Introduction
Endpoint Security Statistics: In 2025, the world is more interconnected than ever, and with that connectivity comes an expanded attack surface. The endpoint, any device that connects to an organization’s network, from laptops and servers to smartphones and IoT devices, has become a prime target for cybercriminals. The evolution of remote work and the proliferation of personal devices in the workplace have fundamentally changed how we approach security.
This article will break down the latest, most crucial endpoint security statistics changing the security landscape, giving you a data-driven look at the threats, costs, and market trends you need to understand. Let’s get into it.
Editor’s Choice
- 68% of organizations have experienced a successful endpoint attack that compromised data or IT infrastructure.
- 81% of businesses have been hit by an attack involving malware.
- 55% of security professionals consider smartphones to be the most vulnerable endpoint.
- The global average cost of a data breach is a record high of $4.88 million in 2024.
- In the United States, the average cost of a data breach is $9.36 million, the highest worldwide.
- Breaches identified and contained within 200 days cost 23% less than those that take longer.
- Ransomware attacks are projected to hit a business or consumer every 2 seconds by 2031.
- 59% of ransomware attacks involve data in the public cloud.
- Phishing and social engineering account for 48% of endpoint security threats.
- The use of AI and deepfake technology in phishing attacks increased by 15% in the last year.
- 70% of organizations allow employees to use their personal devices for work through BYOD policies.
- 67% of IT professionals believe BYOD has decreased their organization’s security posture.
- Personal devices are twice as likely to be infected with malware as company-issued devices.
- 36% of employees who use personal devices for work admit to delaying security updates.
- The global endpoint security market is projected to reach $33.7 billion by 2032.
- 70% of companies plan to increase spending on endpoint security solutions in the next two years.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the fastest-growing segment, with a 8% CAGR.
Cyber Threats to Endpoints
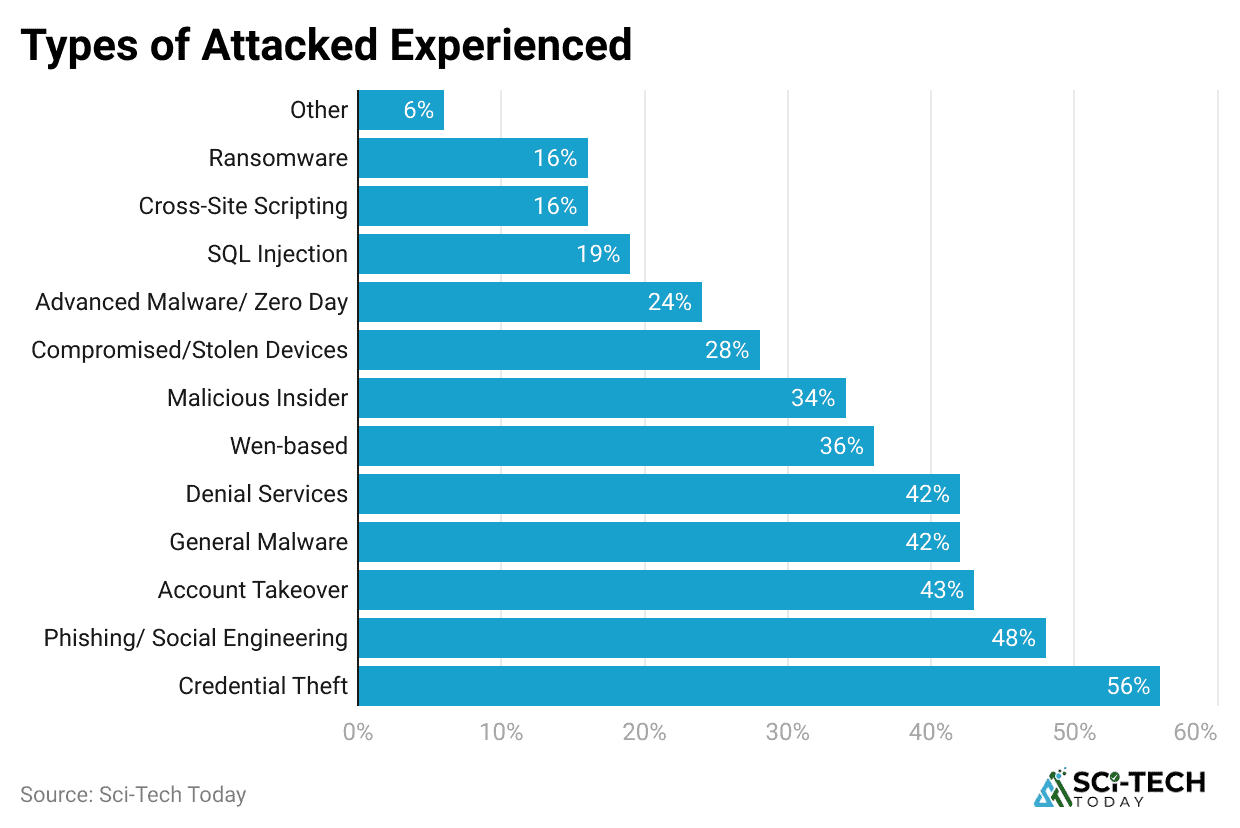 (Reference: scoop.market.us)
(Reference: scoop.market.us)
- 68% of organizations have experienced at least one successful endpoint attack that compromised their data or IT infrastructure. This highlights a clear and present danger that traditional perimeter defenses alone cannot stop.
