Introduction
Cloud Security Statistics: Imagine for a moment that your company’s most sensitive files, customer lists, and financial records are up for sale to the highest bidder. In 2025, it’s not some rumors or hypothetical question; it’s a daily reality for thousands of businesses. One click on the wrong link. One weak password.
The result is devastating financial and reputational loss. This article will show you, with all the data, just how real and pervasive this threat is. In this article, we gathered the most up-to-date Cloud Security statistics. Let’s dive into the article.
Editor’s Choice
- Cybercrime is on track to cost the world $10.5 trillion in 2025 alone. To put that in perspective, if cybercrime were a country, it would have the third-largest economy in the world, right after the U.S. and China.
- The average cost for a company to recover from a single data breach has hit a record high of $4.88 million.
- This isn’t just a one-time fine; it includes everything from investigation and system repair to regulatory penalties and lost business.
- 95% of all cybersecurity incidents involve some form of human error. This proves that technology alone is not enough; your employees are a critical line of defense.
- Don’t assume only large corporations are targets. 60% of small businesses that suffer a major cyberattack are forced to shut down within just six months.
- On average, it takes companies 258 days, nearly nine months, to even identify and contain a data breach.
- An organization is now expected to be hit with a ransomware attack every 2 seconds by 2031. This high frequency has turned ransomware into a constant, unavoidable threat for businesses of all sizes.
- Cybercriminals are now using AI to craft highly convincing phishing emails. These AI-powered attacks have a click-through rate 3 times higher than those written by humans.
- The average Internet of Things (IoT) device, like a smart camera or thermostat, is attacked within 5 minutes of being connected to the internet, highlighting the massive security gaps in our connected world.
The Financial Cost of Cybercrime
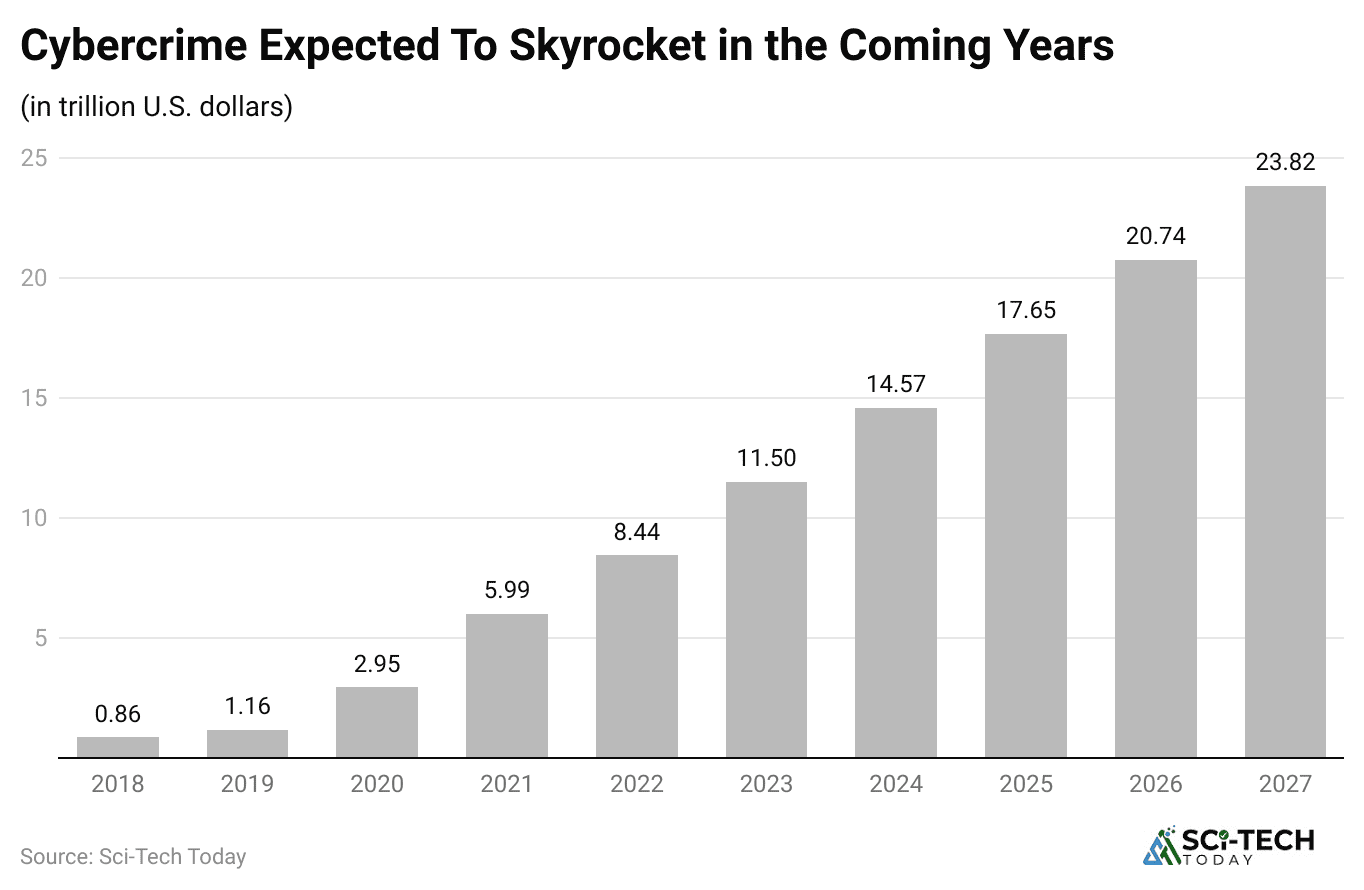 (Reference: researchgate.net)
(Reference: researchgate.net)
- The global cost of cybercrime is growing at a rate of 15% per year, a trajectory that will see it reach over $23 trillion annually by 2027, creating an economic drain larger than the cost of global natural disasters.
