Online Recruitment Statistics: For organizations looking for the current employment landscape, the question isn’t whether to use digital tools, but how to integrate them. The global job market has been transformed; it’s faster, more competitive, and overwhelmingly candidate-driven.
Recruitment has become a data science challenge. So, this article dives deep into the metrics that define success in the modern era of online recruitment. We will peel back the layers on market growth, the dominance of AI and automation, the changing preferences of a mobile-first talent pool, and the impact of diversity on the bottom line.
If you’re looking for a complete analysis of, truth about attracting, assessing, and acquiring top talent in 2025, the following statistics offer the essential blueprint. We’ve compiled the latest figures to provide a clear, objective view of the digital hiring frontier. The data points below are essential reading for any executive or HR professional looking to gain an edge in a market where time is money. Let’s dive into the analysis.
Editor’s Choice
- 70% of passive candidates, those not actively job hunting, account for the global talent pool. Companies must use social media and branding to reach them.
- The global Online Recruitment Technology Market is projected to grow from $15.18 billion in 2025 to $37.76 billion by 2032, exhibiting a robust CAGR of 9%.
- 99% of Fortune 500 companies have implemented an Applicant Tracking System ATS, making tech literacy a mandatory prerequisite for all job applicants.
- 94% of employers believe skills-based hiring is a better predictor of job performance than relying solely on traditional resumes.
- 58% of candidates have actively turned down a job offer specifically because of a poor candidate experience during the hiring process.
- 70% of job seekers insist on knowing the expected salary range first when a recruiter approaches them about a new opportunity.
- 86% of interviews are now conducted virtually, a permanent shift that saves recruitment teams an average of 24% in cost compared to in-person meetings.
- Companies that strongly invest in candidate experience see their average quality of hire improve by 70%, demonstrating a direct link between engagement and talent level.
Global Market Dynamics and The Cost of Hiring
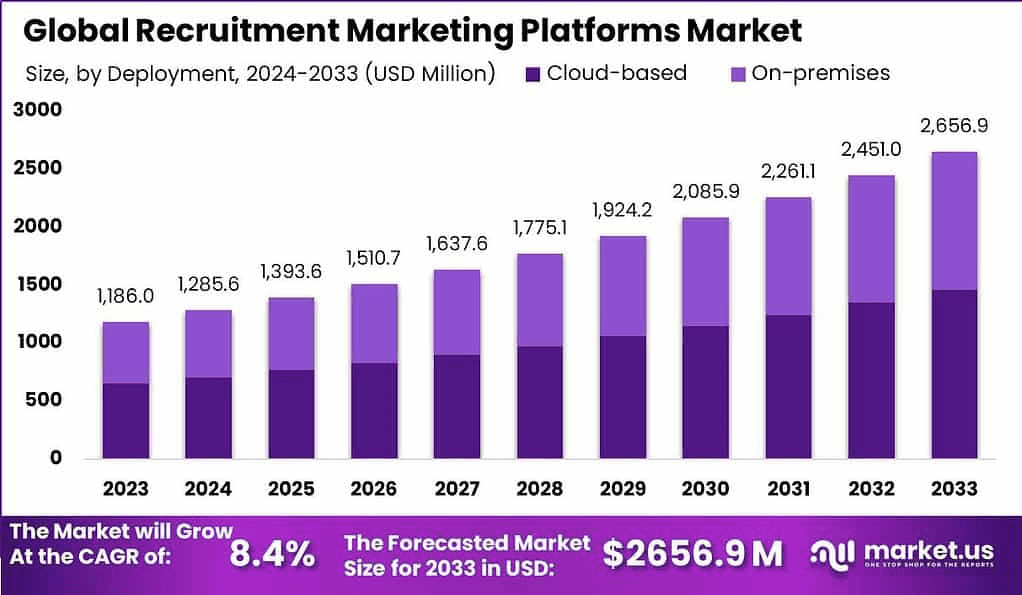 (Source: market.us)
(Source: market.us)
According to industry reports, including Market.us, the business of recruiting is scaling rapidly, driven by technology and a persistent demand for skilled talent. Understanding the financial implications, from market growth to cost per hire, is paramount for setting smart HR budgets.