- 81% of businesses have been impacted by an attack involving some form of malware, and a large portion of these infections start on an endpoint device through a malicious link or file download. This shows the scale and ubiquity of malware as a threat vector.
- 55% of security professionals consider smartphones to be among their most vulnerable endpoints, reflecting the growing risk posed by mobile devices that often access corporate data from unsecured networks. The use of mobile devices for business has introduced a massive blind spot for many organizations.
- 47% of organizations admit they don’t monitor their networks 24/7, leaving a significant window of vulnerability for attacks that can go unnoticed for weeks or even months. This lack of continuous monitoring is a major gap in modern endpoint security practices.
- The human element remains a critical vulnerability, with reports indicating that it is involved in up to 68% of all data breaches. This includes employees falling for phishing scams or using weak passwords on their endpoint devices.
- By 2025, it’s predicted that 45% of global organizations will have faced attacks on their software supply chains, where a compromised software component is used to deliver a malicious payload to an endpoint. This is a particularly insidious form of attack.
- Over 80% of data breaches involve the use of stolen credentials, which are often harvested from endpoint devices through phishing, keyloggers, or other malicious software. This underscores the need for robust identity and access management.
- 62% of cybersecurity experts identify data leaks and data loss as the most significant risks associated with Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) practices. These unmanaged personal devices are a huge liability for corporate data.
- A recent survey found that 36% of employees who use personal devices for work admit they often postpone important security updates. This negligence creates open pathways for attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities on their endpoint.
- In 2024, the United States saw the highest average data breach cost at $9.36 million, which reflects the high value of data and the severity of regulatory penalties in the country. This serves as a stark warning to organizations operating in this region.
- Over 1 million people join the internet every single day, and each new user adds another potential endpoint and another potential point of attack. This ever-expanding digital footprint means the threat landscape is constantly growing.
- Healthcare has been the most expensive industry for data breaches for 14 consecutive years, with the average cost exceeding $9.77 million in 2024. This is largely due to the high value of patient data and the critical nature of their systems.
- Breaches involving stolen credentials take an average of 292 days to detect and contain. This extended time allows attackers to cause far more damage, making early detection a critical component of any endpoint security strategy.
