Introduction
Climate change statistics: Have you thought about how serious climate change really is? Looking at these climate change statistics can give you a clear picture. These aren’t just abstract data; they reveal how our planet is heating up, how weather patterns are shifting, and how ecosystems, economies, and human lives are being affected.
From the rising global temperatures to melting ice caps and sea level rise, the statistics show that the effects of climate change are happening faster than many of us realize. Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent, wildfires are happening in larger areas, and natural disasters are costing billions of dollars every year.
By understanding these statistics, we don’t just see the problem; we see why action is urgent. In this article, I’ll walk you through all the key numbers, trends, and insights about climate change, helping you grasp the scale of this global crisis and why it matters to every one of us. Let’s get into it.
Editor’s Choice
- Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by 1 degree Celsius since the late 19th century, with 2024 among the hottest years recorded, highlighting rapid warming trends.
- CO₂ concentrations exceed 420 ppm, and global emissions in 2024 reached 6 billion tonnes, mainly from fossil fuels and deforestation, driving climate change.
- Global sea levels rise at 3 mm per year, threatening coastal cities and communities, and accelerating risks from storm surges and flooding.
- The frequency and severity of wildfires, heatwaves, and hurricanes have surged. In 2024, 158,000 hectares burned in Spain and Portugal, while heatwaves affected millions.
- Climate change is disrupting ecosystems worldwide, with 84% of coral reefs experiencing bleaching during the 2023 to 2025 event, threatening marine biodiversity.
- Rising temperatures and extreme weather increase heat stress, respiratory problems, and disease spread, with 2024 seeing 6 excessively humid days, putting millions at risk.
