Introduction
Social Media at the Workplace Statistics: Social media has become deeply integrated into our daily lives, and the workplace is no exception. Whether it’s a quick scroll during a coffee break or using social media for professional tasks, social media’s presence at work is undeniable.
In this article, I’m going to walk you through the latest and most insightful social media at the workplace statistics. We’ll explore how common it is, what platforms employees prefer, how it impacts productivity, and the policies companies put in place to manage it. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of this complex relationship between social media and work.
Editor’s Choice
- According to the Pre Research Center, about 68% of employees use social media during work hours, showing it is a common practice in many workplaces.
- Pew Research Center also reports that Facebook and LinkedIn are the most popular platforms employees use for personal and professional purposes, respectively.
- Statista finds that employees expend an average of 32 minutes daily on social media during work hours, with 21% spending over one hour each day.
- Research from Gallup reveals that 60% of employees feel distracted by social media, yet 42% use it to support work tasks like networking and research.
- A Deloitte survey shows 58% of workers use social media to stay connected with friends and family while at work, and 50% rely on it for news and trend updates.
- Deloitte also notes that 45% of employees use LinkedIn for professional networking during work hours.
- Data from Glassdoor and CareerBuilder indicate that 55% of employers are concerned about social media hurting productivity, while 40% strict usage policies.
- Buffer’s 2023 State of Remote Work Report highlights that 55% of employers are concerned about social media hurting productivity, while 40% enforce strict usage policies.
- Buffer’s 2023 State of Remote Work Report highlights that 56% of remote employees use social media daily to maintain engagement and communication with colleagues.
- According to McKinsey and Company, social media improves employee engagement, brand promotion, and collaboration, but poses risks such as security threats and reputation damage that require attention.
| Key Insight | Summary |
| Social media users at work |
68% employees use social media during work |
|
Top social media platforms |
Facebook (55%), LinkedIn (45%), Instagram (38%), Twitter (36%) |
| Average daily social media time at work |
32 minutes, mostly in short sessions |
|
Mixed impact on productivity |
60% distracted, 42% use it for work tasks |
| Primary reasons for use |
Connection (58%), News (50%), Networking (45%), Stress relief (40%) |
|
Employer attitudes |
55% concerned, 40% have strict policies, 35% see value |
| Company social media monitoring |
48% monitor, 30% block access, 22% encourage responsible use |
|
Workplace benefits |
Engagement, knowledge sharing, brand promotion, and recruitment |
| Risks and challenges |
Productivity loss, security risks, reputation damage, conflicts |
|
Post-pandemic trends |
56% remote workers use daily, growing culture integration |
How Common Is Social Media Usage at Work?
(Reference: enterpriseappstoday.com)
- About 68% of employees access social media during work hours, making it widespread. The average employee checks social media 3 to 5 times during the workday, often for brief moments.
- Smartphones and constant internet access enable easy social media usage even during office hours. White-collar professionals are the heaviest users, with 75% engaging regularly during work.
- Blue-collar employees use social media less frequently, between 30% and 40%. Younger employees (under 35) are more active on social media at work compared to older colleagues.
- Social media often blends with work tasks such as industry news research or networking. Many employees view social media use as a way to relieve stress and stay connected. Despite frequent use, most workers believe it does not negatively affect their productivity.
| Statistics Description | Percentage / Number |
| Employees using social media during work |
68% |
|
Average daily social media visits at work |
3 to 5 times |
| White-collar workers accessing social media |
75% |
|
Blue-collar workers accessing social media |
30 to 40% |
| Younger employees under 35 using social media |
70% |
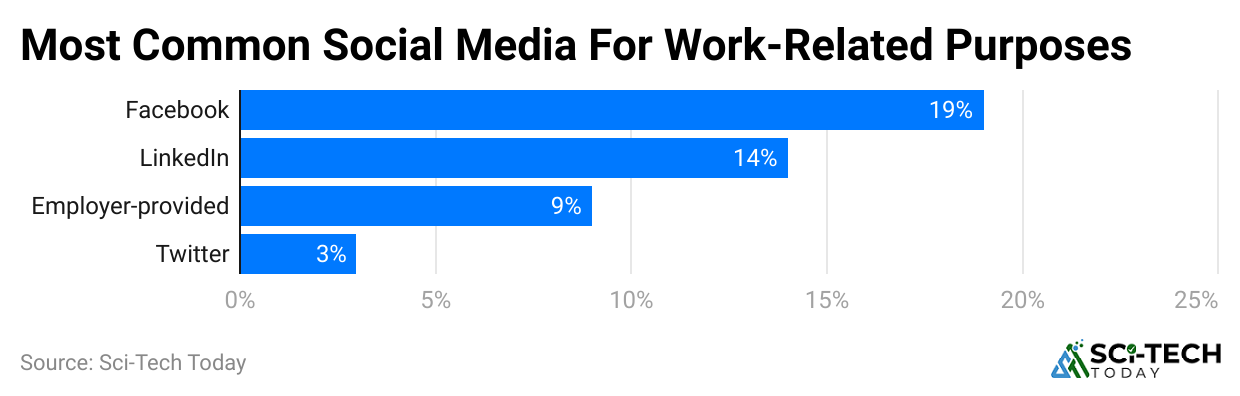
Most Popular Social Media Platforms Used by Employees
(Reference: zippia.com)
- Facebook leads with 55% of employees using it for personal interactions during work breaks. LinkedIn is popular for professional networking and job hunting, with 45% usage.