- The average cost of a data breach for a large corporation (over 25,000 employees) now exceeds $6 million, with costs spiraling due to complex IT environments and extensive regulatory requirements.
- For every $1 lost directly to fraudulent activity in a cyberattack, organizations spend an additional $3.75 on recovery, including technical investigations, customer support, and legal fees.
- Organizations that have fully deployed security AI and automation save an average of $1.76 million per breach compared to those without, proving that investing in advanced technology yields significant returns.
- The “breach tax” is a real phenomenon, with 63% of breached companies increasing the price of their products and services to cover recovery costs, effectively passing the financial burden of cybercrime onto their customers.
- A single minute of IT downtime costs an average of $8,600 for a medium-sized enterprise, which can quickly add up to millions during a prolonged ransomware attack or system outage.
| Global Annual Cost Projection (2025) | $10.5 Trillion |
| Average Data Breach Cost (Overall) |
$4.88 Million |
|
Average Cost for the Healthcare Industry |
$9.77 Million |
| Cost Savings with Security AI |
$1.76 Million Saved per Breach |
|
Percentage of Firms Raising Prices Post-Breach |
63% |
Cloud Security Breaches Statistics
- Cloud security breaches have become common across the world as more companies shift their operations to cloud platforms.
- Around 80% of companies faced at least one cloud security breach in the past year.
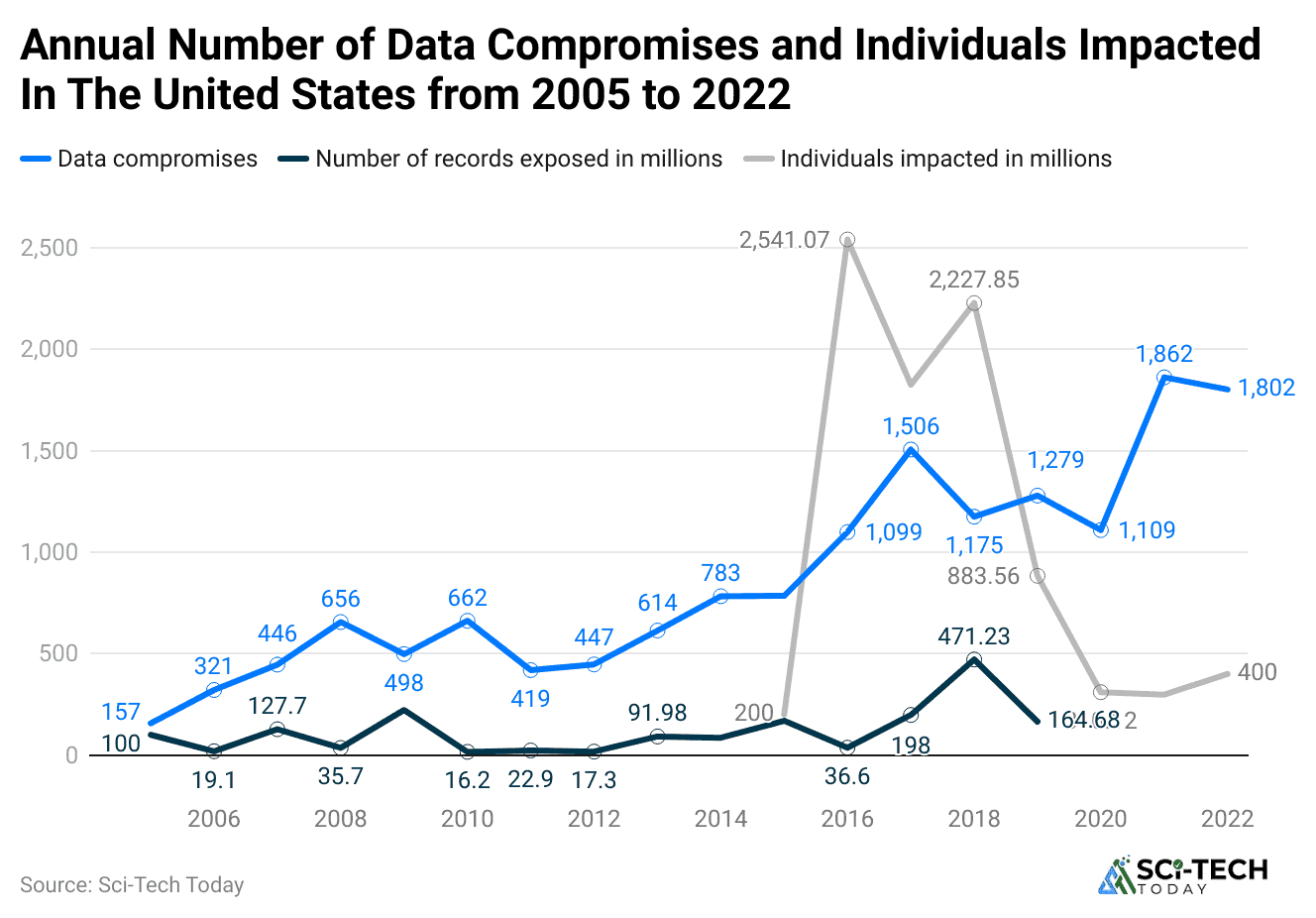
- Nearly 27% of organizations suffered a public cloud security issue last year, showing a 10% rise from the previous year.
- In the last quarter of 2023, more than 8 million data records were exposed worldwide due to cloud breaches.
- Almost 96% of organizations encountered challenges while managing their cloud strategies effectively.
