Introduction
Sea Level Rise Statistics: I’m telling you, sea level rise is basically how the world’s oceans are slowly creeping higher. It might not sound like a big deal at first, but even a few inches of extra water can cause massive problems for cities, islands, and especially coastlines.
This sea level rise happens mainly because our planet is getting warmer. As the Earth heats up, glaciers and ice sheets melt, and the ocean water itself expands. This rise doesn’t happen the same everywhere; some areas see it faster than others.
It’s not just about water covering land; it affects people’s homes, fresh water supplies, farmland, and even the natural habitats of animals. By understanding these sea level rise statistics. We can better prepare for the challenges ahead, protect our communities, and find ways to adapt to a changing planet. Let’s get into it.
Editor’s Choice
- Since 1880, global sea levels have risen by 8 to 9 inches (21 to 24 cm), mainly due to melting glaciers and thermal expansion of seawater.
- The rate of sea level rise has doubled in the last three decades, currently averaging about 5 mm per year.
- In 2023, the global sea level reached 4 mm (3.99 inches) above the 1993 average, marking a record high.
- Thermal expansion contributes significantly to rising seas, as water expands with increasing temperature.
- Glaciers and ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica are losing mass rapidly; Greenland’s ice loss has increased by 50% from 2012 to 2023.
- Sea level rise is not uniform worldwide. U.S. coastlines: projected rise of 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm) by 2050, Europe: rise of 28 to 1.02 meters by 2100, depending on emissions, Asia: some of the fastest rises, especially in Bangladesh and India.
- Historical context: After the last ice age, sea levels rose by about 125 feet (38 meters) over several thousand years.
- Economic and social impacts are that coastal flooding and shoreline erosion are increasing, saltwater intrusion threatens freshwater supplies, and millions may be displaced, creating climate refugees.
- Projections for the future, by 2100, sea levels could rise up to 1.02 meters under high emissions, by 2150, some models estimate a rise up to 5 meters, depending on ice sheet stability.
- Mitigation strategies: reducing greenhouse gas emissions, building coastal defenses, ecosystem restoration, and, in some cases, managed retreat.