- Instagram attracts 38% for entertainment and visual content during work hours. And Twitter is used by 36% for news updates and quick information.
- TikTok and Snapchat are rising in popularity among younger workers for short videos. Messaging apps linked to social platforms, such as WhatsApp, are common for communication.
- YouTube is a source for tutorials and learning during breaks, and professional forums on social media aid in problem-solving and networking. Companies encourage LinkedIn for branding and recruitment purposes.
| Platform | Primary Use | Percentage of Employees Using at Work |
| Personal Social Interaction |
55% |
|
|
|
Professional Networking | 45% |
| Entertainment & Visual Content |
38% |
|
|
|
News and Quick Updates | 36% |
| TikTok | Short Video Entertainment |
20% |
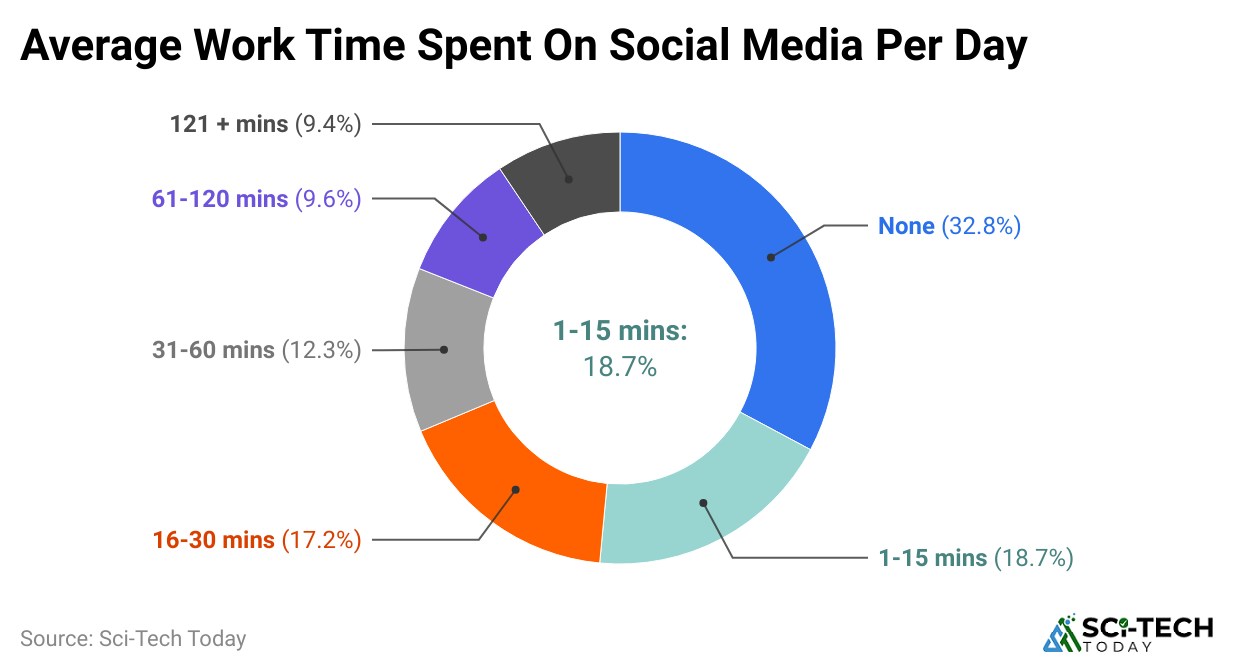
Time Spent on Social Media During Work Hours
(Reference: marketingprofs.com)
- On average, employees spend 32 minutes per day on social media while at work. Social media sessions usually last between 5 to 10 minutes, often multiple times daily.
- 12% of employees spend over an hour daily on social media during work hours, and usage peaks during lunch and mid-afternoon breaks when employees seek mental rest.
- Remote workers typically spend more time on social media compared to office-based colleagues, and social media acts as a stress relief or social connection tool during remote workdays.
