Introduction
AI Cybersecurity Statistics: AI Cybersecurity has become a basic new operating system for both cyber defense and offense. It has essentially altered the threat landscape, with rising attack speeds and an increase in the sophistication of impersonation and fraud.
For organizations, it is important to answer how fast and how effectively they can deploy AI to stay ahead of adversaries already leveraging its power. In this detailed report, I aim to provide a focused, up-to-date analysis of AI Cybersecurity, examining its vital role in reducing data breach costs, its projected market dominance, the growth of AI-enhanced threats, and the widening global skills gap.
This article provides all the essential insights for technology firms, as well as for common tech enthusiasts like us who are navigating the immense challenges of this increasingly intelligent cyber era. So, without further ado, let’s get into the content.
Editor’s Choice
- Attacks leveraging AI agents can automate the entire lifecycle, from reconnaissance to vulnerability scanning to exploitation at machine speed, capable of generating 36,000 automated scans per second.
- Security teams still take an average of 277 days to identify and contain a data breach using traditional systems, compared to 214 days for organizations that have fully deployed AI for threat detection.
- The total global cost of cybercrime is expected to soar to over $10.5 trillion in 2025.
- Organizations that extensively use security AI and automation realize an average cost savings of $2.22 million on data breaches compared to those that don’t, significantly reducing the average breach cost of $4.88 million.
- AI-driven phishing attacks have increased by over 1,200% since 2022, with AI-generated phishing emails becoming four times more likely to deceive recipients due to improved personalization and language.
- As of 2025, 14% of major corporate breaches were reported as fully autonomous, meaning no human hacker intervened after the AI launched the initial attack.
- Deepfake fraud growth has surged over 2,100% since 2022, enabling sophisticated identity spoofing and social engineering.
- Approximately 67% of organizations are currently using AI as part of their cybersecurity strategy.
- Only 5% of organizations feel highly confident in their AI security preparedness, despite 90% actively implementing or planning to explore Large Language Model LLM use cases.
- 75% of CFOs now report leading their organization’s AI strategy, highlighting a significant change in AI risk ownership and accountability, moving away from purely technical teams.
AI in Cybersecurity Market Size
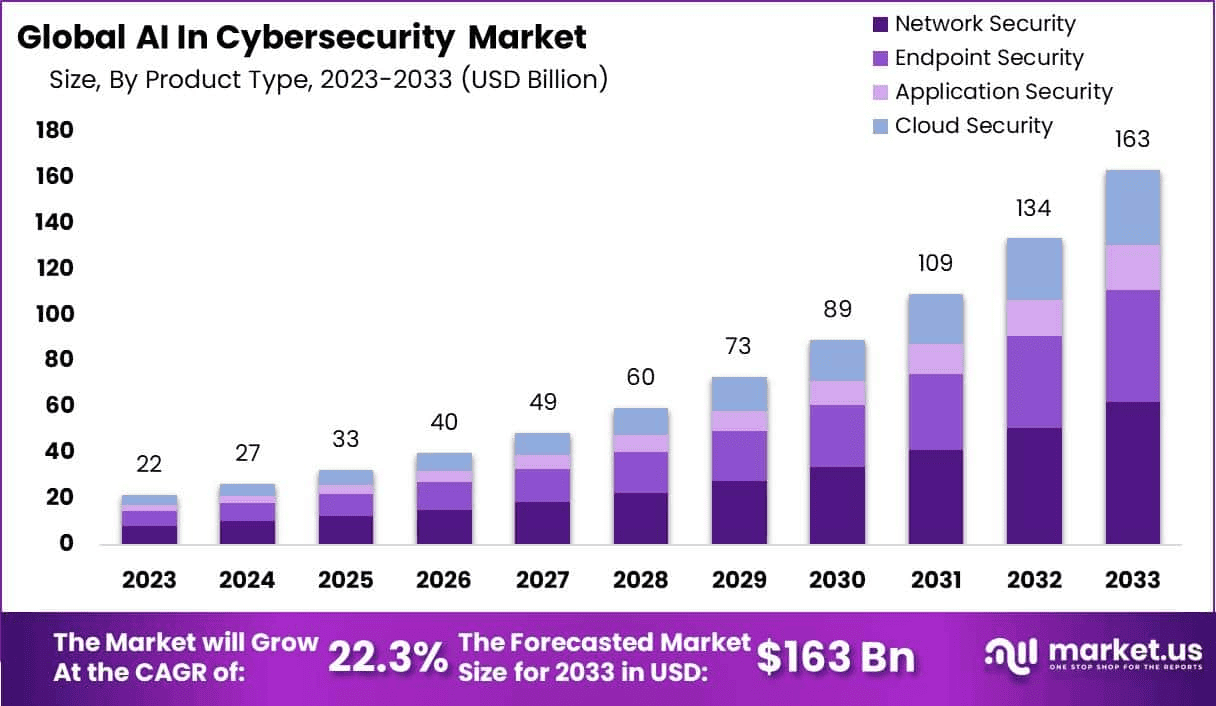 (Source: market.us)
(Source: market.us)
According to Market.us, the global market for AI Cybersecurity is on a massive growth, driven by the need for automated, intelligent defense solutions capable of handling the scale and speed of modern threats. This growth marks a significant shift in the industry from reactive, signature-based tools to proactive, machine learning-driven platforms.