- Technological tools, such as satellites and coastal monitoring systems, are essential for tracking changes in real-time.
- Public awareness and education are crucial for communities to adapt and prepare for the impacts of rising seas.
Global Change in Sea Level From 1993-2008
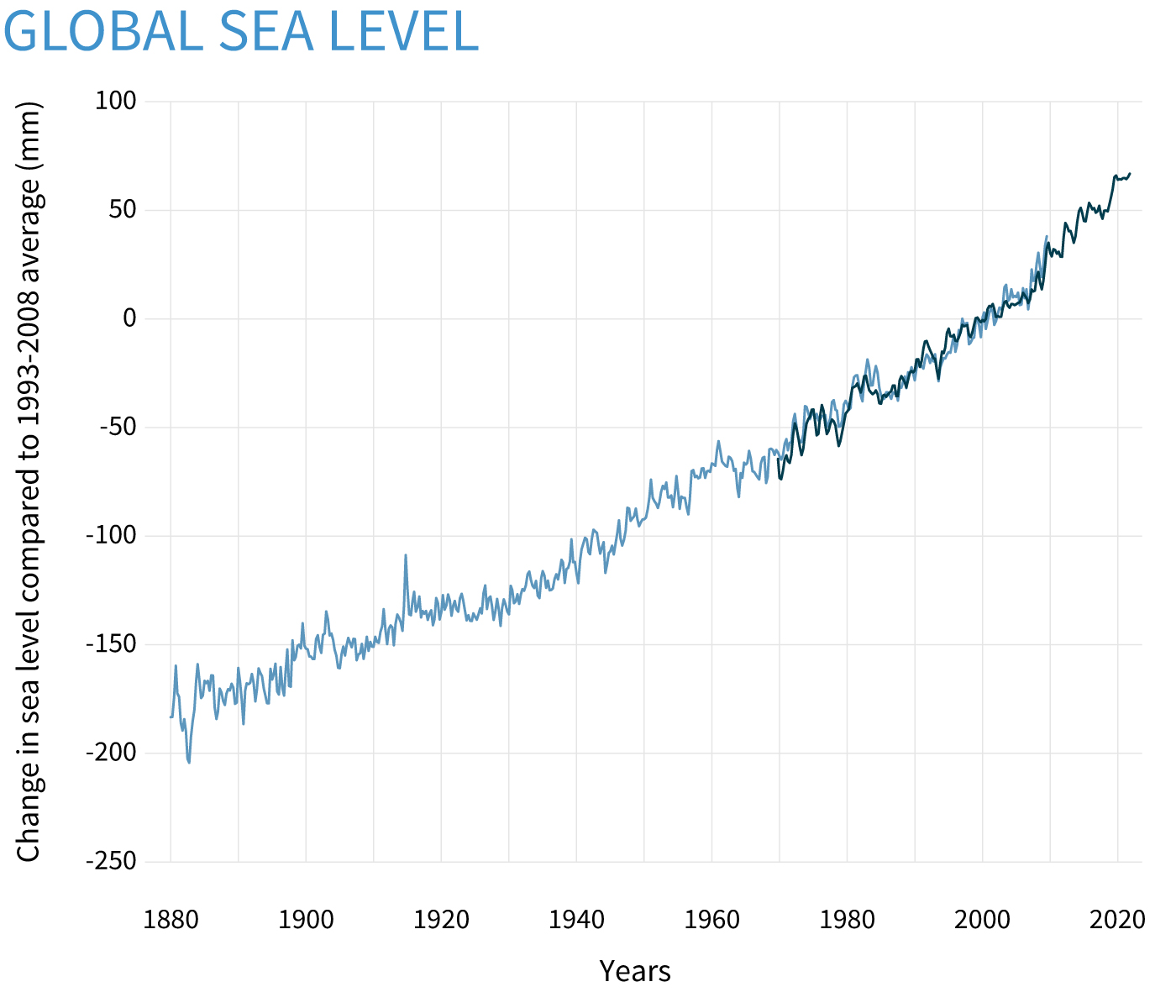 (Source: climate.gov)
(Source: climate.gov)
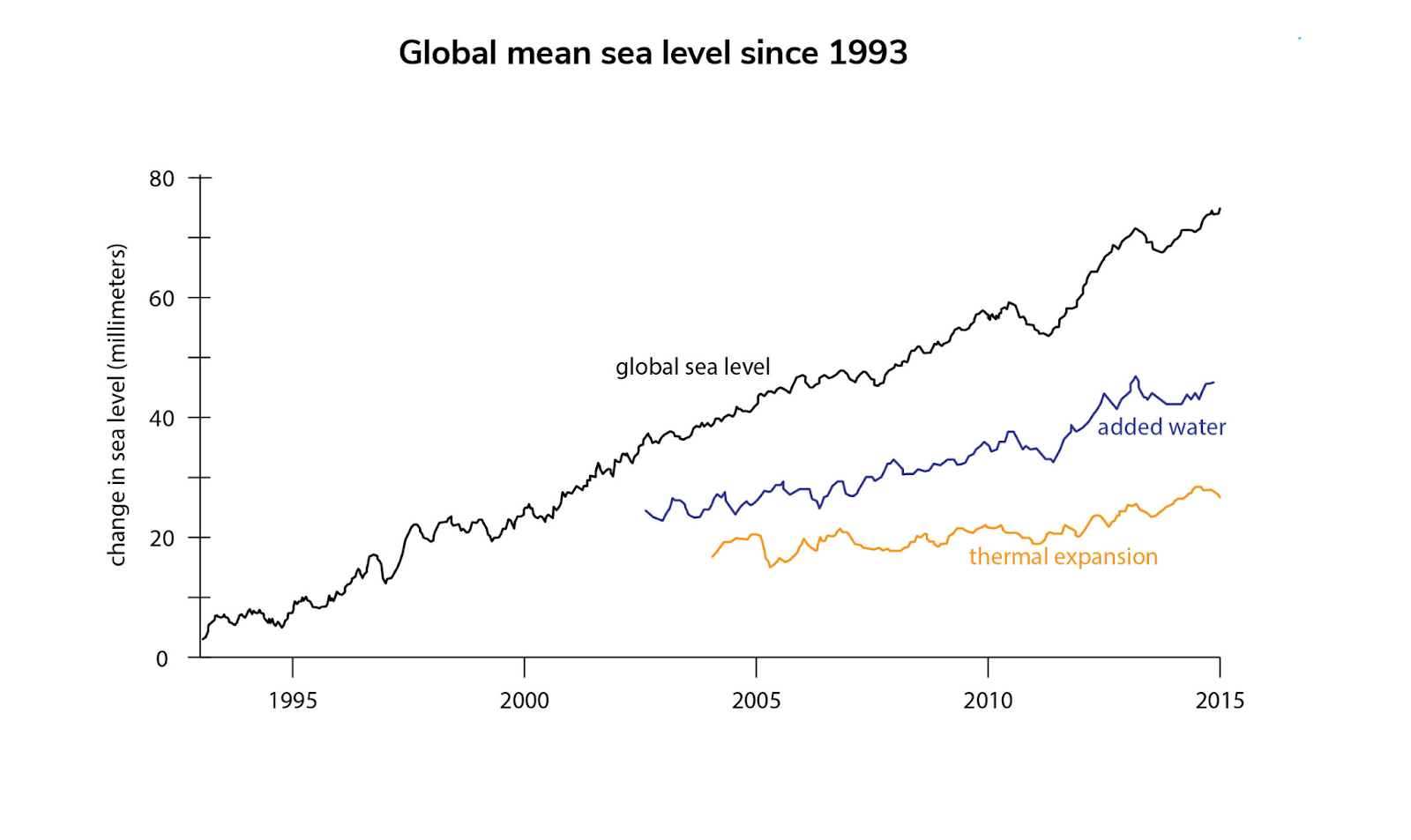
- Since 1880, global average sea levels have risen by approximately 8 to 9 inches (21 to 24 centimeters), primarily due to thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets.
- Over the past three decades, the rate of sea level rise has more than doubled, increasing from about 2.1 mm/year in 1993 to approximately 4.5 mm/year in 2023.
- In 2023, the global average sea level reached a new record high of 101.4 mm (3.99 inches) above the 1993 average, marking a significant increase from previous years.
| Period | Average Sea Level Rise | Notes |
| 1880 to 1993 | 8 to 9 inches (21 to 24 cm) | Gradual increase due to thermal expansion and glacier melt |
| 1993 to 2023 | 4.5 mm/year | Accelerated rise linked to climate change impacts |
| 2023 | 101.4 mm | A record high sea level was reached |