- The average social media time at work has increased by about 10% over the past two years. Flexible social media policies tend to encourage shorter, more controlled usage.
| Time Spent on Social Media at Work | Average Duration per Employee |
|
Average total daily time |
32 minutes |
| Average session length |
5 to 10 minutes |
|
Employees spending over 1 hour |
12% |
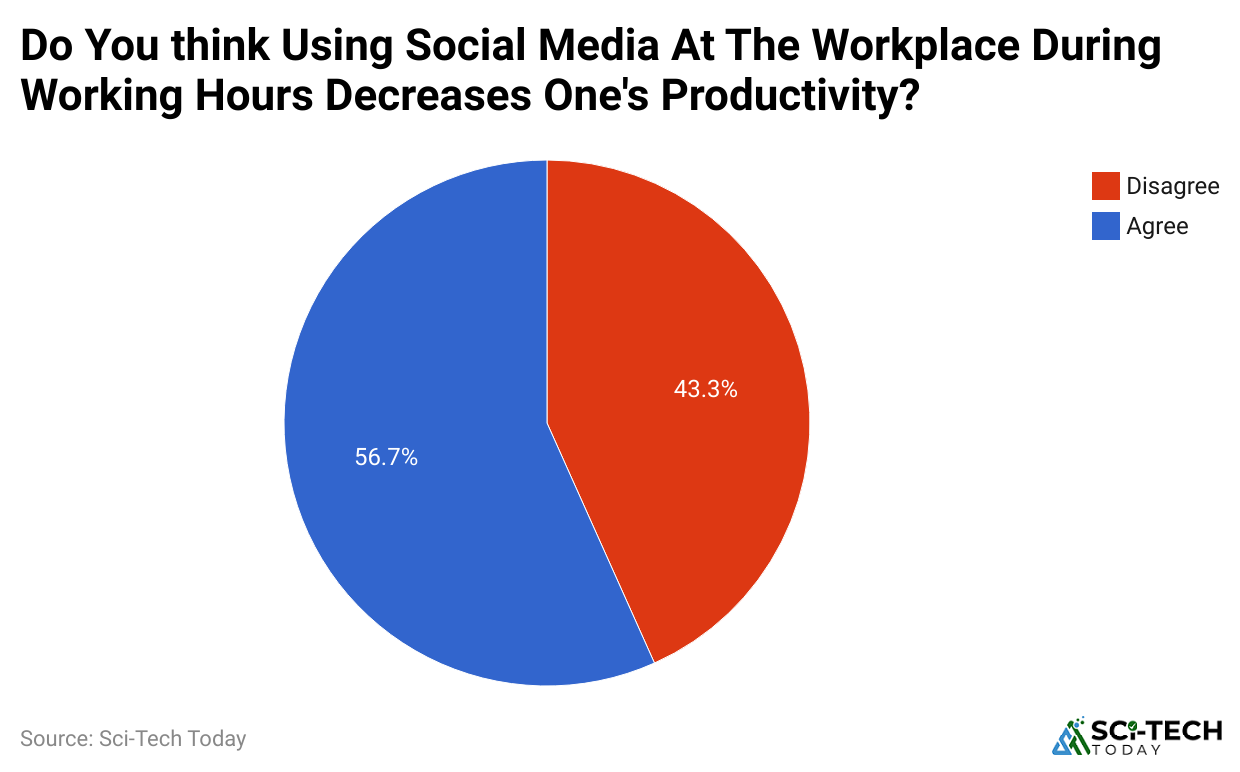
Impact of Social Media on Employee Productivity
(Reference: springer.com)
- 60% of employees report distractions from social media affecting their focus, and 42% use social media for work-related tasks like networking or research.
- Responsible social media use is linked to increased engagement and innovation; it enhances communication, especially in remote or hybrid work setups.
- Younger workers multitask more between social media and work tasks, and 35% believe social media improves communication with colleagues and clients.
- Employers see a mix of positive and negative effects on productivity; productivity loss due to social media is estimated at 1 to 2 hours per week. And Time management training can reduce social media’s negative impacts.