- The Online Recruitment Technology Market is officially valued at $15.18 billion in 2025, positioning digital platforms as a core enterprise investment.
- The average Cost Per Hire for a new employee hovers around $4,700 in the U.S. across all sectors and seniority levels.
- This figure serves as a benchmark, though specialized roles in technology can cost significantly more, often exceeding $12,000 per hire.
- Executive-level positions take an average of 120+ days to fill, compared to the global average time-to-hire of 44 days.
- 69% of organizations still report significant challenges in recruiting for full-time positions, a struggle that has remained consistent since 2016.
- The primary challenge cited by 56% of employers in 2024 was a simple scarcity of qualified candidates, not an abundance of applicants.
- 45% of business leaders currently spend more than half their time on talent acquisition TA tasks, indicating a severe drain on management resources.
- The average revenue decline for US staffing agencies in February 2024 was 5% YOY, reflecting a shifting balance between in-house and outsourced TA.
- Despite this, the broader staffing industry’s total revenue for 2023 was a massive $593 billion, highlighting the volume of temporary and contract hiring.
| Metric Category | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Market Valuation 2025 | Online Recruitment Technology Market Size |
$15.18 Billion |
|
Growth Forecast CAGR 2025-2032 |
Compound Annual Growth Rate | 13.9% |
| Hiring Cost | Average Cost Per Hire U.S. |
$4,700 |
|
Time-to-Hire |
Global Average Time to Hire All Roles | 44 Days |
| Executive Hiring Time | Average Time to Fill Executive Roles |
120+ Days |
|
Recruiting Challenge |
Employers citing Talent Shortage as the primary obstacle |
56% |
The Automation Imperative By ATS and AI in Sourcing
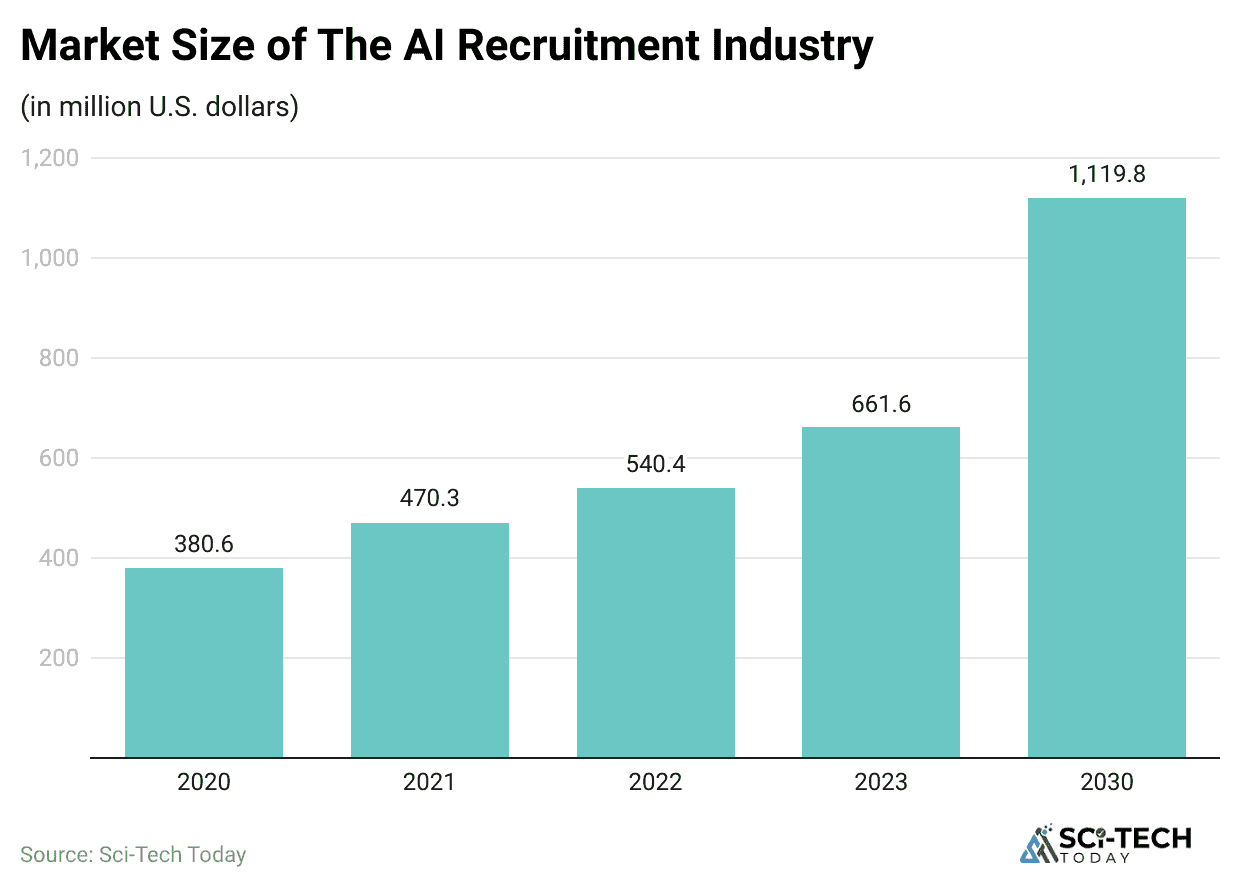 (Reference: demandsage.com)
(Reference: demandsage.com)
- Airing 97.4% of Fortune 500 companies, which is 487 out of 500, rely on an Applicant Tracking System ATS to manage their hiring workflow.