- About 45% of businesses dealt with four or more cloud-related security incidents over the past year.
- In 2022, 62% of organizations believed they were likely to face a cloud data breach within the following year.
- The most common types of cloud security problems included runtime security issues (34%), unauthorized access (33%), misconfigurations (32%), unresolved vulnerabilities (24%), and failed audits (19%).
- The public sector (88%) and startups (89%) were among the most affected groups in 2023.
- Overall, cloud environment breaches increased by 75% between 2022 and 2023, showing a sharp rise in cyber threats targeting cloud systems.
Major Security Breaches Statistics
- In early 2024, National Public Data suffered a major breach that reportedly exposed 2.9 billion records, revealing sensitive personal details of around 170 million individuals across the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
- A ransomware attack targeted Change Healthcare in 2024, affecting the personal data and operations linked to at least 100 million people.
- In May 2024, Dell faced a brute-force cyberattack that led to the exposure of 49 million customer records.
- In June 2023, Toyota accidentally exposed data from 260,000 customers because of a misconfigured cloud environment.
- AT&T experienced a significant security breach where hackers accessed personal information belonging to 73 million current and former users.
- In December 2023, the Real Estate Wealth Network accidentally leaked about 1.5 billion records, putting a large amount of user data at risk.
Cloud Security Market Size
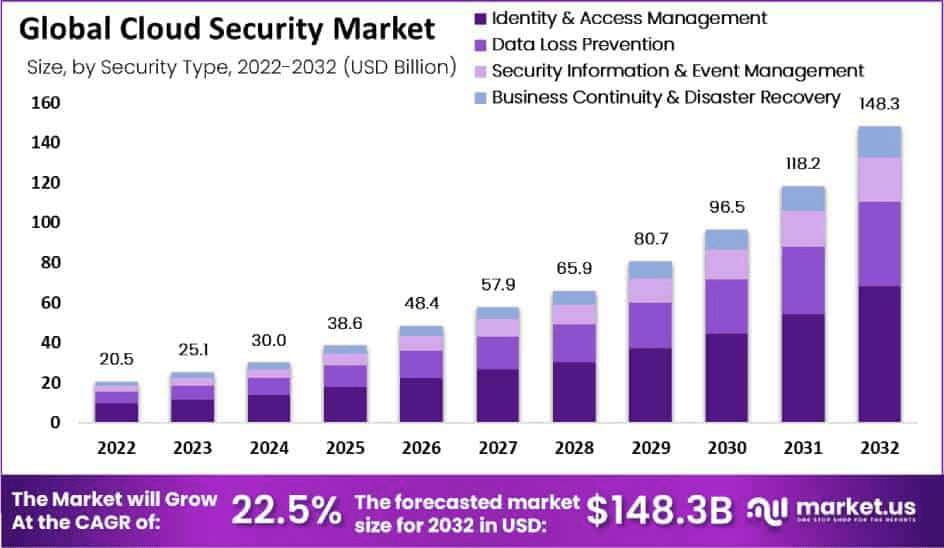 (Source: market.us)
(Source: market.us)
- The global cloud security market was valued at USD 20.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 148.3 billion by 2032, growing at a strong 22.5% CAGR during the forecast period.