Endpoint Security Market Size
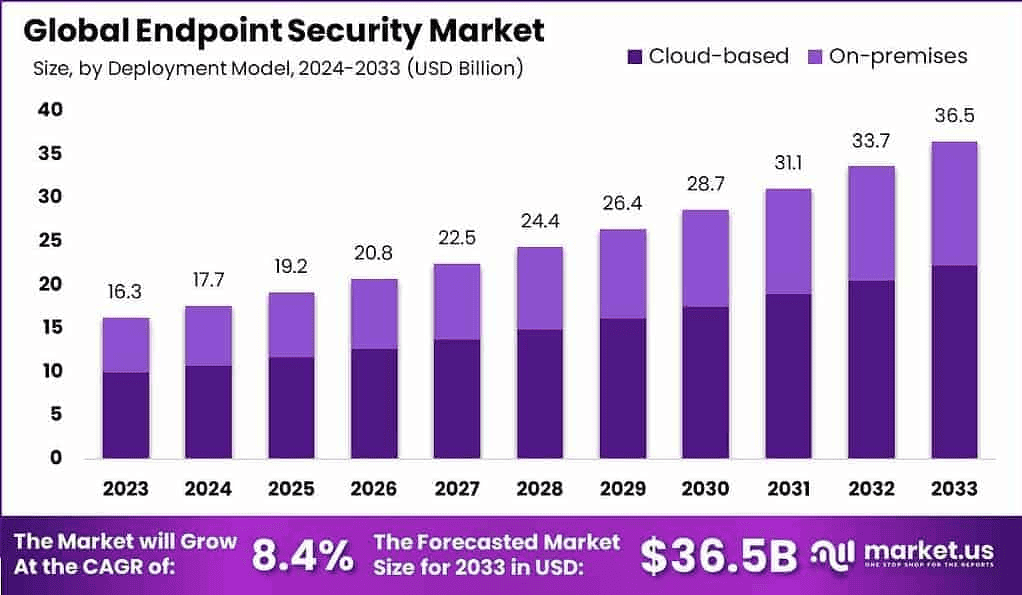
(Source: market.us)
According to Market.Us, the Endpoint Threat Protection market is a critical and rapidly expanding sector of the cybersecurity industry. Driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the widespread adoption of remote work, this market is seeing significant growth and development. Here is a breakdown of the key statistics shaping its landscape.
- The global Endpoint Threat Protection market size is expected to reach $38 billion by 2034, up from $17.42 billion in 2024. This represents a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.10%.
- In 2024, the solution segment dominated the market, capturing more than a 67.3% share of the total market. This dominance is a result of organizations prioritizing robust tools to combat evolving threats.
- The on-premise segment held a leading position in 2024, accounting for over 62.8% of the global market. This highlights the preference for in-house control and integration with legacy systems, particularly among large organizations.
- The large enterprise segment was the dominant end-user in 2024, commanding more than a 71.3% share of the global Endpoint Threat Protection market. This is driven by their extensive IT infrastructure and higher cybersecurity budgets.
- The Government & Defense sector held a significant share in 2024, capturing over 26.7% of the global market. This reflects the critical importance of securing national security systems and sensitive data.
Regional Market Insights
- North America led the Endpoint Threat Protection market in 2024 with a 37.4% share, generating approximately $6.5 billion in revenue.
- The U.S. market alone was valued at $5.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 15.6% CAGR, showcasing its critical role and robust growth.
- Europe’s market is expected to grow steadily, driven by strict regulatory frameworks like GDPR that mandate comprehensive data protection.
- The Asia Pacific region is rapidly adopting endpoint security solutions, fueled by rapid digitalization and an expanding threat landscape.
Analysis by Component, Deployment, and Organization
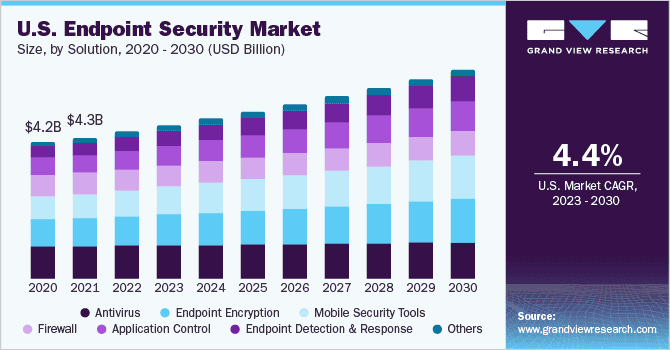 (Source: grandviewresearch.com)
(Source: grandviewresearch.com)
- The solution component is central to the market, with Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and endpoint encryption tools seeing rapid adoption.
- Despite the growth of cloud solutions, on-premise deployment remains the preferred choice for 62.8% of the market, primarily due to concerns over data governance and control.
- Large enterprises, representing 71.3% of the market, are the key drivers of advanced endpoint security adoption. Their need to protect vast, complex networks and comply with regulations pushes them to invest in the most sophisticated solutions.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are an emerging segment, with a growing awareness of cybersecurity risks and a rising demand for affordable, scalable solutions.