| Impact Aspect | Positive (%) | Negative (%) |
| Employees are distracted by social media | – |
60% |
|
Use social media for work tasks |
42% | – |
| Report improved communication | 35% |
– |
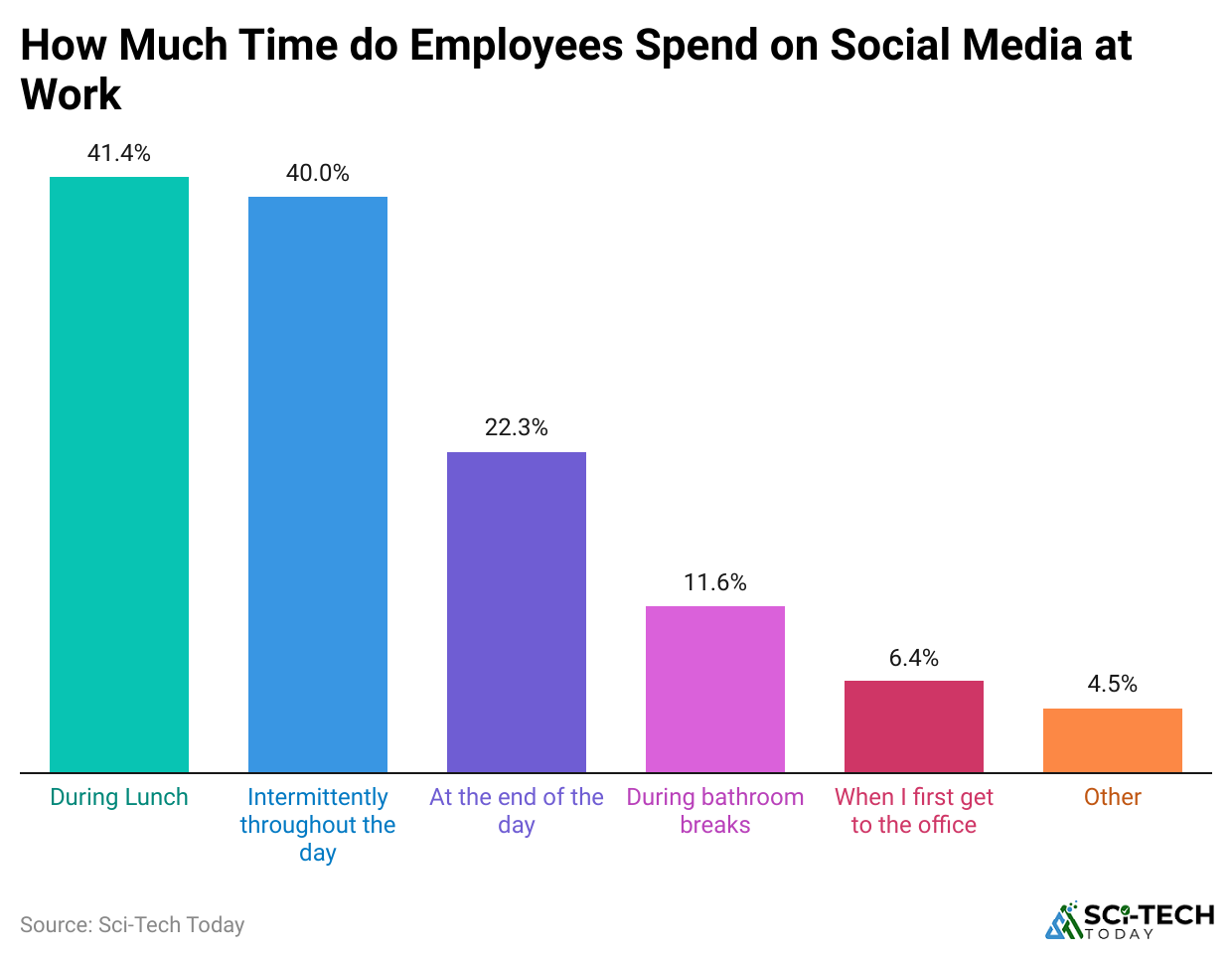
Reasons Employees Use Social Media at Work
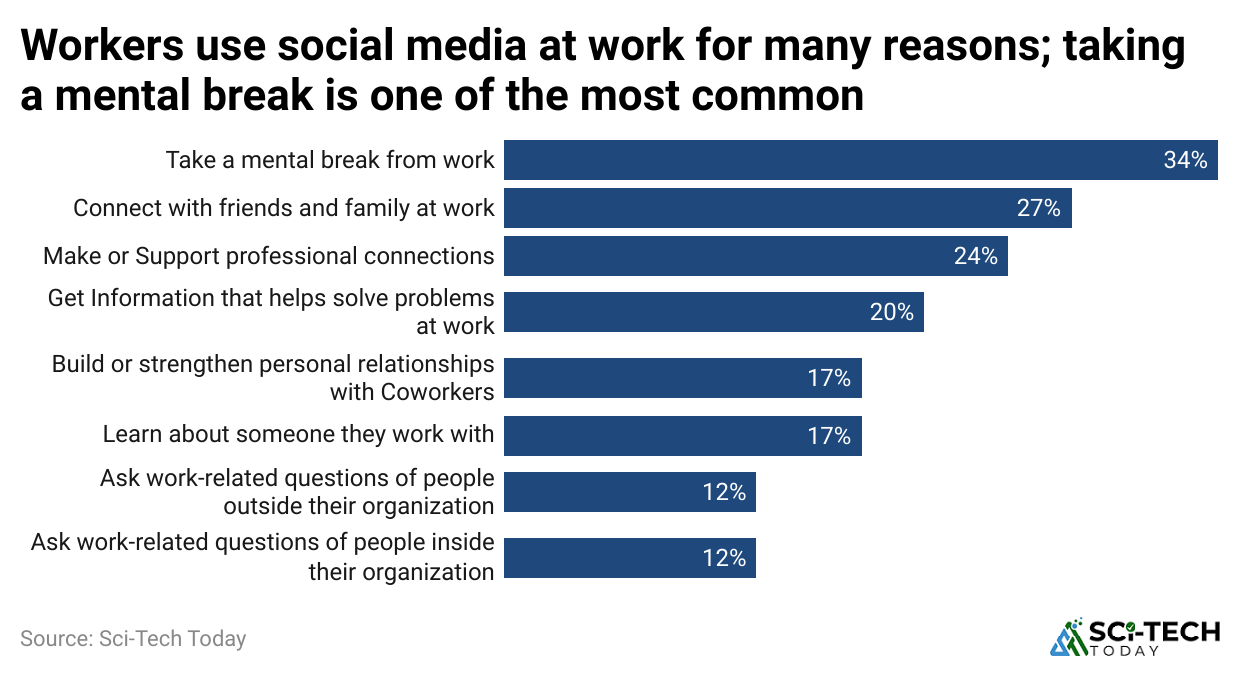
(Reference: pewresearch.org)
- 58% use social media to stay connected with friends and family, and 50% turn to social media to follow news and industry trends.
