Introduction
Cyber Insurance Statistics: The internet has given us convenience and efficiency in most ways possible, including writing this article, but it has also created a new frontier of risk, an unnoticed economy of compromise where the cost of failure is measured in millions.
By the end of 2025, the global cost of cybercrime is projected to hit US$10.5 trillion, making its rank as the third-largest economy globally, right after the U.S. and China. For any business operating today, the question isn’t if they’ll face a major cyber incident, but when, and for the most part, how they’ve planned to manage the inevitable financial fallout.
This is where cyber insurance helps, changing from a niche product into an absolutely vital scheme of modern risk management. This deep dive analysis into cyber insurance statistics will give you all the data you need to know and prove why this kind of coverage is needed, so let’s dive into the analysis.
Editor’s Choice
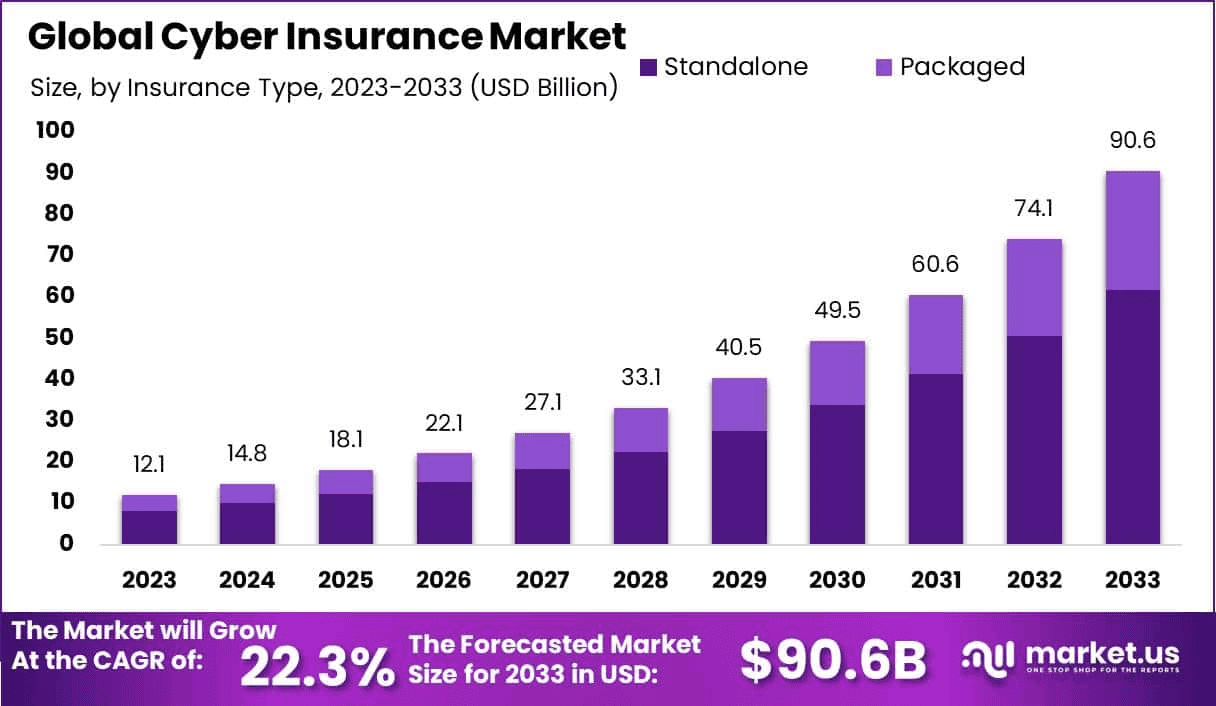
- The Cyber Insurance Market is currently valued at US$16.3 billion (2025) but is projected to skyrocket to US$90.6 billion by 2033, representing an aggressive 3% CAGR.
- The Standalone coverage segment dominates, holding a substantial 2% market share (2025).
- Large Enterprises drive the majority of premium volume, capturing 4% of the market share (2025).
- North America leads global revenues, generating US$4.5 billion in 2025 premiums.