Key Drivers and Challenges
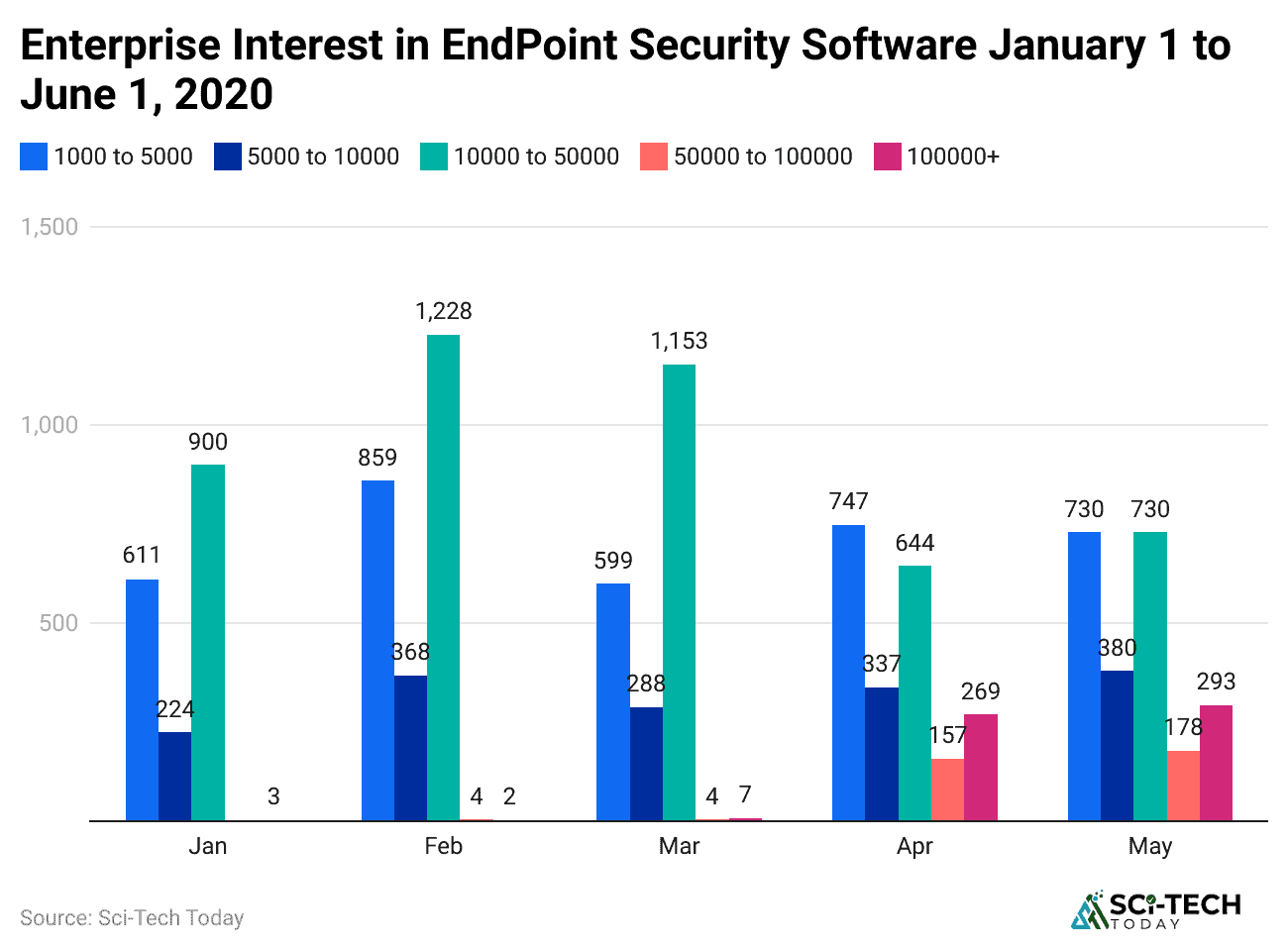 (Reference: trustradius.com)
(Reference: trustradius.com)
- The integration of AI and machine learning (ML) is a major driver, as these technologies enhance threat detection by 15% on average, identifying new and evolving threats more effectively than traditional methods.
- The shift to remote work and BYOD policies has expanded the number of endpoints, creating an opportunity for vendors to offer solutions that secure diverse devices and locations.
- A significant challenge is managing the complexity of diverse endpoint environments. Organizations often struggle to ensure consistent security across multiple device types and operating systems, leaving them vulnerable to undetected breaches.