- The market expansion is driven by the growing need to protect digital data stored on cloud platforms.
- Rising cases of crypto-jacking and other cybercrimes have increased the demand for advanced cloud protection tools.
- The growing adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies in workplaces is further supporting market growth.
- The demand for cloud security solutions continues to rise due to increasing data breaches and more complex cyber threats.
- Key challenges include high implementation costs, data privacy issues, and limited trust in third-party cloud service providers.
- Strict government regulations regarding information security are also slowing down adoption in some regions.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) represents the largest market share at 46%, showing its critical role in controlling data access.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) are other major technologies contributing to market growth.
- Large enterprises dominate adoption due to their wide use of cloud computing and IoT-based systems.
- The IT and Telecommunications sector is expected to record the fastest growth, followed by healthcare and retail industries.
- North America leads the global market, with Europe in second place and Asia-Pacific expected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
- Major companies operating in this field include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks, Trend Micro, Broadcom, Check Point Software, Google, McAfee, IBM, Zscaler, Cisco Systems, and Fortinet.
Industries Most Affected by Cloud Security Breaches
- The public sector has faced one of the highest exposure levels, with 88% of organizations reporting at least one cloud data breach in the past year.
- Startups have shown even greater vulnerability, as 89% reported experiencing a security breach between 2023 and 2024.
- In the healthcare field, more than 60% of providers have been affected, often losing sensitive patient records due to unauthorized access.
- The financial industry has also struggled, with over 70% of institutions reporting breaches mainly caused by weak API protections and poor identity access management settings.
- The real estate sector experienced a major incident in 2023, when nearly 1.5 billion records were leaked, highlighting that attackers are also targeting personal data beyond financial information.
- Government agencies continue to report high breach rates, with 88% citing configuration errors as their main challenge, showing that even tightly regulated systems face gaps in access control and encryption.
Biggest Cloud Breaches of 2023–2025
- According to Spacelift, by 2025 approximately 80 % of companies had faced a cloud security breach within the previous year.
- Spacelift also reports that 60 % of organisations experienced public-cloud incidents during 2024.
- The number of breaches in cloud environments rose by around 75 % between 2022 and 2023, according to Spacelift.
- According to GoAllSecure, the global average cost of a data breach reached about US $4.76 million in 2025, with incidents in the U.S. and U.K. frequently exceeding US $9.5 million.
- Healthcare and financial organisations were especially impacted, with individual breaches averaging US $10–11 million in cost, as noted by GoAllSecure.
- GoAllSecure also estimates that the cost per record breached ranged between US $180 and US $260, depending on sector and region.
- Nearly 45 % of companies reported handling four or more cloud incidents in the past year, based on Spacelift’s findings.
- The 2024 ransomware attack on Change Healthcare affected more than 100 million individuals, making it one of the most disruptive healthcare breaches in U.S. history.
- The 2024 breach of National Public Data exposed approximately 2.9 billion records, ranking among the largest leaks ever recorded.
- In 2023 the zero-day exploit of MOVEit led to the compromise of 94 million users and caused over US $15 billion in damages across 2,500 organisations.
- The 2024 breach of Ticketmaster placed data from 560 million customers up for sale by attackers.
- In 2024 the AT&T breach compromised data from 73 million current and former customers.
- A brute-force attack on Dell Inc. in 2024 exposed 49 million records.
- A misconfiguration at Toyota Motor Corporation in 2023 exposed 260,000 customer records.
- The leak from Real Estate Wealth Network in 2023 exposed 1.5 billion records.
- In 2025 the Roblox Corporation breach exposed data from 4,000 members of its developer community.
- The McDonald’s Corporation cyber incident in 2025 leaked 64 million job-applicant records via a chatbot compromise.
- A social-engineering attack on Google LLC’s Salesforce CRM in 2025 led to access to data from dozens of companies.
- The Yale New Haven Health breach in 2025 exposed records of 5.6 million patients.