- According to Market.us, the global AI in Cybersecurity Market is projected to reach USD 163.0 billion by 2033, increasing from USD 22 billion in 2023, with an annual growth rate of 22.3% between 2024 and 2033.
- As reported by Security Intelligence, the average cost of a data breach in 2022 increased to USD 4.35 million, representing a 2.6% rise from the 2021 average of USD 4.24 million. This indicates a steady rise in the financial impact of cyber incidents globally.
- The World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2023 noted that 84% of organizations are now using AI-based tools to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses, highlighting the growing reliance on artificial intelligence for proactive threat management.
- According to ENISA, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity, the adoption of AI-based security systems has increased by 30% over the past year, as companies focus on protecting sensitive data and enhancing cyber resilience.
- In 2023, the Services segment held a dominant position in the market with over 35% share, reflecting strong demand for AI-driven cybersecurity services and consulting.
- The Network Security segment accounted for more than 38% share, supported by increased use of AI for real-time network monitoring and intrusion detection.
- The Machine Learning (ML) technology segment captured around 47% of the market, confirming its crucial role in predictive analysis and automated threat identification.
- The Fraud Detection and Anti-Fraud segment held a 20% share, driven by rising online transaction volumes and digital payment risks.
- Within end-use industries, the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector dominated with a 28% share, reflecting extensive use of AI for fraud prevention and regulatory compliance.
- North America led the market in 2023 with over 36% share, owing to advanced cybersecurity infrastructure and early adoption of AI solutions across industries.
- As per global surveys, 55% of companies intend to integrate AI into corporate cybersecurity strategies in 2024 to improve real-time threat response.
- Around 21% of IT leaders believe AI can help automate the creation of security rules, reducing manual errors and improving consistency.
- Nearly 19% of respondents expect attack simulation and compliance monitoring to be the most impactful AI applications in cybersecurity during 2024.
- Approximately 63% of cybersecurity professionals agree that AI enhances threat detection and response capabilities, improving overall security posture.
- However, only 12% of experts believe AI will fully replace human roles, while most view it as a support tool.
- About 30% of professionals think AI will enhance their skills, and 28% believe it will provide general operational support.
- Around 24% expect AI to automate major parts of their tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic decision-making.
- According to recent workforce surveys, C-suite executives show 52% familiarity with AI technologies, compared to 11% among staff, indicating a knowledge gap in AI readiness.
- Findings from the State of AI and Security Survey Report reveal that over 55% of organizations plan to deploy generative AI solutions in 2024, signaling a major transformation in cybersecurity approaches.
- The AI-driven Threat Intelligence market alone is projected to escalate from $6.31 billion in 2024 up to $18.67 billion by 2029, indicating a Compound Annual Growth Rate CAGR of 24.2% over this period.
- The broader Artificial Intelligence in Military market, which includes core AI Cybersecurity and defense systems, is estimated at $9.31 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $19.29 billion by 2030, reflecting a solid CAGR of 13.0%.
- In the specialized area of trade surveillance, a sector heavily reliant on AI to detect financial anomalies and market manipulation, the market is expected to grow from $3.00 billion in 2025 to $5.90 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 14.5%.
- North America continues its dominance in the global AI Cybersecurity sphere, capturing the largest market share in 2024.