- Balancing security measures with user privacy and experience is a core challenge. Overly restrictive security can reduce productivity and lead to user frustration, making it essential for solutions to be effective yet unobtrusive.
Endpoint Detection and Response in the Modern Age
 (Reference: innovatecybersecurity.com)
(Reference: innovatecybersecurity.com)
- The EDR market is expanding at a 15.8% CAGR, easily outpacing legacy antivirus tools. This growth is a direct result of organizations seeking more comprehensive protection against advanced threats.
- By 2025, many small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) will abandon traditional antivirus solutions in favor of sophisticated EDR tools. This indicates a growing awareness among smaller organizations of the need for better endpoint security.
- Organizations that use AI and automation can identify and contain breaches almost 100 days faster than those that don’t. This is a powerful testament to the efficiency and effectiveness of modern EDR and XDR solutions.
- 58% of the endpoint security market’s revenue share in 2024 was held by cloud platforms, with this segment projected to grow 15.2% annually to 2030. This shift to the cloud is a key trend driven by the needs of remote and hybrid workforces.
- Only 50% of organizations encrypt sensitive data on their devices, leaving half of all endpoints highly vulnerable to data exfiltration if a breach occurs. Encryption should be a non-negotiable part of any endpoint security strategy.
- The average time to identify and contain a data breach has decreased by 9 days from 2023, now standing at 268 days. This improvement is a direct result of organizations adopting more effective endpoint security tools.
- 70% of companies plan to increase their spending on endpoint security solutions over the next two years. This is a clear sign that organizations are prioritizing these investments to protect their assets.
- The average time for a data breach to be contained is 64 days. EDR solutions are specifically designed to reduce this timeline, which in turn significantly reduces the overall cost and damage of an attack.
- It takes an average of 204 days for organizations to even identify a data breach, which gives attackers ample time to exfiltrate data and move laterally through the network. This highlights the need for continuous, real-time monitoring.
- A recent report found that 32% of all ransomware attacks resulted from an unpatched vulnerability. Modern EDR and patch management solutions are critical for closing these security gaps before they can be exploited.
The Rise of Ransomware and Phishing
 (Reference: checkpoint.com)
(Reference: checkpoint.com)
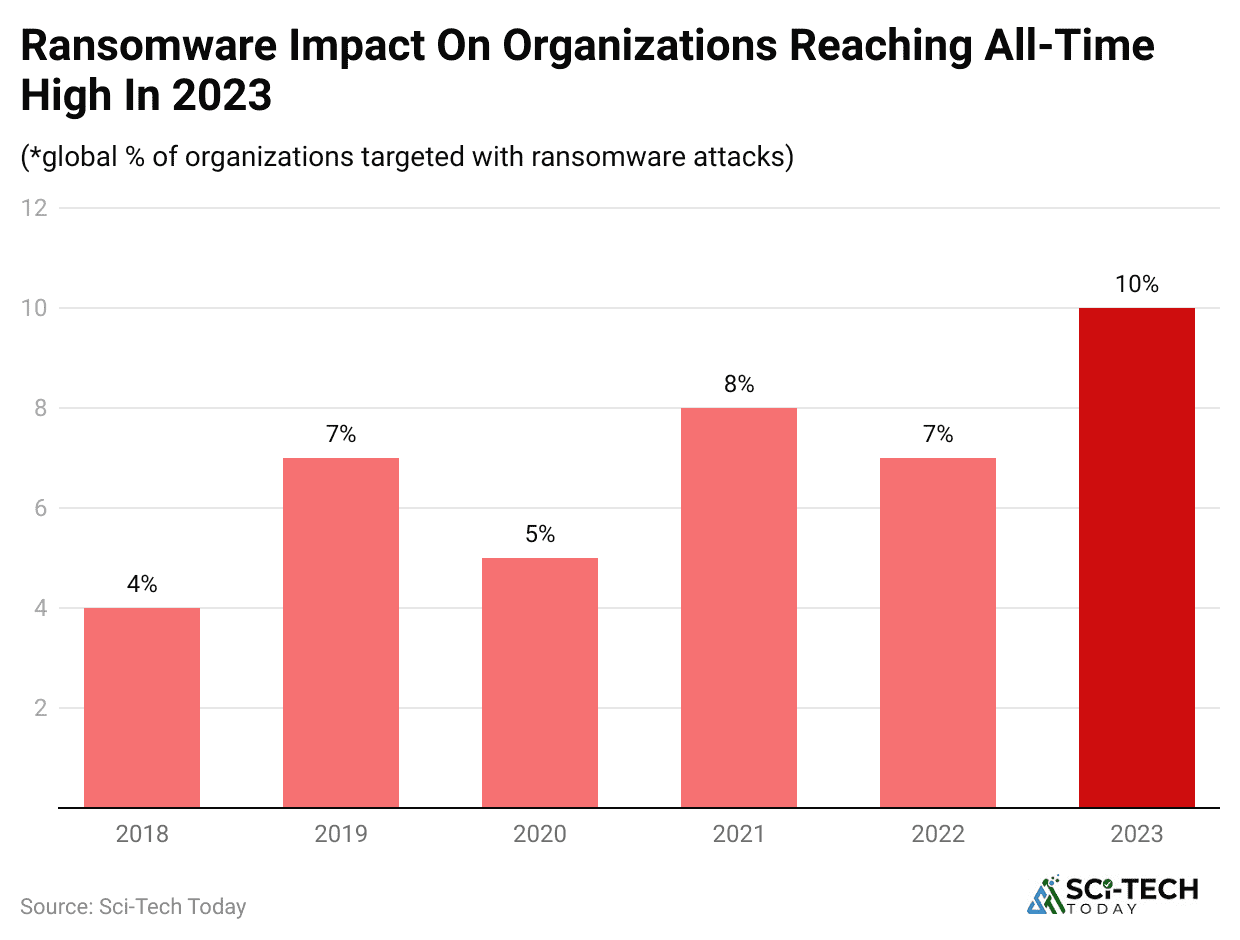
- In the first quarter of 2025, the number of ransomware attacks surged by a shocking 213% compared to the same period in 2024. This shows the explosive growth of this threat.