The Anatomy of a Modern Cyberattack
 (Source: statista.com)
(Source: statista.com)
- Phishing remains the undisputed king of attack vectors, used as the initial entry point in over 80% of all reported security incidents and 95% of breaches with a human element.
- Spear-phishing attacks, which are highly targeted emails aimed at specific individuals, account for 71% of all targeted attacks and are incredibly effective due to their personalized nature.
- Ransomware attacks have evolved beyond simple encryption; in 85% of cases, attackers now also steal a copy of the data before encrypting it, a tactic called “double extortion” used to pressure victims into paying.
- Despite the high stakes, only 57% of organizations that pay the ransom successfully recover their data, meaning paying the criminals offers no guarantee of a solution and often funds their next attack.
- Over 560,000 new pieces of malware are detected every single day, an overwhelming volume that makes it impossible for traditional signature-based antivirus solutions to keep up.
- Insider threats, both malicious and accidental, are involved in over 34% of data breaches, with the average cost of a breach caused by a malicious insider reaching $4.9 million.
- Supply chain attacks, where criminals compromise a trusted third-party vendor to gain access to their targets, have increased by over 78%, as they allow attackers to bypass the strong defenses of a primary target.
| Phishing | Used in over 80% of all security incidents. |
| Ransomware | 85% of attacks now involve data theft (double extortion). |
| New Malware | 560,000 new variants are detected daily. |
| Insider Threats | Involved in 34% of breaches. |
| Supply Chain Attacks | Increased by 78% in the last year. |
Biggest Risk To Cloud Data Security
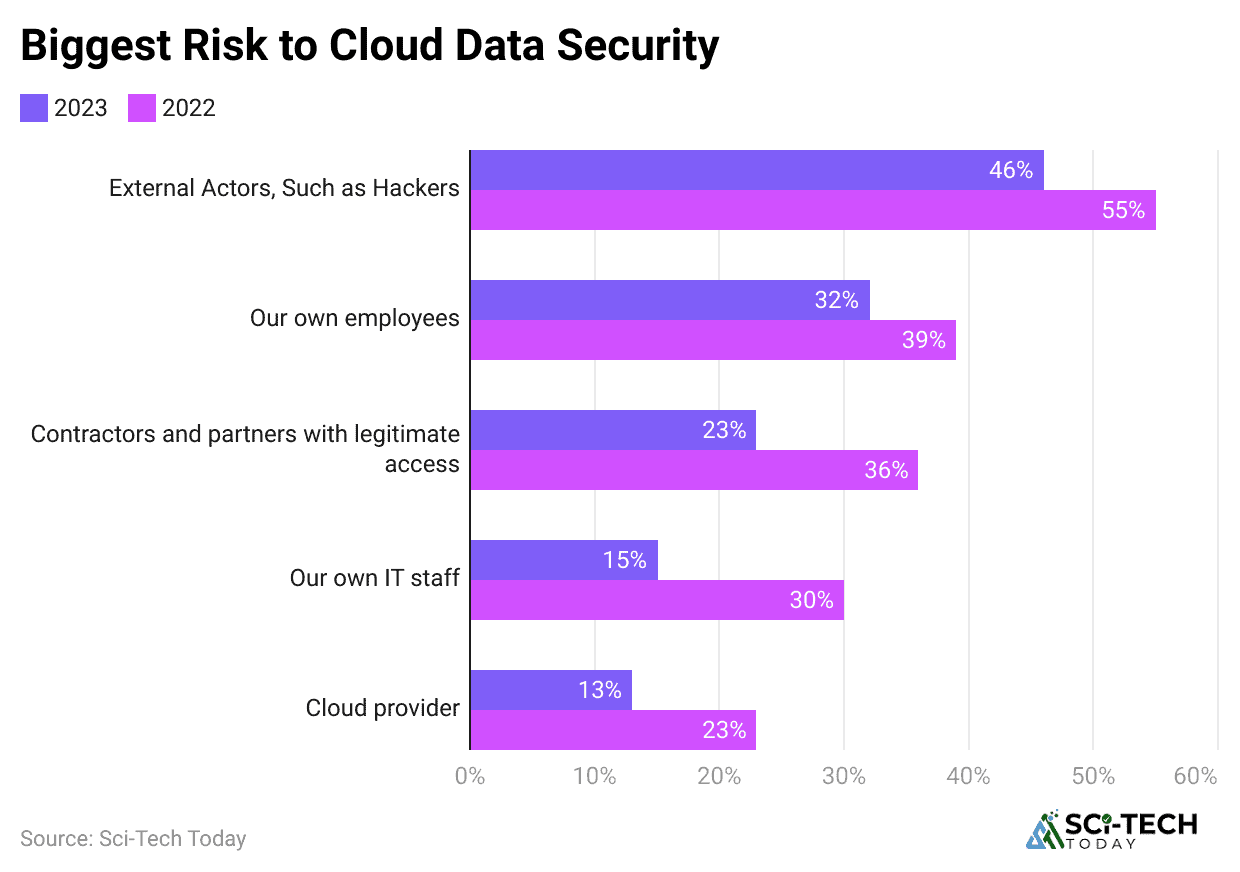 (Reference: stationx.net)
(Reference: stationx.net)
- A shocking 95% of all cybersecurity incidents can be traced back to some form of human error, from clicking a malicious link to misconfiguring a cloud server.