- Specific to a high-value sector, the Aviation Cyber Security market, which integrates significant AI components, is forecasted to grow from $10.62 billion in 2025 to $17.21 billion by 2032, showing a steady CAGR of 7.14%.
| Market Segment | 2024 Value USD | 2029/2030 Value USD | CAGR Rate |
| AI Threat Intelligence | $6.31 Billion | $18.67 Billion 2029 |
24.2% |
|
AI in Military/Defense |
$9.31 Billion | $19.29 Billion 2030 | 13.0% |
| Trade Surveillance Systems AI-Enhanced | $3.00 Billion 2025 | $5.90 Billion 2030 |
14.5% |
Cybersecurity as a Cost Mitigator
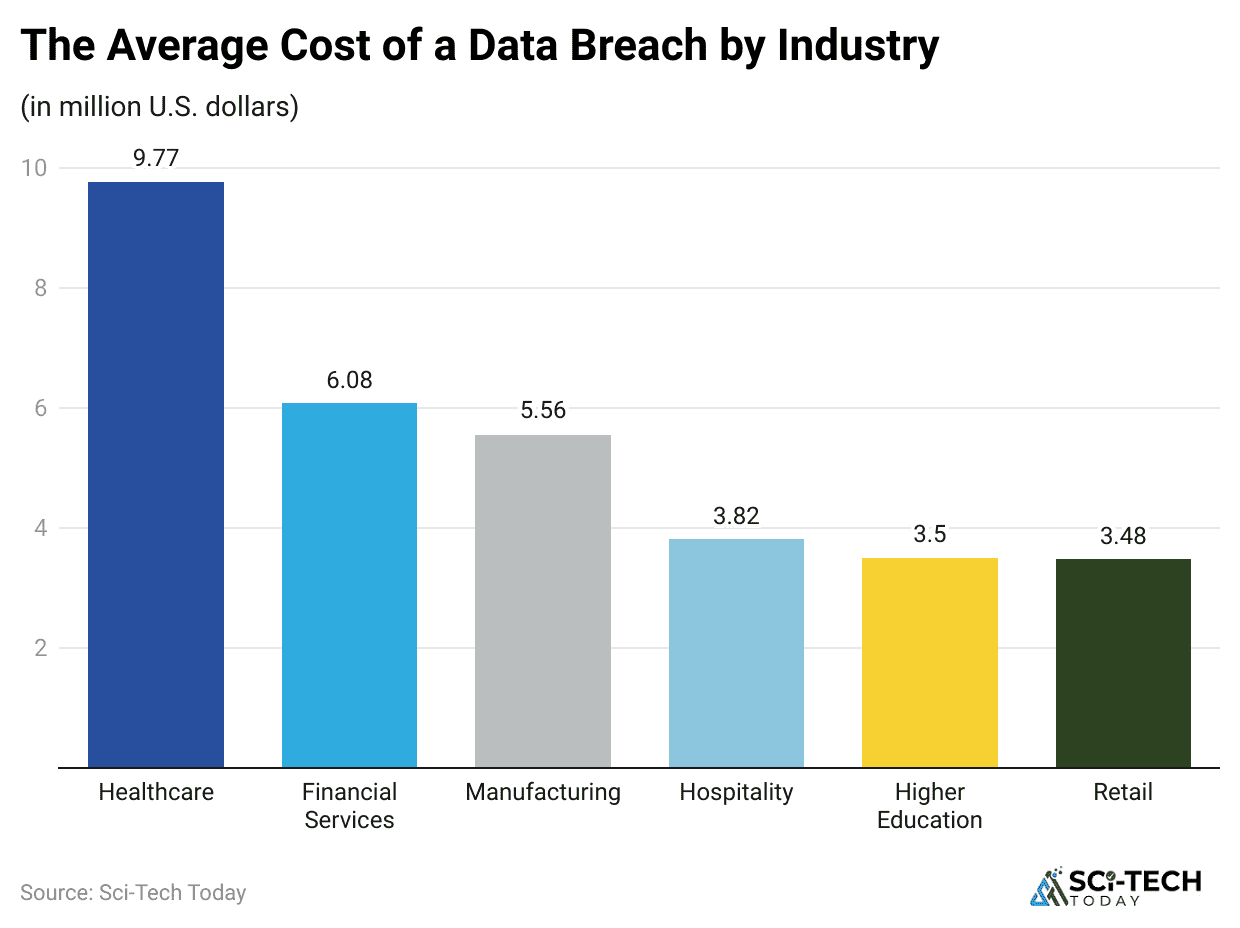 (Reference: vikingcloud.com)
(Reference: vikingcloud.com)
- The global average cost of a data breach is $4.44 million, though this figure has seen a slight decline of 9% from 2024.