- 79% of organizations have already integrated AI or automation directly into their existing ATS platform, moving beyond basic filtering.
- The primary goal of this integration is efficiency, with 64% of survey respondents using AI to automatically filter out unqualified candidates.
- Recruiters who implement an ATS report a remarkable 86% reduction in their overall time-to-hire metric, a huge boost to efficiency.
- This speed is crucial, as 69% of applicants will reject a job offer if the company takes too long to respond after the final interview.
- AI adoption in Human Resources tasks has climbed to 43% in 2025, a substantial increase from just 26% reported in 2024.
- Recruiters are optimistic, with 85% viewing AI as a valuable tool, but 60% also expressing concern that AI could eventually replace their jobs.
- This shift helps address the fact that 65% of candidates say they rarely or never receive an update on their application status.
- Only 15% of business leaders feel 100% confident in their hiring decisions at the time of hire, signaling a systemic issue with traditional candidate evaluation methods.
| Technology Focus | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| ATS Adoption | Fortune 500 Companies Using ATS | 99% |
| Recruiter Confidence | Recruiters reporting ATS’s positive impact | 94% |
| AI Integration | Organizations integrating AI into their ATS | 79% |
| AI Adoption in HR | Companies using AI for at least one HR function 2025 | 43% |
| Time-to-Hire Impact | Recruiters reporting reduced time-to-hire due to ATS | 86% |
| Candidate Ghosting | Candidates who rarely or never receive application updates | 65% |
Social Media, Mobile, and Passive Candidate Engagement
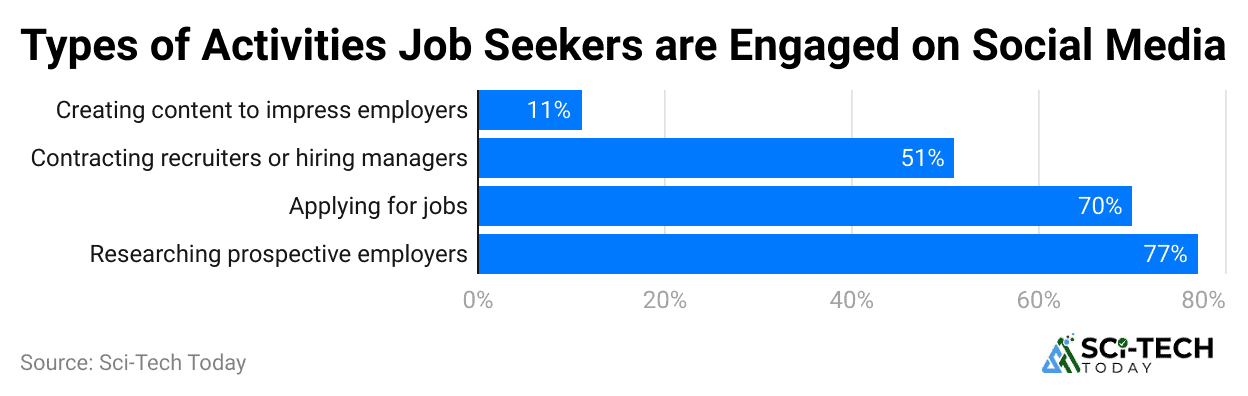 (Reference: scoop.market.us)
(Reference: scoop.market.us)
- 84% of organizations actively utilize social media platforms like LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook for primary talent recruitment and sourcing.