Causes of Sea Level Rise
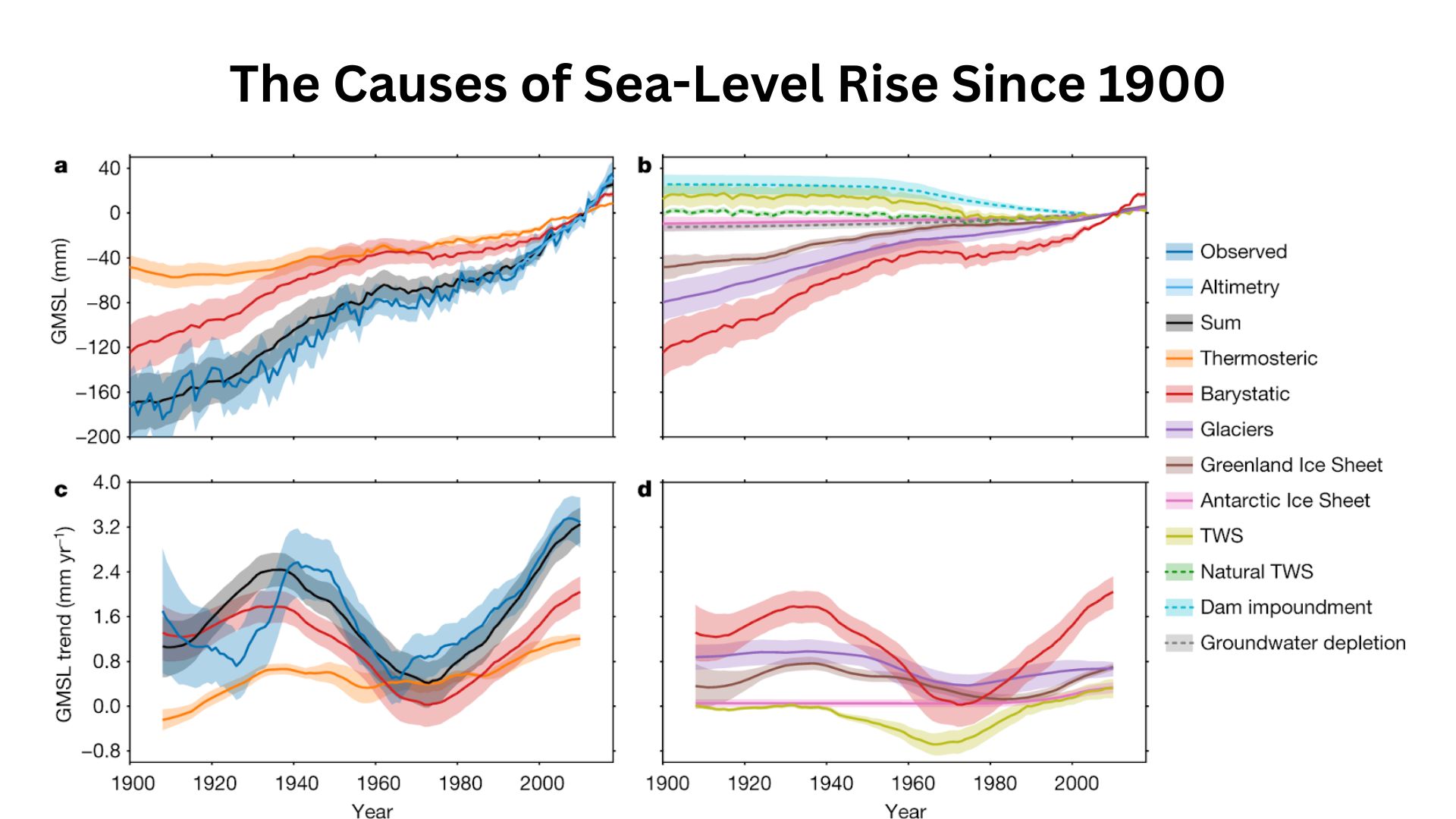 (Source: nature.com)
(Source: nature.com)
- As global temperatures rise, seawater warms and expands, contributing significantly to sea level rise.
- The loss of ice from glaciers and polar ice sheets adds freshwater to the oceans, further elevating sea levels.
- Studies indicate that the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets are losing mass at an accelerating rate, with Greenland’s ice loss increasing by 50% from 2012 to 2023.
- In certain regions, the sinking of land due to natural or human-induced factors exacerbates the effects of sea level rise.
| Cause | Contribution to Sea Level Rise |
| Thermal Expansion | Significant |
| Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets | Major contributor |
| Ice Loss from Greenland and Antarctica | Accelerating loss |
| Land Subsidence | Regional exacerbation |
Regional Variations in Global Sea Level Rise
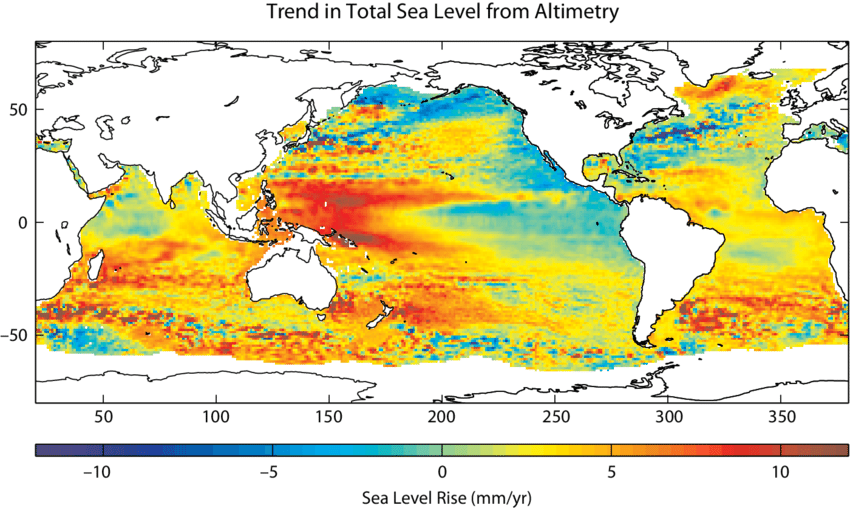 (Source: researchgate.net)
(Source: researchgate.net)
- Along the U.S. coastline, sea levels are projected to rise by 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm) by 2050, equaling the rise observed from 1920 to 2020.