- Organizations that use AI Cybersecurity solutions extensively in their security workflows save an average of $1.9 million compared to those with no AI or automation in their defense strategy, showcasing a 43% difference in breach costs.
- The deployment of AI/Machine Learning Insights is quantified as a Top Cost Mitigator, reducing the average total cost of a data breach by an estimated $223,503.
- AI significantly cuts down the time required to neutralise a threat: organisations extensively using AI and automation reduce the time to identify and contain a breach by nearly 100 days compared to those not using these tools.
- In stark contrast, the use of Shadow AI, unauthorized, unmanaged Generative AI applications within an organization, adds a premium of approximately $670,000 to the average data breach cost.
- Furthermore, Shadow AI breaches take 6 days longer to resolve on average, underscoring the vital need for a governed, AI Cybersecurity policy across the enterprise.
| AI Usage Level | Average Breach Cost Reduction | Response Time Improvement | Added Risk/Cost Factor |
| Extensive AI/ML Use | Saves nearly $1.9 Million | 100 days faster containment | N/A |
| AI/ML Insights Mitigator | Reduces cost by $223,503 | N/A | N/A |
| Shadow AI Unmanaged | Adds $670,000 to the cost | 6 days slower containment | 20% of breaches due to Shadow AI |
The Automated Threat Landscape
 (Reference: darktrace.com)
(Reference: darktrace.com)
- Deepfake files used for fraudulent purposes are projected to increase exponentially, surging from 500,000 instances in 2023 to an estimated 8 million files in 2025, representing a phenomenal growth rate of 1,500%.
- Voice cloning has rapidly become the top deepfake attack vector in 2025, primarily because it is cheap, fast to produce, and has proven highly effective at impersonating executives to authorize fraudulent wire transfers.
- In a prominent 2024 case, a company employee was deceived into transferring $25.6 million after a video conference with deepfake versions of the company’s CFO and other senior leaders.
- Attacks leveraging AI-driven tools accounted for an estimated 16% of all reported cyber incidents over the past year.
- AI phishing attacks are a massive problem, accounting for 37% of all AI-related data breaches, with the use of Large Language Models LLMs allowing cybercriminals to reduce their campaign costs by as much as 95%.
