits.
- Lack of Time: 24% of students quit College because they don’t have enough time to handle school, work, and sometimes family duties all at once.
Economic Impact of College Dropout Statistics
- Over the last six years, more than 2 million students in the U.S. have failed to repay their student loans, according to data from Admissions.
- About 55% of students find it difficult to obtain the necessary funds for College, and 79% of them end up delaying their studies.
- Approximately 51% of students leave school because they can’t afford the tuition and fees.
- After graduating from high school, 53% of students from low-income families either delay College or don’t attend at all. In comparison, only 11% of students from higher-income homes skip College.
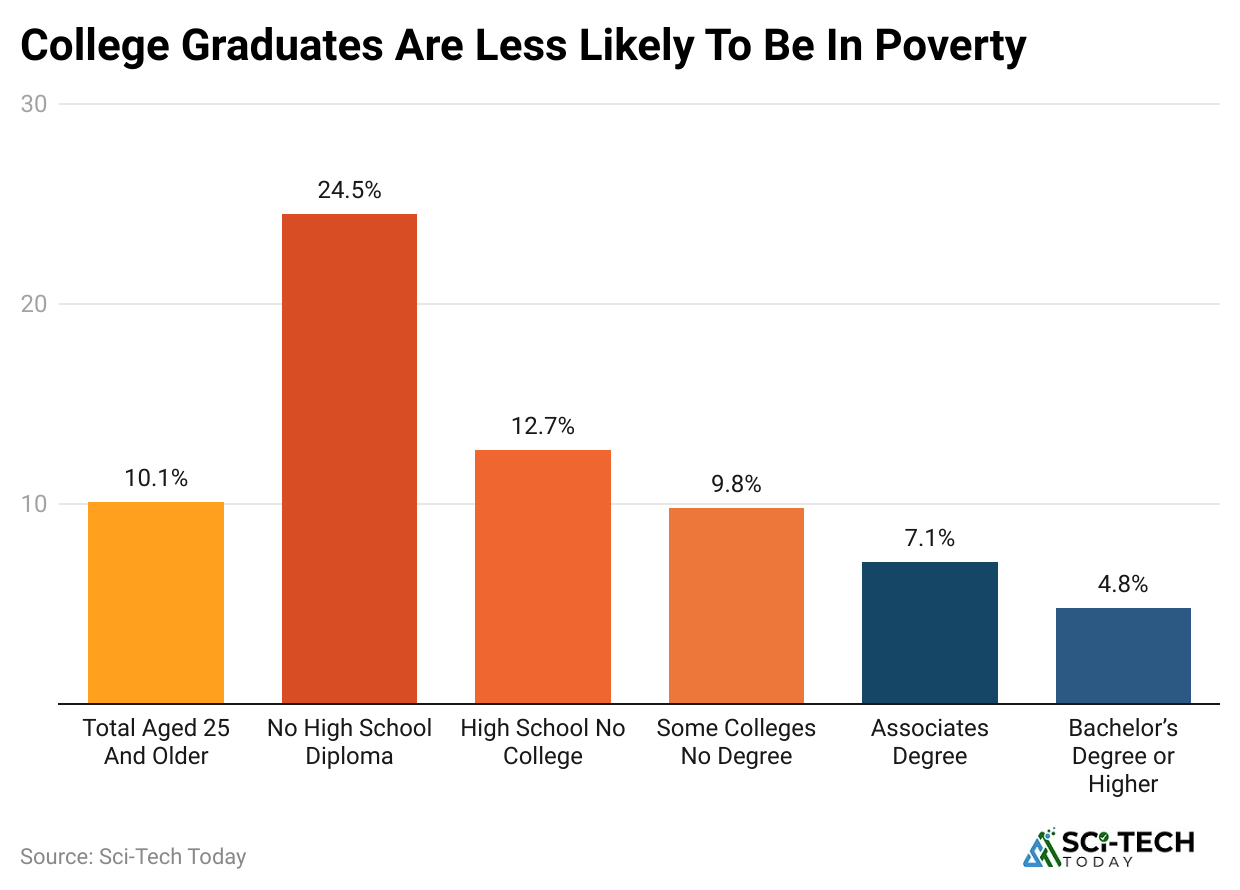
- According to an EDI report, 12.7% of people with only a high school diploma live below the poverty line, while just 4.8% of those with a bachelor’s degree are in the same situation.
- As of 2021, people aged 25 without a degree earned a median weekly wage of USD899, and their unemployment rate was 5.5%.
- On average, college dropouts make 35% less in yearly income than those who graduate.
- Recent numbers show that only 42% of students from low-income families are more likely to go for a 2-year associate degree, while just 32% choose to work toward a bachelor’s degree.
- Approximately 51% of these students enrol in programs that last two years or less.