- Climate-related disasters cause trillions in damages globally, including billions from wildfires in Europe, hurricanes in the Caribbean, and agricultural losses worldwide.
- Efforts like the Paris Agreement target limiting warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, with countries investing in renewable energy, reforestation, and carbon capture to mitigate climate change.
| Topic | Key Statistic/Fact | Impact |
| Global Temperature | +1.1 degrees Celsius since the 1880s |
Accelerated global warming |
|
CO₂ Levels |
420 ppm | Major driver of climate change |
| Sea Level Rise | 3.3 mm/year |
Coastal flooding & erosion |
|
Extreme Weather |
158,000 hectares burned (2024 wildfires) | Property & ecosystem damage |
| Ecosystems | 84% coral reefs were bleached |
Biodiversity loss |
|
Human Health |
35.6 excessively humid days (2024) | Heat stress & disease risk |
| Economic Costs | Trillions globally |
Infrastructure & agriculture loss |
|
Global Initiatives |
Paris Agreement |
Reducing emissions & climate adaptation |
Global Temperature Rise
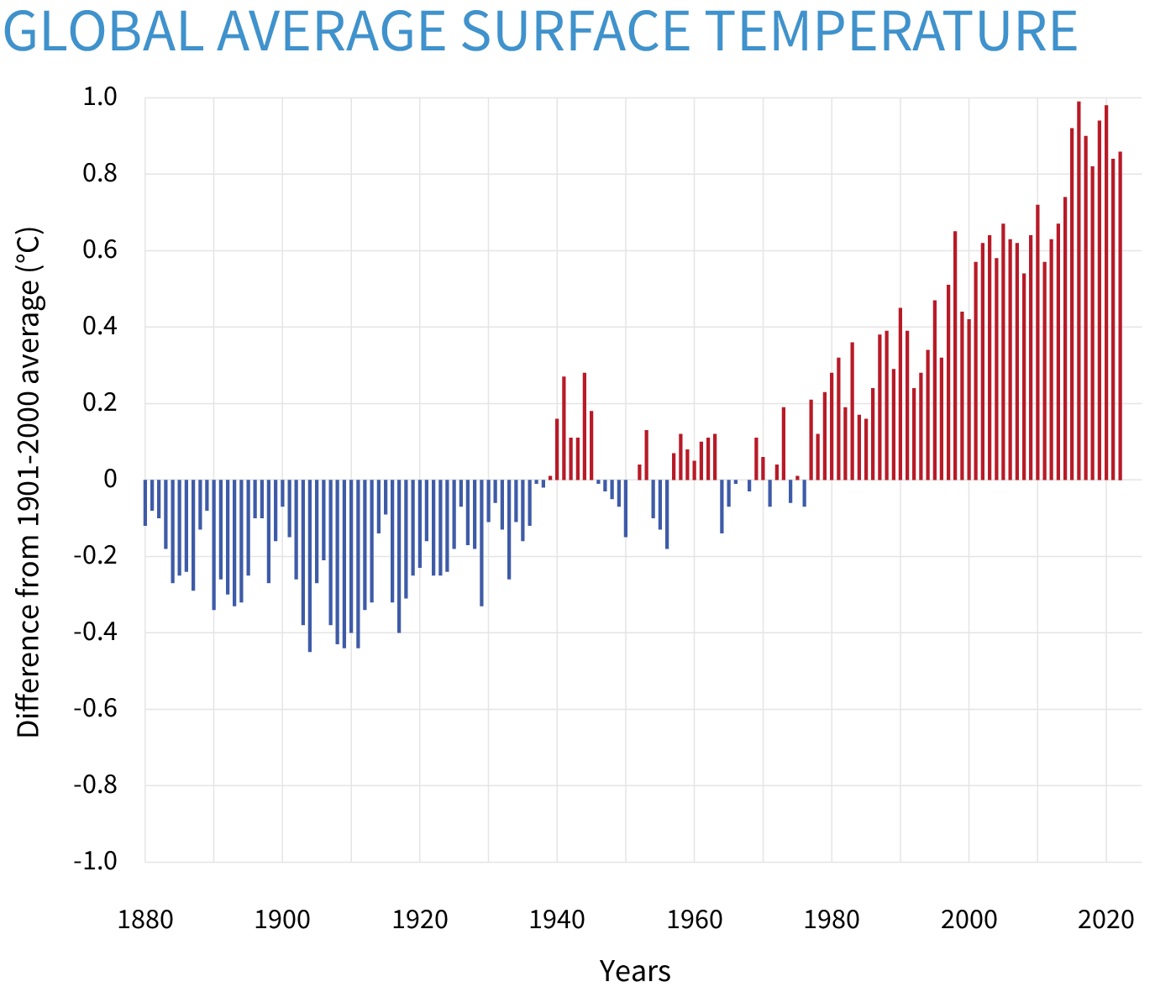 (Source: climate.gov)
(Source: climate.gov)
- The Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by about 1.1 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century, largely due to human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- The last decade has consistently been the hottest on record, with 2024 standing out as one of the warmest years ever recorded, emphasizing the accelerating pace of global warming.
| Metric | Statistic |
| Increase since the 1880s | +1.1 degrees Celsius |
| Hottest Decade | 2010 to 2019 |
| 2024 Temperature Anomaly | +1.47 degrees Celsius |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
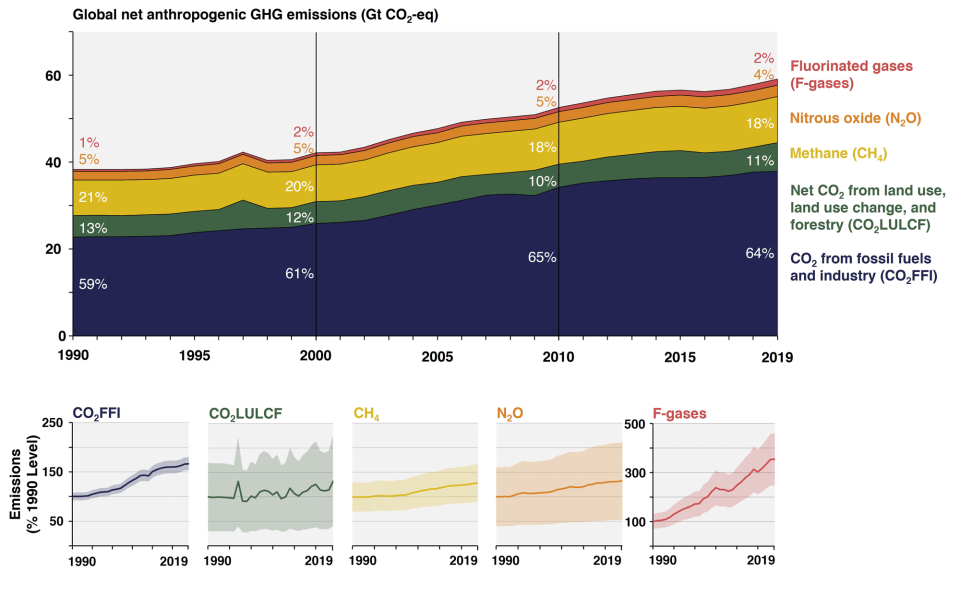 (Source: epa.gov)
(Source: epa.gov)
- Global greenhouse gas emissions continue to climb, with CO₂ concentrations reaching over 420 ppm, the highest level in over 3 million years.