- The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is expected to be the fastest-growing
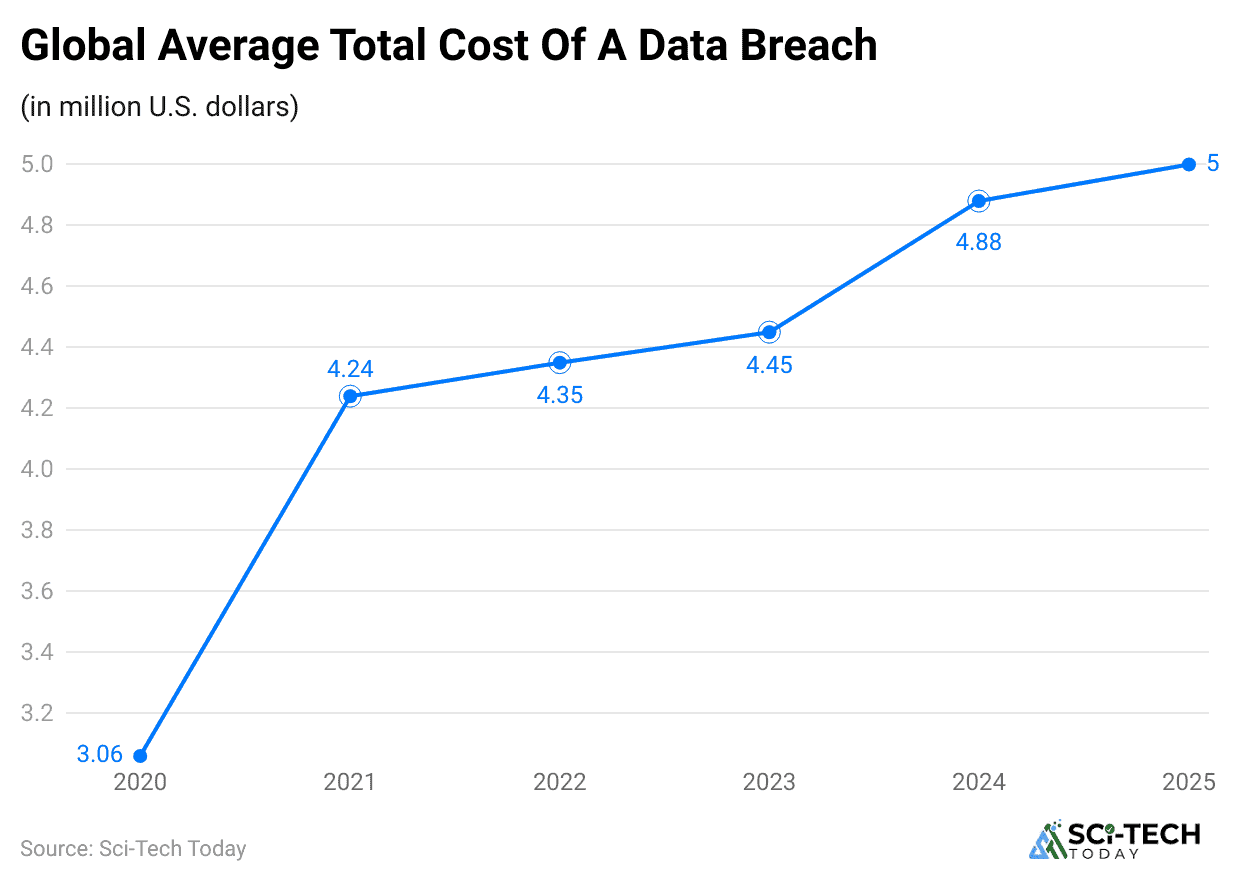
- The Global Average Cost of a Data Breach has reached an all-time high of US$4.44 million in 2025.
- The Healthcare Industry faces the highest average breach costs at over US$10.93 million, due to the sensitivity of Personal Health Information (PHI).
- The total projected criminal economy from cybercrime is a massive US$10.5 trillion in 2025.
- A major component of financial loss is Business Interruption (BI), which is a substantial percentage of the overall cybercrime figure.
- The maximum potential fine under GDPR is €20 Million / 4% of Global Annual Turnover.
- Ransomware claim severity increased by a frightening 68% in the first half of 2025.
- The average ransom demand has escalated to US$1.52 million in 2025.
- The United States is the primary target, accounting for approximately 50% of all reported ransomware attacks globally.
- Organizations with exposed login panels (like RDP or VPNs) are 1 times more likely to experience a claim.
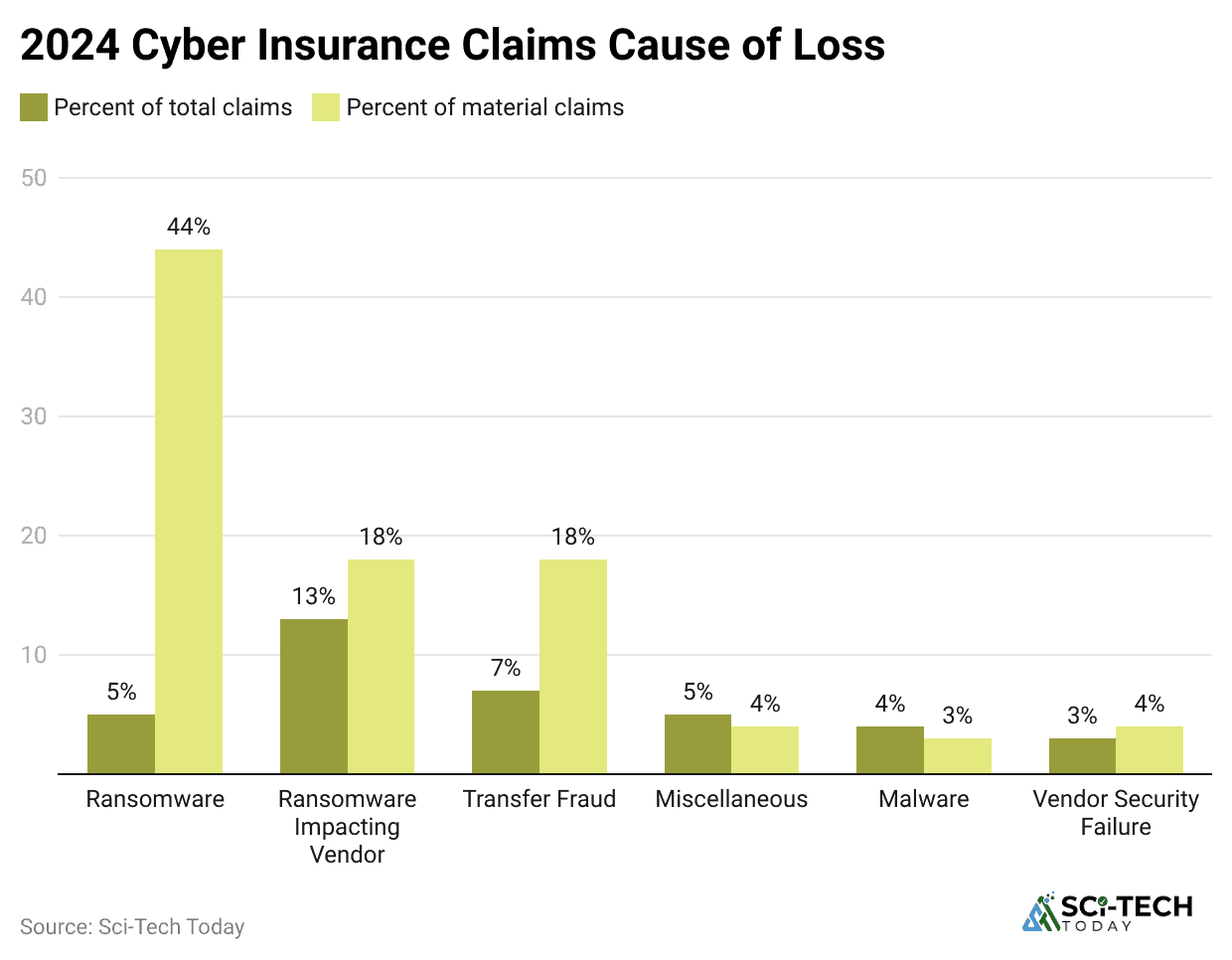
- Third-party risk accounts for a significant 31% of all cyber insurance claims in
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) remains the most frequent attack vector, driving nearly 33% of all reported claims.
- Transfer Fraud (FTF) resulting in actual payouts represents 18% of incurred claims.
- The 3 non-negotiable security controls now mandated by insurers are Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions, and Immutable Backups (The Big Three).
- Policyholders who adopted these strict controls saw premium rate stabilization or decreases of 50% to 60%.
- An estimated 72% of Small to Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), despite recognizing their risk, still lack essential Cyber Insurance coverage.
The Market Size of Cyber Insurance
 (Source: market.us)
(Source: market.us)
According to Market.us, the financial figures for the Cyber Insurance sector confirm it is one of the most dynamic and non-negotiable insurance lines in the world. The market’s dramatic expansion is a direct reflection of escalating global cyber risk, with every key metric underscoring an imperative shift in how businesses handle digital risk transfer.