- 45% use platforms like LinkedIn to advance professional networking, and 40% use social media for stress relief during busy days.
- Others use it for entertainment and mental breaks, and social media supports learning and skill development.
- Younger employees combine personal and professional use more often, and remote workers rely on social media for social connections. Many believe social media sparks creativity and fresh ideas.
| Reason for Use | Percentage of Employees |
| Personal connection |
58% |
|
News and trends |
50% |
| Professional networking |
45% |
|
Stress relief |
40% |
Employer Attitudes Toward Social Media Use
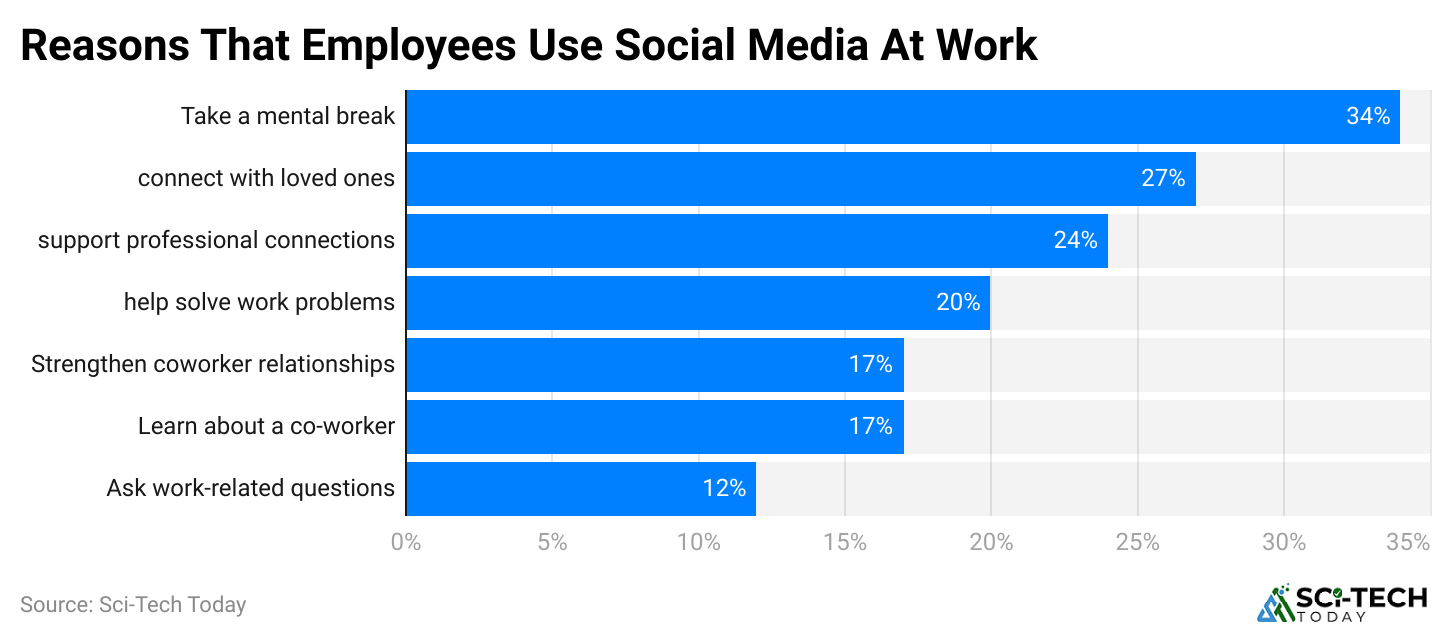
(Reference: enterpriseappstoday.com)
- 55% of employers worry about lowered productivity due to social media, and 40% have strict restrictions on access during work hours.
- 35% recognize social media’s value for marketing and recruitment, and many balance restrictions with encouragement for professional use.
- Social media training is becoming more common than outright bans, and 48% monitor employee social media use during work.