When it comes to school choice:
- 28% of low-income students go to public colleges
- 18% attend community colleges
- 2% enroll in for-profit schools
Meanwhile, students from higher-income families make different choices:
- 54% go to public colleges
- 26% attend private schools
- 18% choose community colleges
- 2% pick for-profit institutions
College Dropout Employment Rates
- Employees with 25 years of experience and some college education but no degree earn a medium salary rate of around USD 935, with an unemployment rate of 3.5% among workers with
- This level of experience.
- College dropouts have an almost 43.6% higher income than high school diploma dropouts.
 (Reference: thirdway.org)
(Reference: thirdway.org)
- Employees with a complete bachelor’s degree have a salary 48.4% higher than those without a college degree.
- College dropouts earn almost 11.1% higher than the average salary of a worker who has completed only a high school diploma.
- Associate degree holders make around 7.1% more than workers aged 24 and above with some college experience but no degree.
- Employees above 24 years old and without a college degree earn a median of USD 899 per week, which is 14.9% less than the average.
College Dropout Rates of Students with Disabilities
- The students who suffer from depression don’t finish their degrees.
- College Dropout Statistics stated that almost 47% of the students who have schizophrenia leave College halfway.
- Around 49% of the students who have an A and are given enough medicine are prone to doubt the Count.
Community College Dropout Rates
- At community colleges, only 13% of students complete their degree.
- More than 85% of students take 2 years or more to graduate, while almost 22% graduate within 3 years and 28% within 4 years.
- More than 40% of the students who attend community college enroll in remedial classes.
- Almost 30% of college freshmen in the United States drop out of College before the year ends.
Share of Students with a bachelor’s degree by Family Income
 (Reference: coolest-gadgets.com)
(Reference: coolest-gadgets.com)
Dropout Rates by Family Income:
- If the family makes USD35,000 or less, about 52.4% of students leave College without finishing.
- Families earning USD35,001 to USD55,000 see a 41.8% dropout rate.
- Those with incomes between USD55,001 and USD75,000 have a 37.3% dropout rate.
- If income is between USD75,001 and USD115,000, about 31.4% of students drop out.
- Students from families with incomes of USD115,001 or more have the lowest dropout rate, at 23.9%.
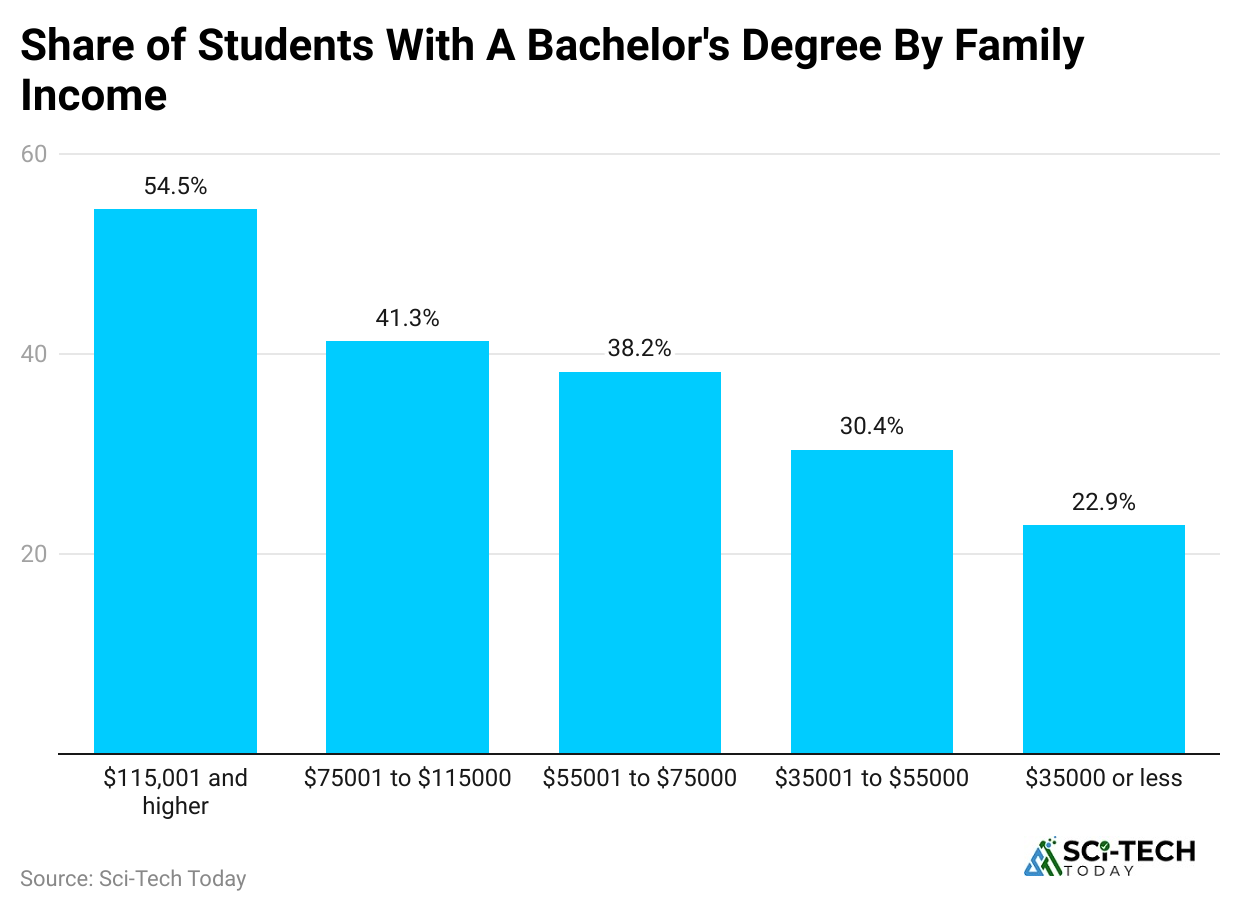
Graduation Rates by Income Level:
- Only 22.9% of students from families earning USD35,000 or less complete a bachelor’s degree.