- Ransomware attacks are projected to hit a business or consumer every two seconds by 2031, which would amount to 43,200 attacks per day. This is a massive leap from the 7,850 attacks per day in 2021.
- Ransomware was responsible for a full 59% of all cyberattacks faced by organizations in 2024. This makes it a primary threat that every business needs to prepare for.
- 53% of organizations reported being hit by a successful ransomware attack in 2021, representing a 148% increase YoY. This trend continues to accelerate, with no signs of slowing down.
- 59% of ransomware attacks that involve data encryption involve data stored in public cloud environments like Office 365 or Amazon Web Services (AWS). This shows how attackers are adapting to modern cloud infrastructure.
- Phishing scams are the root cause of 80-95% of all human-associated breaches, making them the most common attack vector. An effective endpoint security strategy must include robust phishing defenses.
- In the first quarter of 2025, the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) observed over 1 million phishing attacks, marking a significant increase and highlighting the sheer volume of these threats.
- Business email compromise (BEC) attacks, a form of phishing, were reported by 64% of businesses in 2024, with a typical financial loss averaging $150,000 per incident. These targeted attacks are a major threat to corporate finances.
- Phishing attacks that mimic government bodies have increased by 35%, often leveraging claims about overdue taxes or fines to trick unsuspecting employees. This plays on people’s fear and sense of urgency.
- The use of AI and deepfake technology in phishing attacks increased by 15% in the last year, making it harder for employees to distinguish between a real message and a malicious one. This shows how attackers are leveraging new technologies.
Remote Work and BYOD Statistics
 (Reference: securelist.com)
(Reference: securelist.com)
- 98% of remote workers would continue to work remotely for the rest of their careers, and 66% believe it should be a legal right. This indicates that remote work is here to stay, and so are the security challenges it brings.
- 70% of organizations allow employees to use their personal devices at work through Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies. This shows that the practice is widespread and a core part of modern business.
- 67% of IT professionals believe the use of BYOD devices has decreased their organization’s security posture. This is a significant concern, as personal devices are often not as well-protected as company-issued equipment.
- Studies show that personal devices are twice as likely to become infected with malware compared to company-issued devices. This is a direct consequence of lax security practices on personal endpoints.