- This is a significant shift: 78% of recruiters expect their activity to increase outside of LinkedIn this year, specifically targeting platforms like TikTok and niche forums.
- 75% of potential candidates meticulously investigate a company’s values and culture on social media before they even apply.
- More than 65% of all job applications are now submitted via mobile devices, reinforcing that an unoptimized, non-mobile application process is a guaranteed filter for drop-offs.
- In fact, 60% of candidates have abandoned an application midway because the process was too long or complex, often due to poor mobile design.
- 70% of passive job seekers, those not actively looking but open to a new offer, make up the largest available talent pool globally.
- 73% of job seekers between the ages of 18 to 34 report that they found their most recent job through social media channels.
- Only 55% of organizations currently use social media as their primary recruitment strategy, despite its high effectiveness for sourcing and branding.
- This gap indicates a massive missed opportunity, as employee referrals, often driven by social sharing, generate 4x more high-quality candidates than job boards.
| Sourcing Channel | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Social Media Use | Organizations actively using social media for recruitment | 84% |
| Candidate Research | Candidates researching company values on social media before applying | 75% |
| Mobile Applications | Percentage of job applications submitted via mobile devices | 65% |
| Candidate Drop-Off | Candidates who abandon applications due to length/complexity | 60% |
| Recruiter Focus Shift | Recruiters expecting increased activity outside of LinkedIn | 78% |
| Passive Talent Pool | Share of the global candidate pool that is passive | 70% |
The Remote and Hybrid Workforce Effect
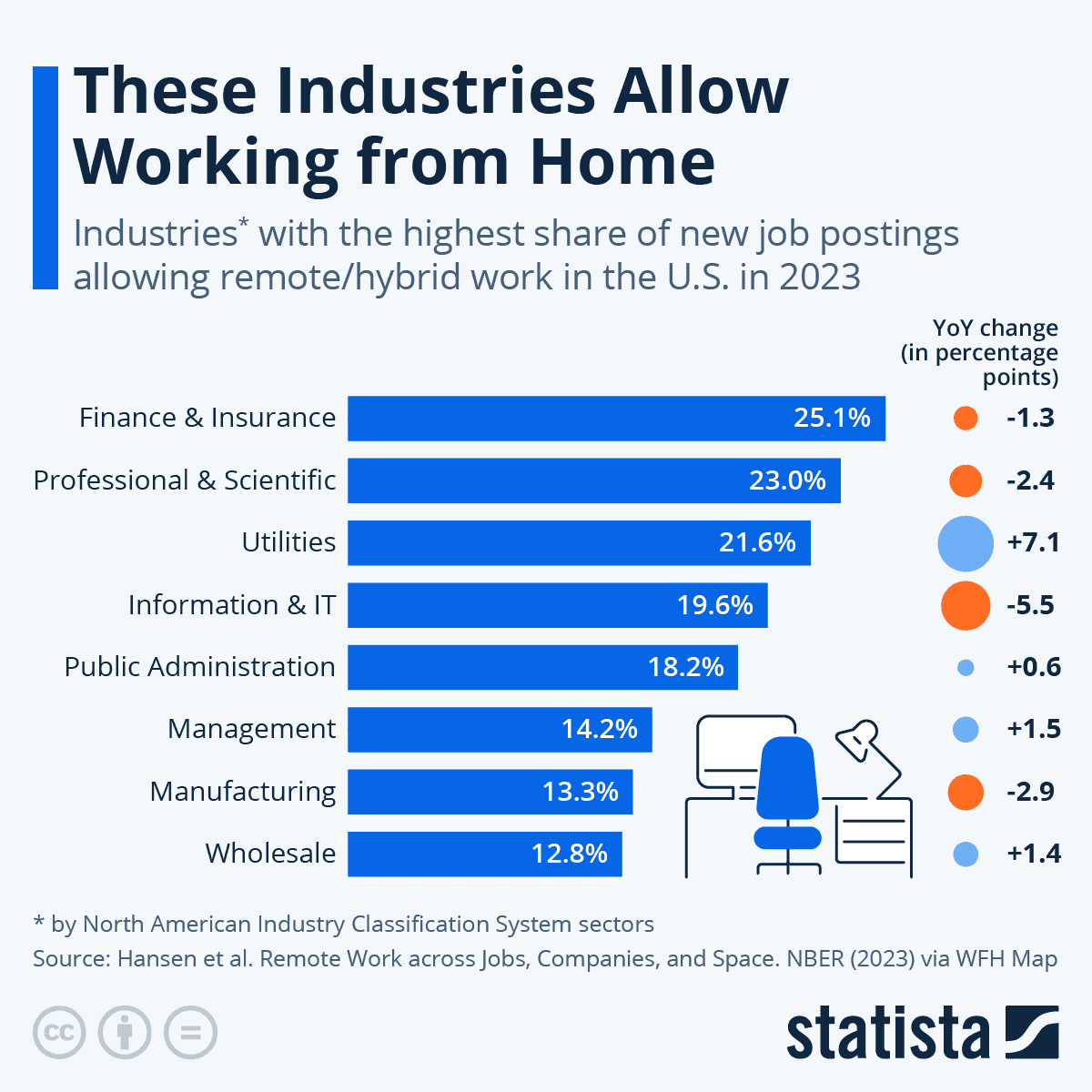 (Source: statista.com)
(Source: statista.com)
- In 2025, 52% of U.S. remote-capable employees currently operate in a hybrid work environment, making it the most common model.