- Attitudes vary by industry, with tech firms more lenient than finance or manufacturing, and employers use social media for wellness and engagement initiatives. Policies are evolving with remote work trends.
| Employer Attitude | Percentage of Employers |
| Concerned about productivity |
55% |
|
Have strict social media policies |
40% |
| View social media positivity for work |
35% |
Social Media Monitoring Policies in Companies
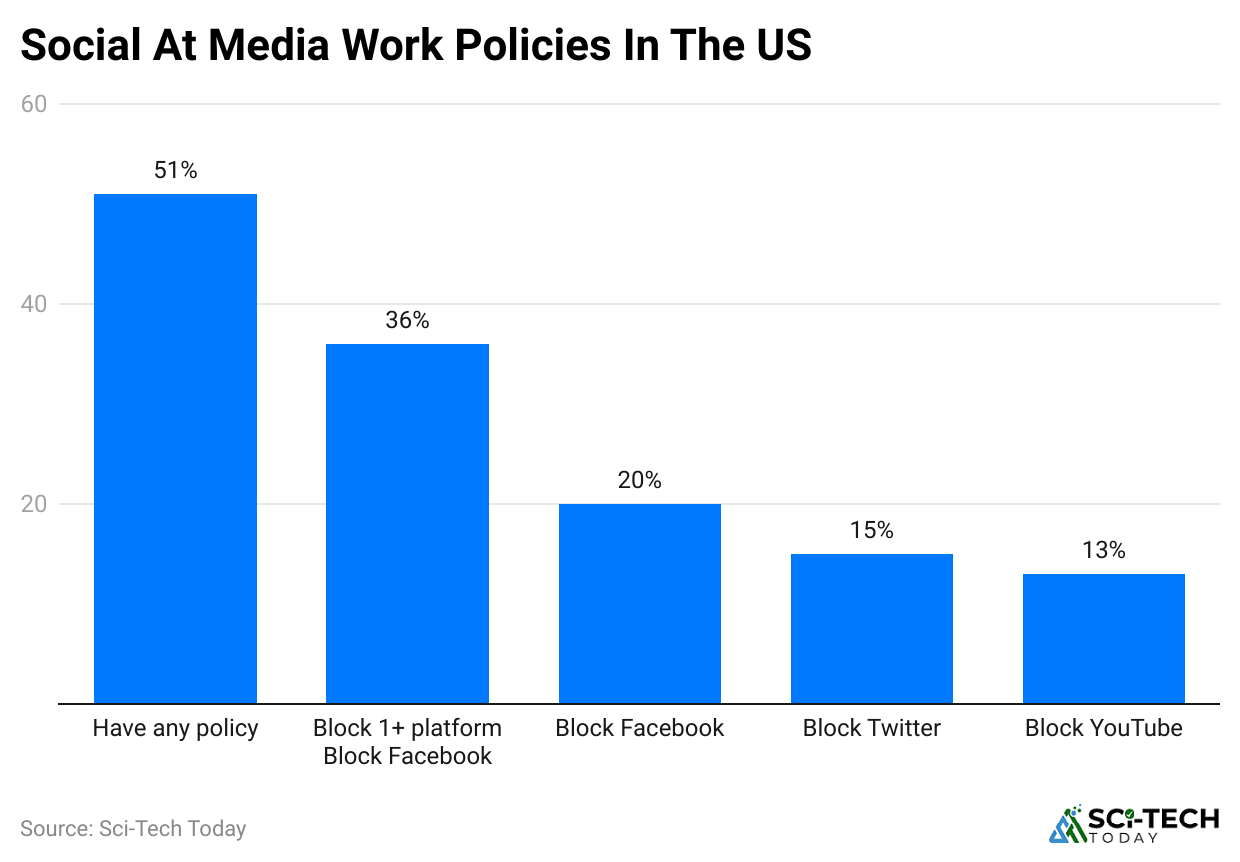
(Reference: enterpriseappstoday.com)
- 48% of companies monitor social media to protect data and prevent misuse, and 30% block access to social media on a company’s networks or devices.
- 22% encourage responsible use through guidelines, not bans, and monitoring tools that track time spent or flag inappropriate content.
- Some restrict social media during core work hours only, and transparency about monitoring builds trust.