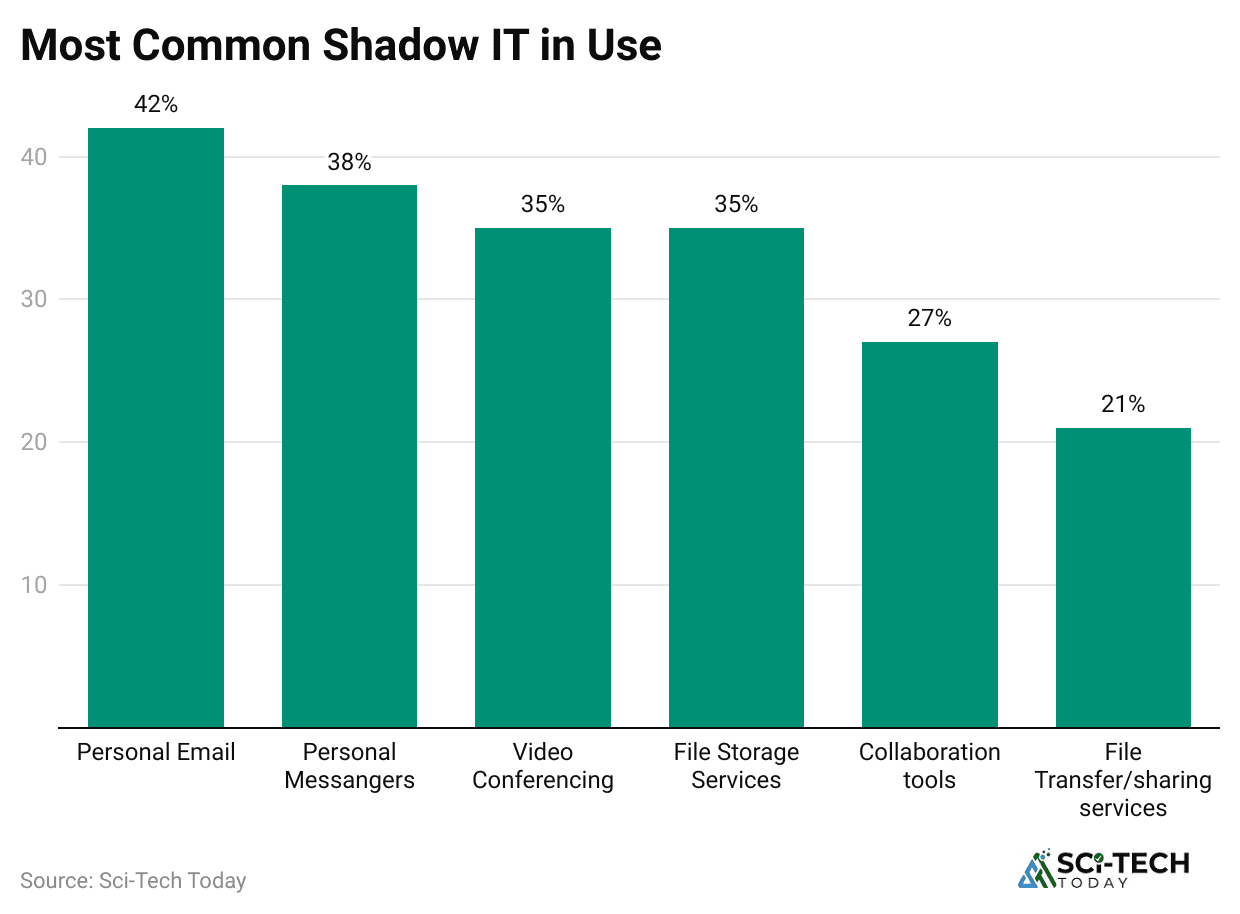
- 39% of organizations list security concerns as the top obstacle to adopting BYOD. This fear is well-founded, given the high risk of data breaches and malware infections associated with personal devices.
- The BYOD security market is projected to grow from $53.1 billion in 2025 to $285.9 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.2%. This massive growth shows that companies are actively seeking solutions to manage this risk.
- Only 15% of companies offer employees a work-issued smartphone, with 61% of organizations expecting employees to be accessible remotely, even if they don’t provide a company device. This pushes the security burden onto the employee.
- 40% of organizations admit to delaying patch rollouts to avoid potential conflicts, which creates a significant window of vulnerability for remote workers on their endpoint devices. This is a critical security gap that needs to be addressed.
- Over 80% of senior IT directors have faith that smartphones play a crucial role in employee productivity. This high reliance on mobile devices means that their security must be a top priority.