- Password hygiene remains a massive problem, with 68% of people reusing the same password across multiple accounts, meaning one breach can lead to a cascade of compromised services.
- Only 38% of global organizations state they have the resources to conduct effective security awareness training, leaving a majority of employees unprepared to recognize and report modern threats.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, a form of social engineering where attackers impersonate executives, result in an average loss of $120,000 per incident.
- Despite the risks, 53% of employees admit to using their personal devices for work, creating a “shadow IT” problem where sensitive data is stored on unsecured, unmanaged hardware.
| Breaches from Human Error | Contributes to 95% of all incidents. |
| Password Reuse | 68% of users reuse passwords across multiple sites. |
| Security Training Readiness | Only 38% of organizations feel prepared. |
| Shadow IT | 53% of employees use personal devices for work. |
Cloud Security Challenges Statistics
- As organizations shift from on-premises systems to cloud environments, they face new and constantly changing security challenges that require fresh approaches and compliance adjustments.
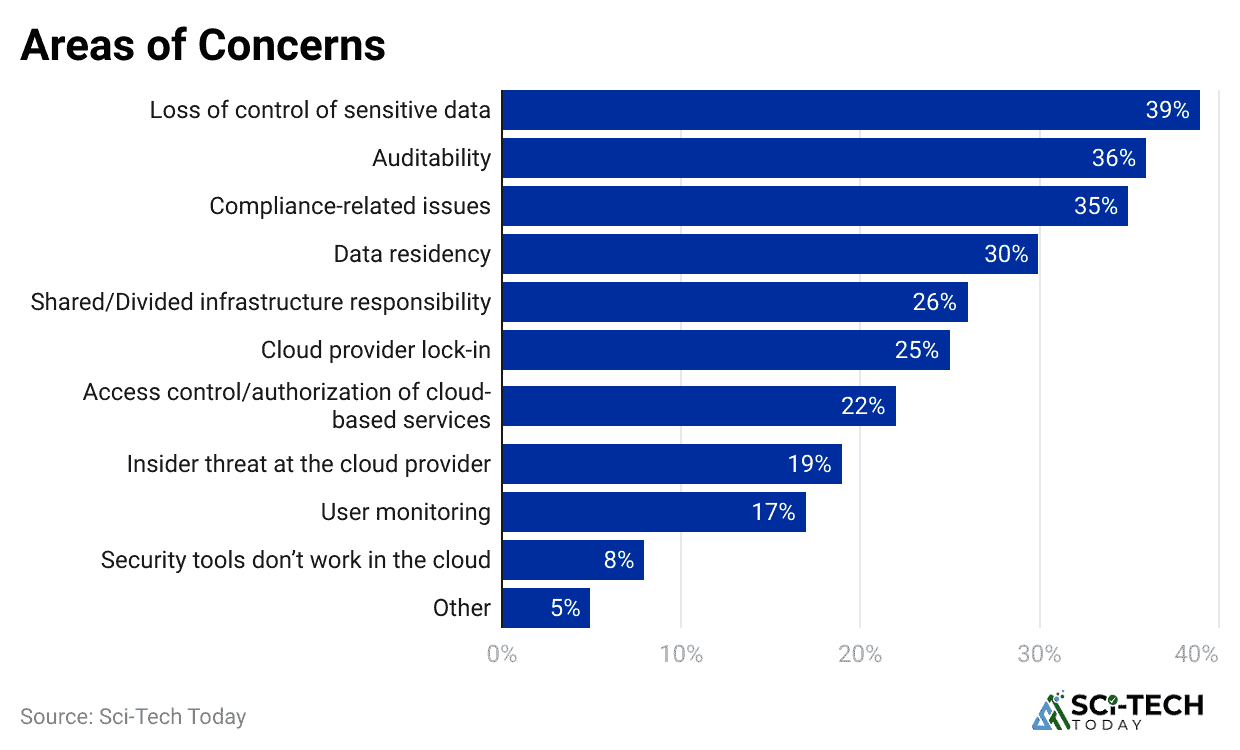
- Around 35% of IT professionals worry about account or service hijacking when moving to the cloud.