- Conversely, only 26% work exclusively remote, and 22% are fully on-site, showing a consolidation toward a flexible middle ground.
- A resounding 60% of remote-capable employees prefer a hybrid work arrangement, while less than 10% prefer to work on-site full-time.
- 54% of hiring managers have had candidates decline interviews or job offers primarily due to a lack of remote work options or flexibility.
- 83% of companies that embrace remote work report tangible benefits, including improved flexibility, cost savings, and, most importantly, greater access to talent.
- The shift to virtual hiring has allowed 73% of companies to increase international hiring with a remote work model, massively expanding their talent pool.
- 95% of employers report no negative impact on productivity from employees working remotely, while 51% actually noticed an increase in productivity.
- 93% of employers who currently conduct virtual interviews plan to continue doing so indefinitely in the future.
- This acceptance ensures that the 86% rate of virtual interviews will not drop off, permanently cementing video as the standard for initial and mid-stage screening.
| Flexibility Metric | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Dominant Model | U.S. remote-capable employees currently working Hybrid environment | 52% |
| Candidate Preference | Remote-capable employees who prefer a Hybrid arrangement | 60% |
| Talent Loss | Candidates declining offers due to a lack of flexibility | 54% |
| Employer Benefit | Companies reporting remote work improve access to talent | 83% |
| Productivity Impact | Employers reporting no negative impact on productivity from remote work | 95% |
| Virtual Interview Future | Employers planning to continue virtual interviews | 93% |
Diversity, Equity, and Skills-Based Hiring
 (Reference: fitsmallbusiness.com)
(Reference: fitsmallbusiness.com)
- Companies that boast racial and ethnic diversity are 35% more likely to financially outperform their racially homogenous competitors in profitability.