- The highly personalized, grammatically flawless messages generated by AI have proven to be as effective as traditional phishing, with a 60% success rate against recipients.
- The global financial loss from Generative AI fraud, including deepfakes and other sophisticated AI Cybersecurity threats, is projected to multiply by 32% to reach an astonishing $40 billion annually by 2027.
| AI-Driven Attack Type | Growth/Frequency | Financial/Impact Statistic | Human Detection Rate |
| Deepfake Fraud Files | Projected 8 Million by 2025 from 500K in 2023 | GenAI fraud projected to hit $40 billion annually by 2027 | High-quality video deepfakes are detected by humans only 24.5% of the time. |
| AI-Driven Incidents | Involved in 16% of reported cyber incidents | One case involved a $25.6 million transfer due to deepfake deception. | N/A |
| AI Phishing | Accounts for 37% of all AI-related breaches | LLMs cut campaign costs by up to 95% for attackers | 60% success rate against recipients. |
Gaps, Skills, and Preparedness
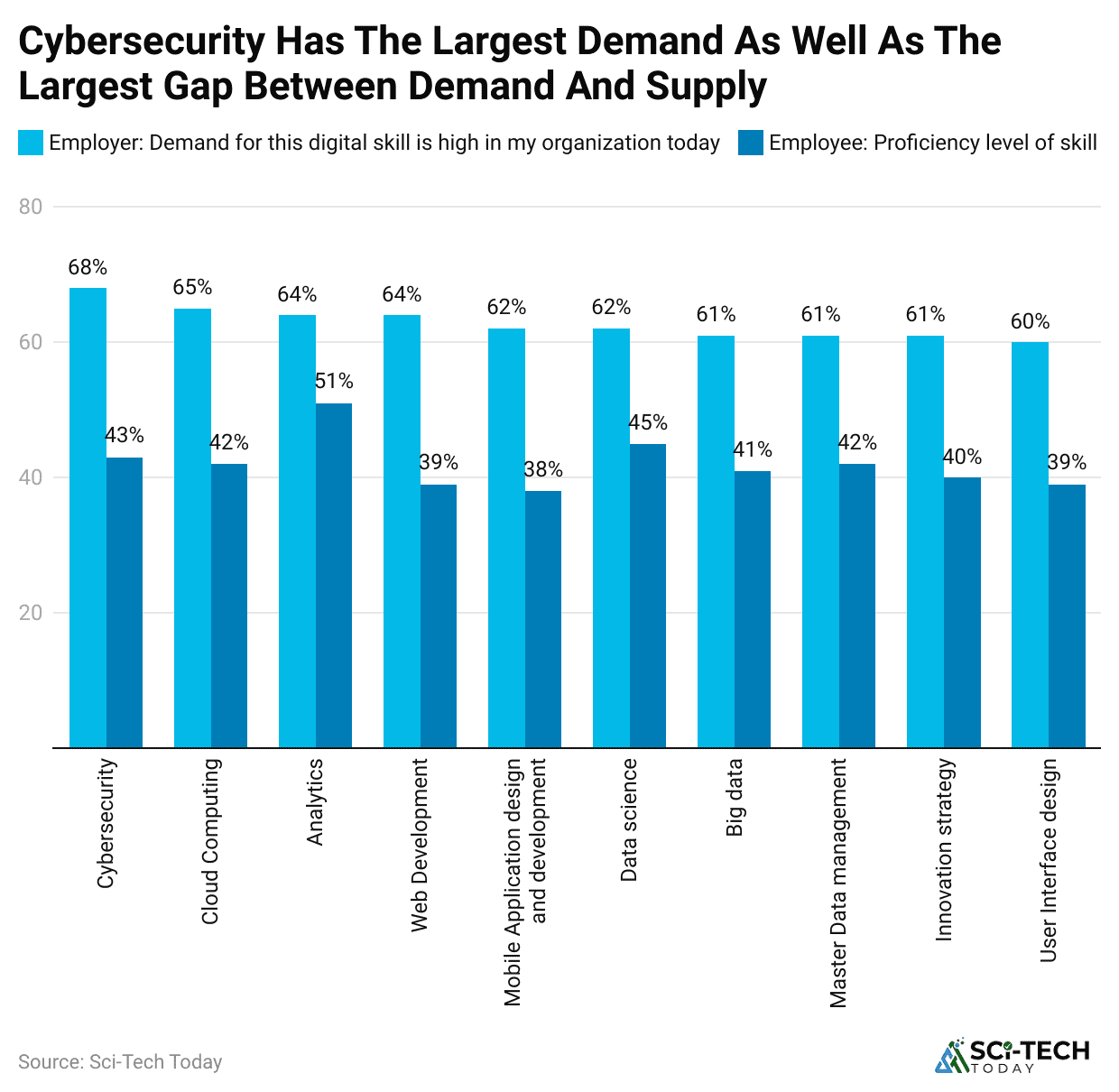 (Source: consultancy.uk)
(Source: consultancy.uk)
- The global cybersecurity workforce gap currently stands at 4,763,963 people, representing a severe talent shortage that forces organizations to adopt AI Cybersecurity and automation simply to manage the volume of daily alerts and threats.
- This gap has widened by 19.1% in the past year, highlighting an inability for training and hiring to keep pace with digital demand.
- 59% of business and IT leaders openly admit that AI cyber threats are advancing faster than their security team’s expertise and knowledge base to effectively deal with them.
- In spite of the threat, only 48% of organizations have developed a clear, formal framework for granting or limiting the autonomy of Agentic AI systems within their security infrastructure.
- 76% of security and compliance teams report a significant reduction in employee burnout thanks to the use of AI and automation tools that take over tedious and manual tasks like log analysis and initial alert triage.
- A major challenge to widespread deployment is the simple lack of internal competence, with 39% of middle market executives identifying a vital shortage of in-house expertise as a key barrier to successful enterprise-wide AI implementation.
- This forces a significant 70% of companies using Generative AI to rely on external consultants to fully optimize the tool’s value, adding cost and complexity.