- About 31% of respondents identify malware and ransomware attacks as major risks.
- Another 31% express concerns about data privacy and compliance issues, such as GDPR violations.
- Nearly 28% highlight unauthorized access as a frequent threat during cloud operations.
- Around 26% report concerns over cyberattacks linked to nation-state actors targeting cloud infrastructure.
- The most pressing fear among companies using public cloud platforms is losing sensitive data, noted by 64% of professionals.
- Misconfiguration and weak security settings are reported by 51% of respondents as serious issues in cloud management.
- The same 51% are equally worried about unauthorized access to their cloud applications and data.
- Accelerated software development cycles cause security difficulties, including 35% citing lack of visibility and control during the development process.
- About 34% mention that software is sometimes released without complete security checks or testing.
- Roughly 33% admit that different development teams follow inconsistent security practices.
- Another 33% of developers overlook security measures to meet deadlines.
- Nearly 31% state that new software builds are launched with existing vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
- Only 40% of professionals report that security is strictly enforced during development and implementation stages.
- About 2% say that other teams never involve the security department in decision-making processes.
- Within DevOps, 56% of experts identify secret management as their top security concern.
- Around 52% find managing workforce identity and access control to be one of the hardest security challenges.
- Nearly 45% of respondents struggle to complete security-focused sprints within Scrum workflows.
- An overwhelming 96% of professionals express concern about their ability to manage growing security risks effectively.
- 41% of those surveyed believe that poor security awareness among employees poses a major threat.
- Around 36% cite weak integration and lack of interoperability between security tools as ongoing issues.
- A severe shortage of skilled cybersecurity workers is noted by 76% of respondents.
- 91% of security leaders plan to use artificial intelligence as a core part of their cybersecurity strategy.
- A significant 40% of organizations report receiving more than 40 security alerts each day, making it hard to prioritize responses.
- 54% of professionals find it difficult to manage compliance and cloud governance across different systems.
- About 49% struggle with integrating cloud applications into older legacy infrastructures.
- Finally, 72% of experts worry that a compromise in the underlying infrastructure could lead to major security failures.
Industry-Specific Metrics
 (Reference: orca.security)
(Reference: orca.security)
- Healthcare remains the most targeted and most expensive industry for data breaches, with an average cost of $9.77 million.
- The value of a single patient health record can be up to 50 times more valuable than a credit card number on the dark web.
- The Financial Services sector faces an average of $6.08 million in breach costs. This industry experiences the highest number of credential-stuffing attacks, where criminals use stolen passwords from other breaches to try and access bank accounts.
- Manufacturing and Industrial sectors have seen a 232% increase in ransomware attacks. These attacks are particularly devastating as they can halt production lines, disrupt supply chains, and cause immediate, massive financial losses.
- Government entities are prime targets for state-sponsored espionage and attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Over 47% of all attacks against government agencies are linked to nation-state actors seeking to steal secrets or cause chaos.
- The Education sector is surprisingly vulnerable, experiencing the highest volume of weekly cyberattacks
| Healthcare | Data Theft & Ransomware | $9.77 Million |
| Financial | Credential Stuffing & Phishing | $6.08 Million |
| Manufacturing | Ransomware & Operational Disruption | $4.73 Million |
| Government | Espionage & State-Sponsored Attacks | $2.9 Million |
Cloud Security Attack Statistics
- Around 45% of professionals stated that managing cloud security consumes a large portion of their engineering resources.
- Nearly 77% mentioned that poor training and weak teamwork make their security operations harder.
- About 41% said that using cloud-native systems adds more complexity to their work.
- Roughly 54% struggled to maintain consistent compliance standards across multiple cloud environments.
- Close to 49% found it difficult to connect new cloud tools with their older legacy systems.
- A shortage of skilled experts was reported by 71% of respondents, showing a clear talent gap in cloud cybersecurity.
- Approximately 91% expressed fear that their systems cannot handle zero-day threats or unknown attacks.
- In financial and insurance sectors, 70% faced deployment delays due to concerns about API security.
- Half of all surveyed professionals, or 50%, were highly concerned about cloud account hijacking and unauthorized access.
- Around 44% of data theft cases within organizations started from employees’ personal cloud applications.
- Nearly 88% of government agencies saw misconfigured cloud setups as a major security risk.
- About 70% of chief information officers felt that adopting cloud technologies reduced their overall control.
- Roughly 58% of companies believed their existing SaaS security measures protected only half of their SaaS applications.
- Around 7% admitted that they lacked any monitoring of their SaaS environments.