- Similarly, those with gender-diverse executive teams are 15% more likely to achieve above-average profits, proving diversity directly impacts the bottom line.
- 75% of US job seekers now consider a diverse workforce to be a key, essential factor when they are evaluating job offers.
- The desire for an inclusive environment is a major differentiator, with 60% of workers prioritizing diversity when choosing a new employer.
- The gender pay gap in the US averages around 17%, a persistent disparity that severely impacts the recruitment and retention of top female talent.
- Furthermore, for every 100 men promoted from entry-level to manager, only 81 women are promoted, indicating a systemic leakage at key career stages.
- 94% of employers believe that skills-based hiring is a significantly better predictor of a candidate’s actual job performance than a traditional resume.
- This shift is active, with 81% of companies now utilizing skills-based hiring practices, up from just 56% two years prior.
- Candidates from Historically Underrepresented Groups are 67% more likely to experience ghosting, sudden, unexplained communication cessation after an interview than white candidates.
- More than 50% of employers now state that attracting diverse talent is their primary DEI obstacle, a challenge that has risen sharply from just over 40% last year.
| DEI and Skills Metric | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Racial Outperformance | Companies with racial diversity are more likely to outperform | 35% |
| Gender Outperformance | Companies with gender diversity are more likely to outperform | 15% |
| Candidate Priority | Job seekers view a diverse workforce as a key factor | 75% |
| Skills vs. Resume | Employers believe skills better predict performance | 94% |
| Ghosting Disparity | URG candidates are more likely to be ghosted than white candidates | 67% |
| Primary DEI Obstacle | Employers cite attracting diverse talent as the main challenge | 50% |
Candidate Experience By The New Standard for Online Recruitment Success
 (Source: selectsoftwarereviews.com)
(Source: selectsoftwarereviews.com)
- A massive 58% of candidates have made the decision to turn down a job offer that was otherwise acceptable due to a poor candidate experience during recruitment.
- Half of all workers 50% have rejected a job offer at some point because of a negative recruitment experience, showing this is a widespread, systemic issue.
- 72% of candidates who have a bad experience will tell friends and family about it, actively damaging the company’s reputation.
- Only a tiny fraction, 5% of job seekers, prefer to apply via a complex online application form, while the vast majority 48% prefer to simply submit a CV to an online system.
- This preference highlights the need to drastically simplify the application funnel to prevent the 60% application drop-off rate.
- A positive candidate experience makes a candidate 38% more likely to accept a job offer from the organization when one is extended.
- 52% of candidates report that they had to wait three months or even longer to receive a definitive response from an employer after submitting their initial application.
- This extended silence is the main source of frustration, with 63% of candidates unhappy with the lack of communication following an application.
- Only 25% of employers actively follow up by asking candidates for feedback on their experience via candidate surveys.
| Candidate Experience Metric | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Offer Rejection Rate | Candidates who turned down an offer due to poor experience | 58% |
| Communication Gap | Candidates waiting 3 months or more for an application response | 52% |
| Positive Impact | The likelihood of a candidate accepting an offer after a positive experience | 38% more |
| Reputation Damage | Candidates who will tell others about a bad experience | 72% |
| Preferred Method | Candidates preferring to submit a CV to an online system vs. a form | 48% |
| Employer Feedback | Companies that actively survey candidates for feedback | 25% |
Conclusion
Overall, thank you for diving into these core online recruitment statistics. The data tells a story: the future of hiring is driven by efficiency, by technology, and centered on the candidate.
From the necessity of an ATS for corporate scale to the overwhelming candidate preference for hybrid work, these data points are actionable insights for your recruitment needs. The organizations that thrive in the coming years will be the ones that treat their candidates with the speed and respect demanded by the market, leverage AI to free up their teams for engagement, and actively pursue the proven financial benefits of a truly diverse workforce.
I hope this article will help in any of your hiring processes. If so, I would be the happiest person on the planet. Thanks for staying up till the end. If you find this one useful, kindly share it with your friends who are looking for the right recruitment. Thanks.