- The issue of AI governance is pervasive, as an estimated 63% of all organizations lack a dedicated AI governance policy framework to guide the ethical, secure, and compliant deployment of intelligent technologies.
| Human/Readiness | Key Statistic 2024 to 2025 |
| Global Workforce Gap | 4,763,963 people, a short 19.1% increase |
| Threat vs. Expertise | 59% of leaders say AI threats outpace their team’s expertise |
| Agentic AI Governance | Only 48% have a framework for autonomous AI |
| Burnout Reduction | 76% of teams report less burnout due to AI automation |
| In-house Expertise | 39% cite lack of internal expertise as an adoption barrier |
AI Cybersecurity in Action
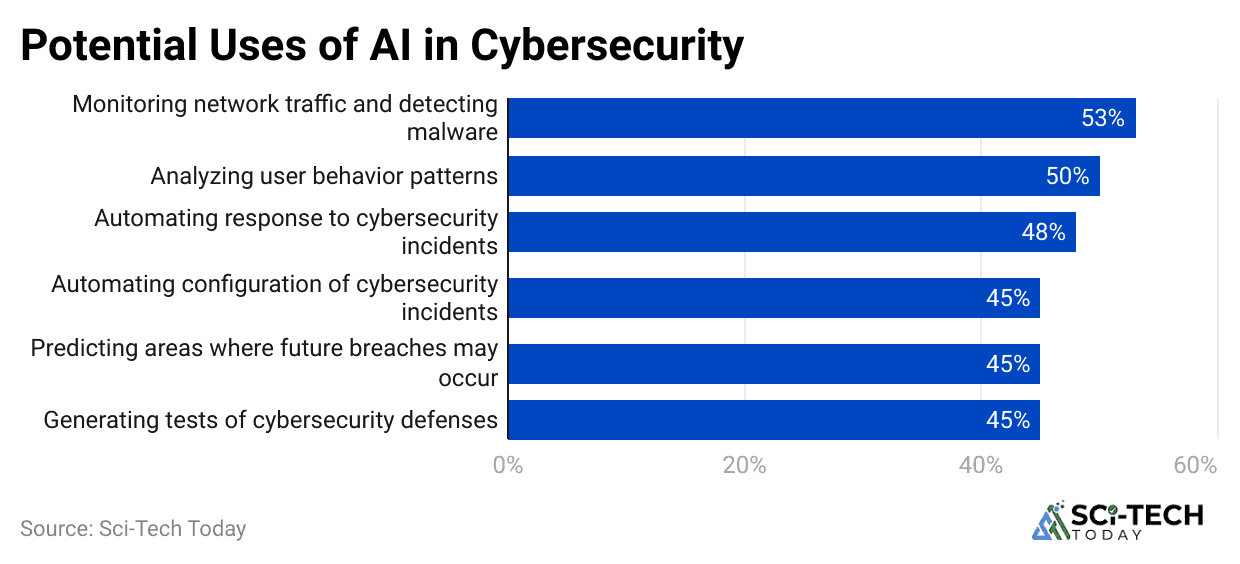 (Reference: lakera.ai)
(Reference: lakera.ai)
- Security breaches are detected and contained with noticeably greater speed, with 63% of all security breaches being detected more quickly when an element of AI Cybersecurity is integrated into the systems.
- In the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance BFSI sector, a highly targeted industry, 50% of bank CEOs have their compensation directly tied to their organization’s cybersecurity performance.
- 97% of all AI-related data breaches were found to have lacked proper access controls and clear, segmented permissions around AI data and models.
- DevSecOps approaches, which increasingly rely on AI to scan code and infrastructure for vulnerabilities in actual, rank as the single most effective cost mitigator, reducing the average cost of a breach by $227,192.
- An estimated 80% of all new AI-driven security systems are being rigorously tested against the emerging and difficult category of Adversarial AI attacks.
| AI Cybersecurity Defense Metric | Numeric Data Point |
| Faster Detection | 63% of breaches are detected faster with AI integration |
| Executive Accountability | 50% of bank CEO compensation is tied to cyber performance |
| Breach Root Cause | 97% of AI-related breaches lacked proper access controls |
| DevSecOps Cost Savings | Reduces breach cost by $227,192 |
| Adversarial AI Testing | 80% of new AI systems are tested against Adversarial AI |
Conclusion
Overall, these AI Cybersecurity statistics are the most necessary technology for defense in the current cyber landscape. We are past the inflection point where AI was an option; it is now a basic requirement.
These data clearly demonstrate the two forces making the future: the massive financial benefit of using AI for defense by the $1.9 million in savings per breach, set against the exponential threat growth, evidenced by the 1,500% surge in deepfake fraud files.
So, accelerate the governed deployment of AI Cybersecurity tools to fill the near 5 million person skills gap and drastically cut incident response times to under 241 days. Simultaneously, industry leaders must focus on Governance, establishing clear policies to prevent the dangerous financial fallout of Shadow AI and the vulnerability introduced by inadequate access controls. That’s it, thanks for staying till the end. If you have any questions, kindly let us know in the comments section. Thanks.