- In Europe, sea levels have risen by approximately 21 cm since 1900, with projections indicating a rise of 0.28 to 0.55 meters under low-emissions scenarios and up to 1.02 meters under high-emissions scenarios by 2100.
- Coastal regions in Asia, particularly in countries like Bangladesh and India, are experiencing some of the most rapid rates of sea level rise, posing significant risks to densely populated areas.
| Region | Projected Sea Level Rise by 2050 | Notes |
| United States | 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm) | Comparable to the rise from 1920 to 2020 |
| Europe | 0.28 to 1.02 meters | Varies based on emissions scenarios |
| Asia | High rates | Particularly in low-lying coastal areas |
Future Sea Level Rise Projections
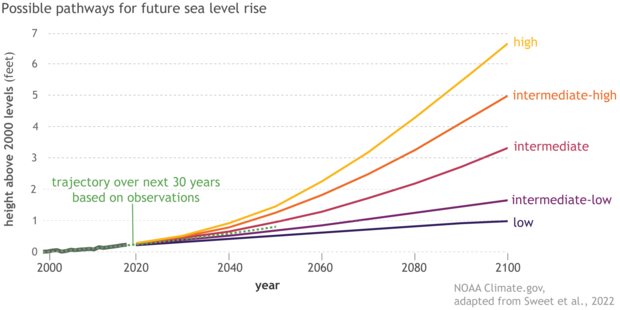 (Source: climate.gov)
(Source: climate.gov)
- By 2100, under high emissions scenarios (SSP5-8.5), global sea levels could rise by up to 1.02 meters, with potential for even higher increases if polar ice sheets undergo rapid disintegration.
- By 2150, some models suggest a rise of up to 5 meters, depending on the extent of ice sheet instability and global warming trajectories.
| Timeframe | Projected Sea Level Rise | Emissions Scenario | Notes |
| 2100 | Up to 1.02 meters | SSP5-8.5 | High emissions scenario |
| 2150 | Up to 5 meters | Varies | Dependent on ice sheet dynamics |
Impacts of Sea Level Rise
 (Source: berkeley.edu)
(Source: berkeley.edu)
- Coastal Flooding, increased sea levels lead to more frequent and severe coastal flooding, affecting infrastructure and communities.
- Erosion of Shorelines, rising seas accelerate the erosion of coastlines, leading to loss of land and habitats.
- Saltwater Intrusion, higher sea levels can cause saltwater to intrude into freshwater aquifers, compromising water supplies.
- Displacement of Populations, low-lying islands and coastal areas face the risk of displacement due to rising seas, leading to potential climate refugees.