- Smaller companies often have informal rules rather than formal monitoring, which helps avoid security threats and maintains professionalism. Policies update regularly to keep up with new social trends.
| Policy Type | Percentage of Companies |
| Social media monitoring |
48% |
|
Blocking social media websites |
30% |
| Encouraging responsible use |
22% |
Benefits of Social Media in the Workplace
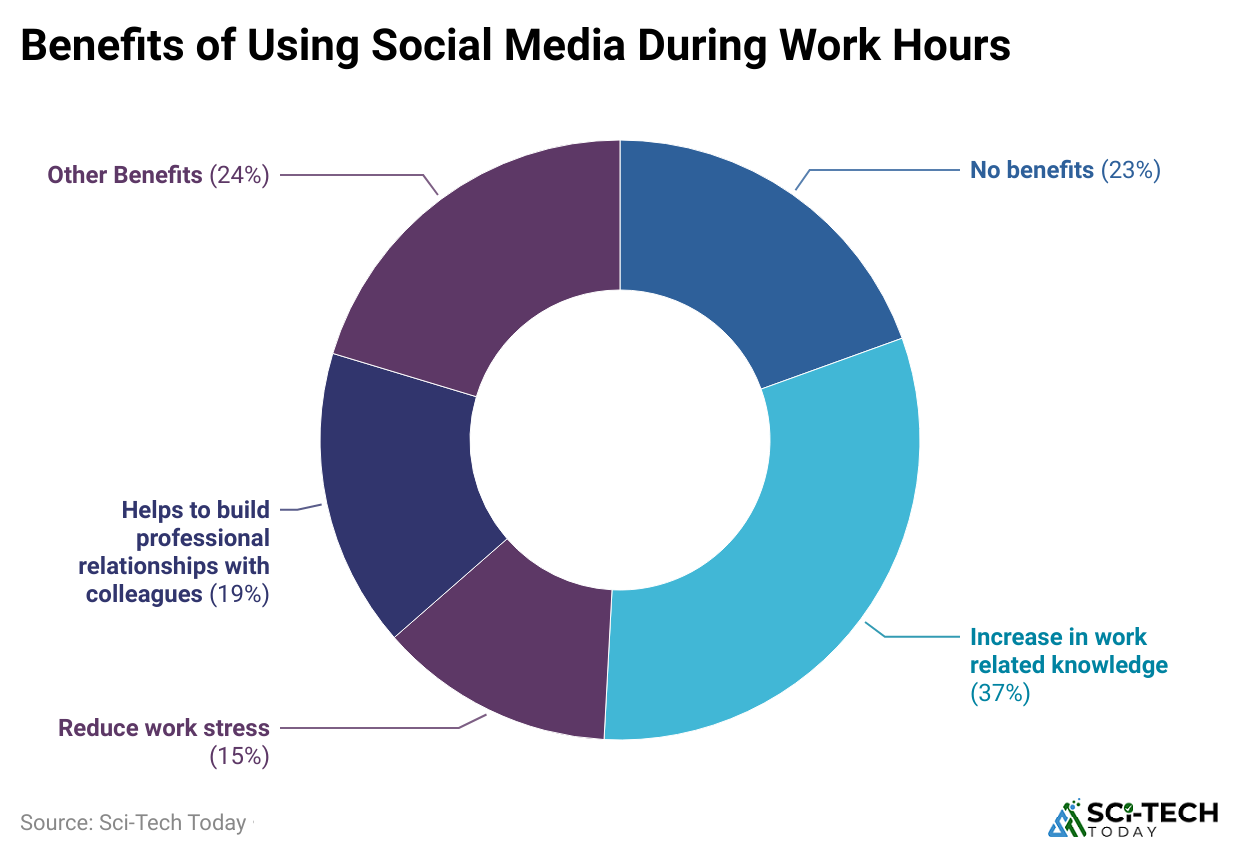
(Reference: jobera.com)
- Social media boosts employee engagement through informal communication, and it facilitates quick knowledge sharing and peer support.
- Employees promote company brands by sharing content online. It expands recruitment reach via social channels.
- Social media fosters collaboration, especially in remote teams, and supports professional growth and ongoing learning.
- Provides entertainment and social connection during breaks. Used in wellness and team-building programs. Viewed as a strategic asset in many companies.