- 30.4% of students from the USD35,001 to USD55,000 income group graduate.
- 38.2% of those from families making USD55,001 to USD75,000 earn a degree.
- Graduation goes up to 41.3% for families earning USD75,001 to USD115,000.
- Students from households with an income of USD115,001 or more have the highest graduation rate, at 54.5%.
- From families earning USD35,000 or less, only 60% of students enrol in college.
- Of those with a family income of USD115,000 or higher, 82% attend college.
- These are students whose parents didn’t attend College.
- Approximately 40% of them either consider dropping out or are at risk of not graduating.
Effects of College Dropout Rate Statistics
- People who are 25 or older and work full-time but didn’t finish College make about USD39,900 a year on average.
- Those who earn an associate’s degree usually make around USD41,000 per year.
- Workers with a bachelor’s degree or higher bring in about USD91,000 annually on average.
- Men who drop out of College earn about 35.3% less than men who finish their degrees.
- Male dropouts make around USD53,280 a year, while those with a degree earn between USD82,370 and USD142,340.
- Women who leave College early earn around 33.1% less than women who graduate.
 (Reference: coolest-gadgets.com)
(Reference: coolest-gadgets.com)
| College Graduates are less prone to poverty. | % |
|
Bachelor’s Degree or Higher |
4.8% |
| Associate degree |
7.1% |
|
Some Colleges have No Degree |
9.8% |
| High School No College |
12.7% |
|
No High School Diploma |
24.5% |
| Total Aged 25 and older |
10.1% |
- Women who leave College without finishing make about USD41,190 a year, while those who graduate earn between USD61,580 and USD100,460 a year.
- The jobless rate for people ages 25 to 64 without a college degree is 6.4%, compared to 3.6% for people who finished at least a bachelor’s degree.
- For men, the rate is 4.8%, and for women, it’s 5.9%.
- Colleges lose around USD16.5 billion each year in tuition when students drop out.
- People who drop out and have student loans are 4 times more likely to stop making payments than those who graduate.
- College dropout statistics state that only 53% of college dropouts have jobs, while 72% of college graduates are employed.
- Their average yearly pay is about USD30,000, while college graduates earn around USD52,000 per year.
- 26% of people who drop out work part-time, compared to just 16% of those who earn a degree.
Conclusion
Students who drop out of College may do so due to a lack of time, finances, lack of support, or high academic standards. College dropout numbers clearly show that leaving school early can lead to long-term financial and career struggles. Many students stop attending College due to financial difficulties, personal or family problems, or because they feel it’s not the right path for them.
Dropout rates are highest among low-income families, first-generation college students, and those attending part-time. People who don’t finish College usually earn less, face higher chances of being unemployed, and often work in lower-paying jobs compared to those with a degree
Overall, College Dropout Statistics demonstrate the importance of providing better financial aid, support systems, and career guidance to help students stay in school and graduate.
Sources
- Educationdata
- Research
- Quadc
- Coursmos
- Nces
- Educations
- Essayhub
- Economics
- Statista
- Statista
- Discoveryaba
- Missiongraduatenm
- Bestcolleges
- Prosperityforamerica
- Forbes
- Indiastat
- Rte
- Collegetransitions
- Skillademia
- Ontocollege
- Sci-Tech Today
- Admissionsly
- Coolest Gadgets
- Nutmegeducation
- Psychologytoday
- Graduateway