- Annual CO₂ emissions in 2024 reached approximately 41.6 billion tonnes, contributing significantly to global warming and climate instability.
| Gas | Concentration/Emission | Impact |
| CO₂ | 420 ppm | Global warming |
| Methane | 1.9 ppm | 28x more warming than CO₂ |
| Annual CO₂ Emissions | 41.6 billion tonnes | Fossil fuels & deforestation |
Sea Level Rise
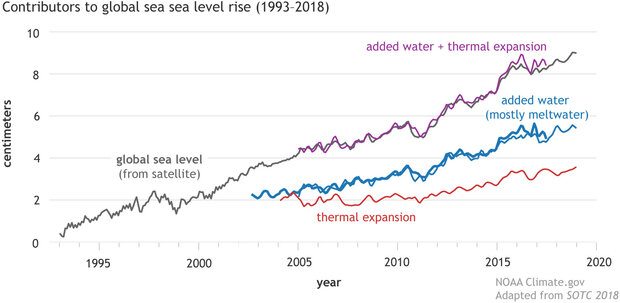 (Source: climate.gov)
(Source: climate.gov)
- Global sea levels are rising at about 3.3 mm per year, driven by melting ice sheets and the thermal expansion of oceans.
- Rising seas threaten coastal cities and communities, increasing the risk of flooding and eroding vital land resources.
| Metric | Statistic |
| Annual Rise | 3.3 mm/year |
| Ice Sheet Contribution | Greenland & Antarctica |
| Major Threat | Coastal flooding |
Extreme Weather Events
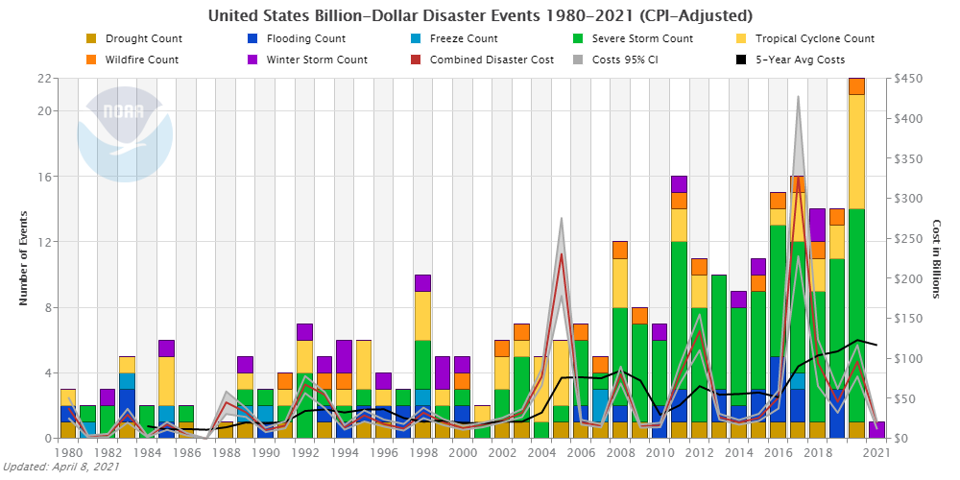 (Reference: forbes.com)
(Reference: forbes.com)
- The frequency of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, wildfires, and heatwaves, has increased dramatically over the past few decades.