| Benefit | Description |
| Employee engagement |
Builds connections among colleagues |
|
Knowledge sharing |
Allows quick information exchange |
| Brand awareness |
Employees act as brand ambassadors |
|
Recruitement |
Social channels expand hiring reach |
Risks and Challenges of Social Media Use at Work
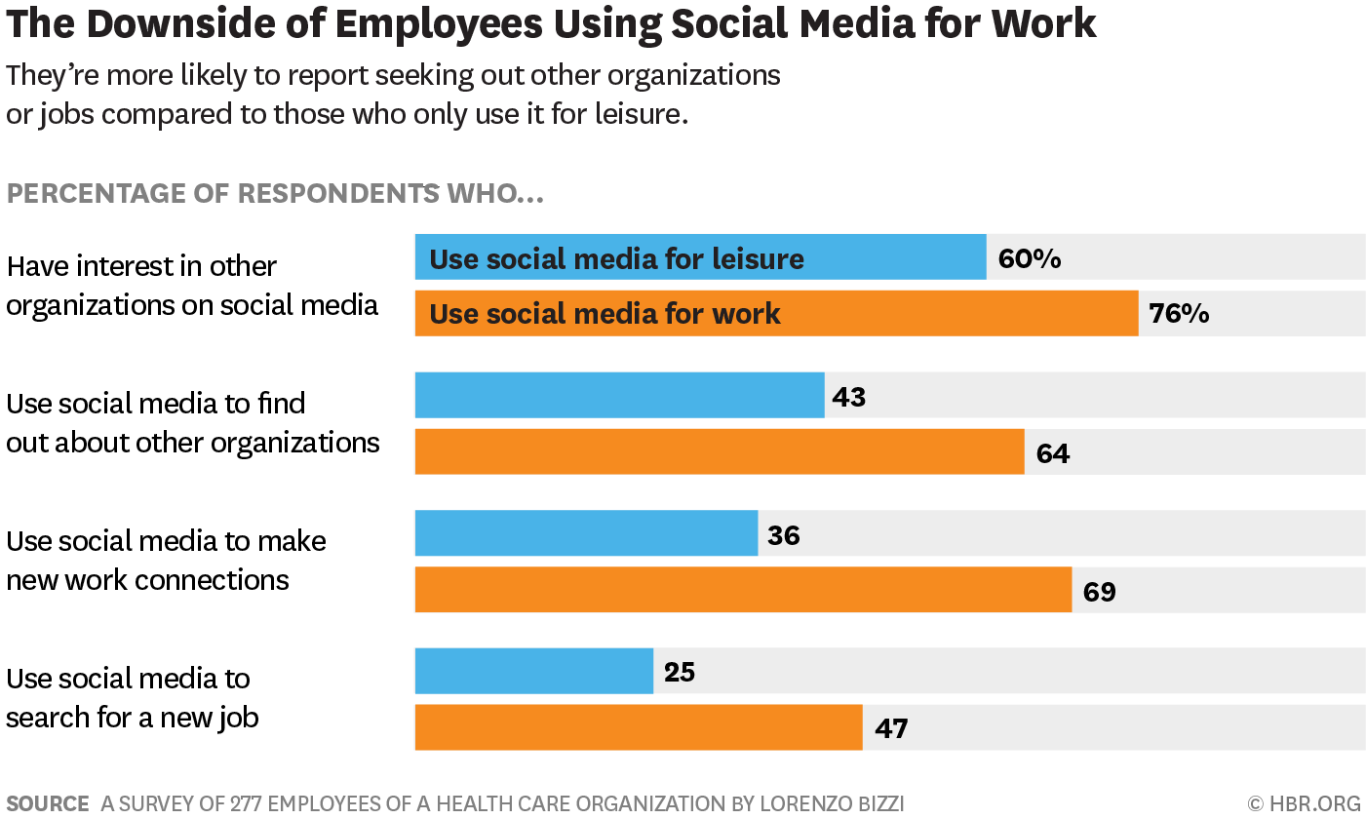
(Source: hbr.org)
- Excessive use causes productivity losses of 1 to 2 hours weekly, and social media introduces security risks like phishing and data leaks.
- Inappropriate posts can damage a company’s reputation, and social media misunderstandings may spark workplace conflicts.
- Blurred personal professional boundaries complicate HR issues, and overuse can reduce face-to-face team interaction.
- Constant connectivity may lead to burnout, and monitoring raises privacy and trust concerns. Balancing freedom and control remains challenging.
| Risk | Description |
| Productivity loss |
Time wasted on work-related content |
|
Security threats |
Potential for cyberattacks or leaks |
| Reputation damage |
Harm to the company’s image due to social posts |
|
Workplace conflicts |
Disagreements fueled by social media |
Trends in Social Media Use Post-Pandemic
(Source: frontiersin.org)
- Remote work increased daily social media use for communication and connection. 56% of remote employees use social media daily to stay engaged with teams.
- Microsoft Teams, Slack, and LinkedIn usage soared during and after the pandemic. Companies integrate social media into their culture for wellness and engagement.
- Personal and professional social media lines are more blurred in remote setups and virtual events, and online communities expanded via social media.
- Social media use is expected to grow with hybrid work models. Employers invest in training and tech to enhance safe social media use. New platforms adapt to evolving communication needs in the workplace.
| Post-Pandemic Trend | Percentage / Description |
| Remote employees use social media daily |
56% |
|
Growth in professional social platforms |
Significant |
| Integration into corporate culture |
Increasing |
Conclusion
Social media has become an integral part of the modern workplace, as shown by the latest social media in the workplace statistics. Its widespread use connects employees to both personal networks and professional resources, offering benefits like improved communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. However, these statistics also highlight the challenges, including distractions, productivity loss, and security risks, that organizations must carefully manage.
Striking the right balance through responsible use, clear policies, and monitoring is essential to maximize the advantages of social media while minimizing its downsides. As work environments continue to evolve, especially post-pandemic, understanding social media at the workplace statistics helps companies create smarter strategies that keep employees engaged, informed, and productive. In the end, the impact of social media at work depends not just on how often it is used, but on how thoughtfully it is integrated into workplace culture to make connections, innovation, and growth.