- A recent survey found that 80% of executives frequently send work-related communications from their personal devices, which puts highly sensitive information at risk. This shows that the security problem extends to the highest levels of an organization.
Future of the Endpoint Security Market
 (Source: rootsanalysis.com)
(Source: rootsanalysis.com)
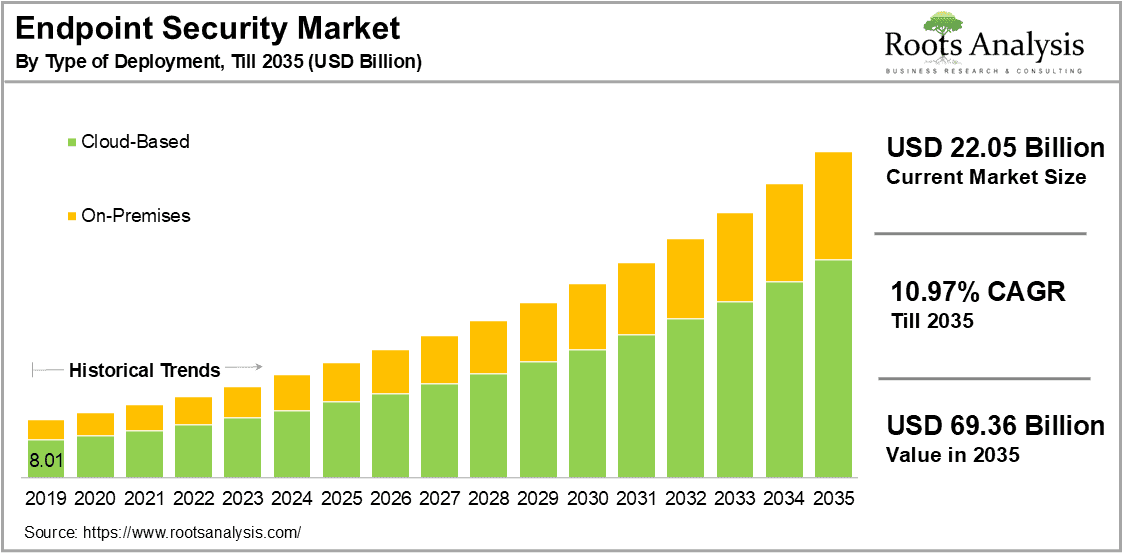
- The global endpoint security market is expected to reach approximately $33.7 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% from 2024 to 2033. This consistent growth shows the enduring demand for these solutions.
- North America is predicted to maintain its position as the largest market for endpoint security solutions, while the Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing market. This highlights the global nature of the cybersecurity challenge.
- The number of connected IoT devices is projected to reach 40 billion by 2030, and each of these devices is a new endpoint that needs to be secured. This massive proliferation of devices is a key driver of market growth.
- The Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market, which bundles endpoint security with other networking and access controls, is predicted to exceed $25 billion by 2027. This shows a move toward more integrated, unified security platforms.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) represent the fastest-growing buyer block in the endpoint security market, with a projected 13.8% CAGR. Subscription licenses and automated remediation are making advanced solutions more accessible to these smaller businesses.
- The global cybersecurity spending will grow 12.2% in 2025, crossing $377 billion by 2028. A significant portion of this investment will be directed toward endpoint security solutions as organizations fortify their defenses.
- More than 43% of global business leaders will focus on technology modernization, and 34% will invest in ongoing security training in 2025. This shows a proactive shift in strategy beyond just buying new software.
- The use of cloud-based endpoint security solutions will grow at an annual rate of 15.2% by 2030, driven by the need for scalable and flexible solutions that can protect a distributed workforce.
- The banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector held a 20.8% revenue share in the endpoint security market in 2024. This highlights the critical importance of protecting financial data and the regulatory pressure on this industry.
Conclusion
Overall, this endpoint security statistics evidence confirms that it is the cornerstone of modern defense, moving far past its previous role as a simple addition. With 68% of successful attacks breaching the network via an endpoint and the average cost of a data breach soaring to $4.88 million, the financial and operational necessity is undeniable.
The market’s projected surge to $38 billion by 2034, driven by the shift to remote work, the rise of sophisticated ransomware, and the need for advanced EDR/XDR solutions, signals that every device, from a laptop to an IoT sensor, is a high-value asset that must be secured. I hope you like this article. Thanks for staying up till the end.