- For example, in 2024, Spain and Portugal experienced wildfires burning over 158,000 hectares, while heatwaves affected millions across Europe and Asia.
| Event Type | Frequency/2024 Stats | Impact |
| Wildfires | 158,000 hectares burned (Spain & Portugal) | Property & ecosystem damage |
| Heatwaves | 35.6 excessively humid days | Human health risk |
| Hurricanes | Increased intensity | Coastal infrastructure damage |
Impact on Ecosystems
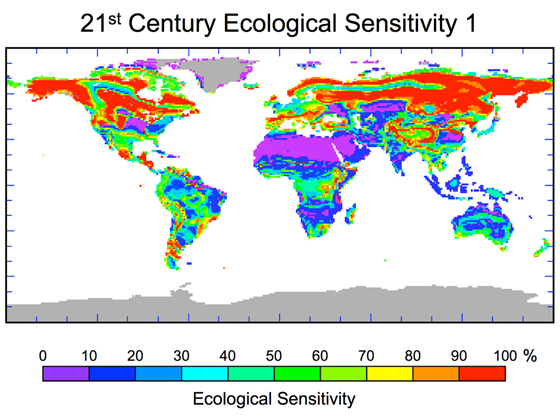 (Source: nasa.gov)
(Source: nasa.gov)
- Climate change disrupts ecosystems, causing habitat loss, coral bleaching, and species migration.
- About 84% of the world’s coral reefs experienced bleaching during the 2023 to 2025 global coral bleaching event, threatening marine biodiversity.
| Ecosystem | Effect | Statistic |
| Coral Reefs | Bleaching | 84% affected |
| Forests | Species migration & die-offs | Increasing |
| Wetlands | Reduced area | Rising temperatures & human impact |
Human Health Implications
 (Source: linkedin.com)
(Source: linkedin.com)
- Rising global temperatures and extreme weather directly impact human health, increasing heat-related illnesses and respiratory problems.
- Excessively humid days rose to 35.6 in 2024, posing risks of heat stroke and exacerbating vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue.
| Health Aspect | Statistic | Effect |
| Excessively Humid Days | 35.6 (2024) | Heat stress & illness |
| Vector-borne Diseases | Increasing | Malaria, Dengue expansion |
| Respiratory Illness | Higher due to pollution & heat | Increased hospitalizations |
Economic Costs of Climate Change
 (Source: wartsila.com)
(Source: wartsila.com)
- Climate change has caused trillions of dollars in damage globally due to extreme weather, agricultural loss, and infrastructure destruction.
- For instance, the 2024 wildfires in Europe alone caused billions of dollars in economic losses, affecting homes, businesses, and the tourism industry.
| Event | Economic Cost | Region |
| Wildfires | Billions USD | Spain & Portugal |
| Hurricanes | Billions USD | Caribbean & US |
| Agricultural Loss | Trillions globally | Worldwide |
Global Initiatives and Actions
- The Paris Agreement aims to limit warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, ideally 1.5 degrees Celsius, through national pledges to reduce emissions and transition to renewable energy.
- Many countries are implementing renewable energy projects, reforestation efforts, and climate adaptation policies to mitigate climate change risks.
| Initiative | Goal | Progress |
| Paris Agreement | Limit warming to 2 degrees Celsius | 193 countries signed |
| Renewable Energy Transition | Replace fossil fuels | Increasing adoption |
| Reforestation & Carbon Capture | Reduce CO₂ | Expanding programs |
Conclusion
Looking at all these climate change statistics, it’s clear that our planet is undergoing massive changes at a scary pace. From rising temperatures and greenhouse gas emissions to extreme weather events and ecological disruptions, the evidence shows that climate change is happening right now.
Understanding these statistics isn’t just about knowing the facts; it’s about realizing the urgency for action. By acknowledging the scale of the problem, supporting sustainable initiatives, and making informed choices, we can help slow down these trends and protect our planet for future generations. Every data point is a call to act, and together, we can make a difference. I hope you guys like this article. If you have any questions or need any clarification, kindly let me know in the comments section.