| Impact | Description |
| Coastal Flooding | Increased frequency and severity of flooding |
| Erosion of Shorelines | Accelerated loss of land and habitats |
| Saltwater Intrusion | Contamination of freshwater resources |
| Displacement of Populations | Risk of forced migration from affected areas |
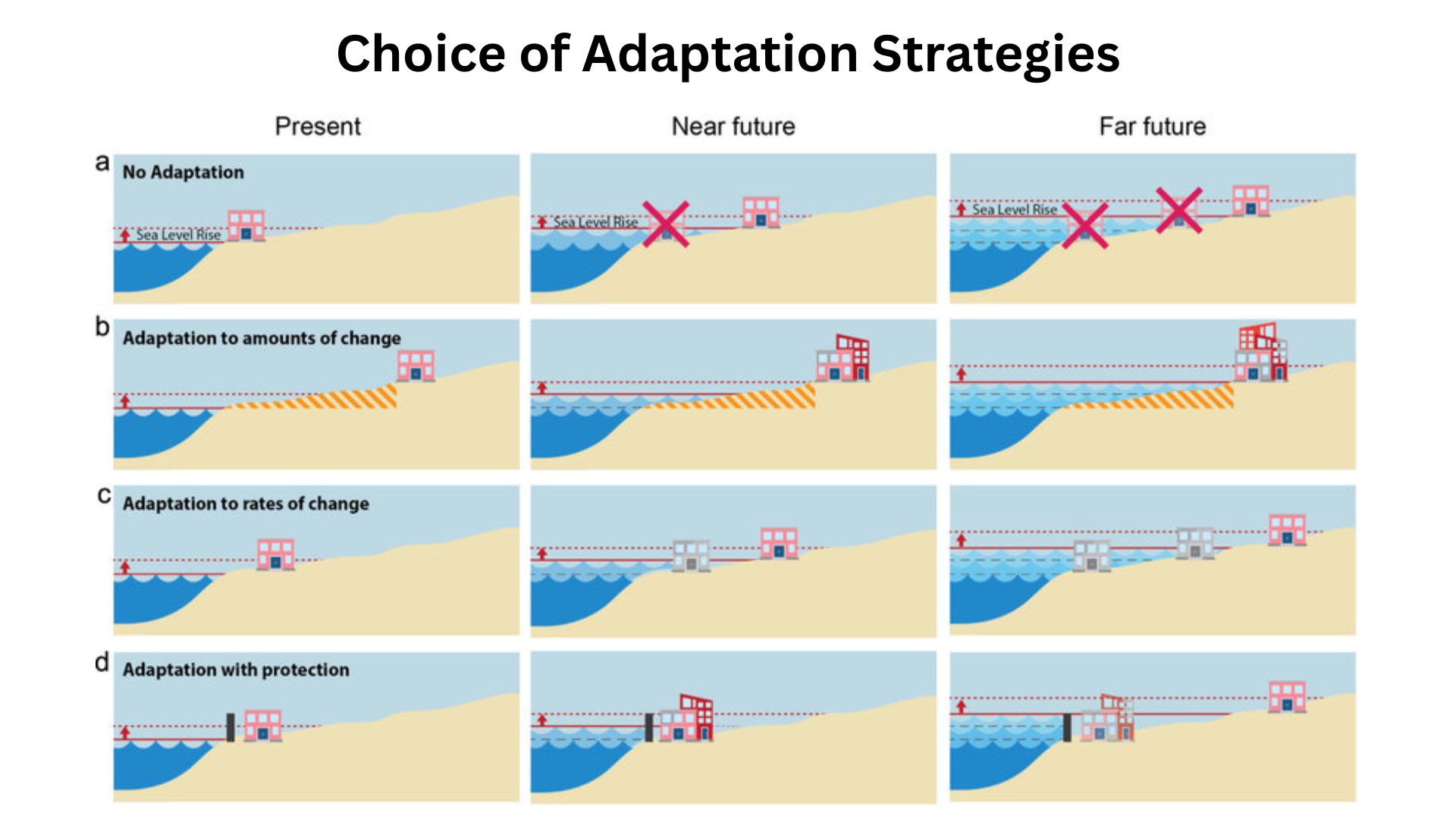
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
 (Source: researchgate.net)
(Source: researchgate.net)
- Emissions Reduction, limiting greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to slowing the rate of sea level rise.
- Coastal Defenses, implementing sea walls, levees, and other structures can protect vulnerable areas.
- Managed Retreat, in some cases, relocating communities away from high-risk areas may be necessary.
- Ecosystem Restoration, restoring natural barriers like mangroves and wetlands can help absorb wave energy and reduce flooding.
| Strategy | Description |
| Emissions Reduction | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions |
| Coastal Defenses | Building protective infrastructure |
| Managed Retreat | Relocating communities from high-risk areas |
| Ecosystem Restoration | Restoring natural coastal ecosystems |
Conclusion
Overall, understanding these sea level rise statistics is more important now than before. The oceans are slowly getting higher, and this affects our homes, cities, and the natural world around us. While the numbers might seem small, even a few inches can cause flooding, erosion, and displacement.
The good news is we can take action, by reducing emissions, protecting coastlines, and preparing our communities. Stay informed, spread awareness, and support initiatives that help fight climate change, because every step is more important in protecting our planet from the impacts of sea level rise. I hope you like this one, if you got any questions, kindly let me know in the comment section.