- Another 7% of cloud storage systems holding sensitive data were found to be publicly accessible.
- When it comes to attack targets, about 31% of incidents were directed at SaaS applications, 30% at cloud storage, and 26% at cloud management systems.
Biggest Cyber Breaches in Recent History
 (Reference: securiti.ai)
(Reference: securiti.ai)
- This was not a breach of the cloud platform itself, but a massive supply chain attack. Hackers used credentials stolen from third-party contractors and info-stealer malware to access the Snowflake accounts of over 165 high-profile customers, including Ticketmaster and Santander Bank.
- In a stunning example of social engineering, attackers from the “Scattered Spider” group spent just 10 minutes on the phone with the MGM help desk, impersonating an employee to gain initial access.
- The resulting ransomware attack crippled the company’s operations for over a week, shutting down everything from hotel key cards to slot machines and costing the company an estimated $100 million in damages.
- This was a classic zero-day exploit. A vulnerability was discovered in the popular MOVEit file transfer software, and before a patch could be widely applied, the Clop ransomware gang exploited it to steal data from over 2,700 organizations globally, affecting more than 93 million individuals.
Cloud Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Most cloud security problems happen because of basic mistakes, not advanced hacking techniques. Issues such as wrong storage settings, weak access rules, forgotten systems, and unsafe APIs are common reasons for data breaches.
- Misconfiguration is the biggest risk, like when storage is left public, access is too open, or data is not properly encrypted. These mistakes cause around 23% of all cloud security issues.
- Human error plays a major role in breaches. About 88% of incidents happen because of people’s mistakes rather than software bugs, showing that human behavior often weakens security.
- Phishing continues to be the most frequent cyberattack. In 2024, around 84% of businesses and 83% of charities that faced a breach reported phishing as the main cause.
- Insecure APIs are becoming a bigger danger, especially with the rise of multi-cloud systems and AI-based applications. Many companies connect systems quickly without adding enough security checks.
- Too much access and poor identity management let attackers move freely inside networks once they get in, making it easier to steal data or gain control.
- When attacks happen, responses are often too slow. Only 6% of security incidents are stopped within an hour, while most take more than 24 hours to contain.
Cloud Misconfiguration Statistics
- According to StrongDM, simple setup mistakes in the cloud, such as exposed storage or weak access permissions, are responsible for nearly one-fourth of all cloud security incidents.
- About 15% of data breaches start because of a misconfiguration, making it one of the most frequent entry points for attackers.
- When such an error leads to an attack, it usually takes around 186 days to detect and another 65 days to stop the threat, showing how long the impact can last.
- Each misconfiguration-related breach costs organizations an average of $3.86 million, highlighting its serious financial burden.
- As reported by CloudZero, nearly 68% of companies see cloud misconfiguration as their biggest security concern.
- According to Exabeam, around 82% of misconfigurations are the result of human error, not system flaws.
- StrongDM also projects that by 2025, almost 99% of cloud security failures will occur because of mistakes made by customers rather than by the cloud service providers.
Multi-cloud and Hybrid Cloud Security Challenges
- Many companies are no longer using a single cloud provider because they need more flexibility, better scalability, and freedom from vendor lock-in.
- Around 79% of organizations now use more than one cloud platform to improve reliability and operational flexibility.
- Managing security across these multiple environments is complex, and about 56% of companies find it difficult to protect data consistently.
- Nearly 69% of organizations admit they cannot maintain the same level of security controls across all their cloud providers.
- Visibility into system activities is limited, and enforcement of policies often becomes fragmented, which leads to higher risks of configuration errors and compliance failures.
- Hybrid cloud setups are particularly vulnerable because they mix on-premises and cloud resources, increasing the chance of weak monitoring and security gaps.
- The shortage of skilled professionals makes the issue worse, as 45% of businesses lack staff capable of managing multi-cloud security effectively.
- The growing number of security tools also creates confusion; many teams suffer from alert fatigue and respond only to a portion of threats.
- As a result, organizations detect just 35% of cyber threats through their automated systems, leaving significant blind spots in defense.
Conclusion
Overall, in 2025, Cloud Security is not an IT issue; it’s a fundamental pillar of business survival and success. The statistics are clear: threats are becoming more frequent, more sophisticated, and more costly every single year. From multi-million dollar ransomware demands to the slow drain of data theft, the risks have never been higher.
The good news is that awareness is the first step toward defense. By understanding these data, you can see that the most common attacks prey on the simplest weaknesses: human error, weak passwords, and delayed patching. By focusing on these fundamentals and embracing a proactive security culture, organizations can significantly reduce their risk and protect themselves in this challenging digital world. I hope you like this context. Thanks for staying up till the end.