- The Cyber Insurance market is currently valued at a formidable $16.3 billion in 2025, showcasing its already significant role as a financial shield against digital threats and setting the stage for phenomenal future expansion.
- This colossal market size is projected to balloon more than sixfold, soaring to an estimated $90.6 billion by 2033, reflecting an astonishing Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.3% from 2025 to 2033..
| Key Growth Statistics in a Nutshell | 2025 Value | 2033 Projection |
| Current Market Valuation | $16.3 Billion |
— |
|
Forecasted Market Value |
— | $90.6 Billion |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) | 22.3% (2025 to 2033) |
— |
Dominant Segments in Cyber Insurance Coverage
- The Standalone segment overwhelmingly led the market in 2025, capturing a substantial 68.2% of the total market share.
- Within the coverage structure, the Third-Party Coverage segment secured the largest slice, with a commanding 62.1% share in 2025.
- In terms of clientele, the Large Enterprises segment was the undisputed market leader, responsible for a massive 72.4% of the overall market share in 2025.
- The BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) sector stands out as the highest-value industry for Cyber Insurance, with a 28.3% market share in 2025
| Segment Dominance in a Nutshell (2025) | Market Share Percentage |
| Standalone Coverage | 68.2% |
| Third-Party Coverage | 62.1% |
| Large Enterprises | 72.4% |
| BFSI Sector | 28.3% |
North America – The Epicenter of Cyber Insurance Premiums
- North America cemented its leadership position by capturing a substantial 37.6% market share in 2025, demonstrating a significantly greater adoption rate and premium volume compared to other global regions.
- This regional dominance translated into concrete financial returns, with North America generating an impressive $4.5 billion in revenue in 2025 from Cyber Insurance premiums alone.
| Regional Leadership in a Nutshell (2025) | Statistical Value |
| North American Market Share | 37.6% |
| North American Revenue | $4.5 Billion |
| Primary Growth Driver | Prevalence of Cyberattacks |
The Costs Driving the Demand for Cyber Insurance
 (Source: certbar.com)
(Source: certbar.com)
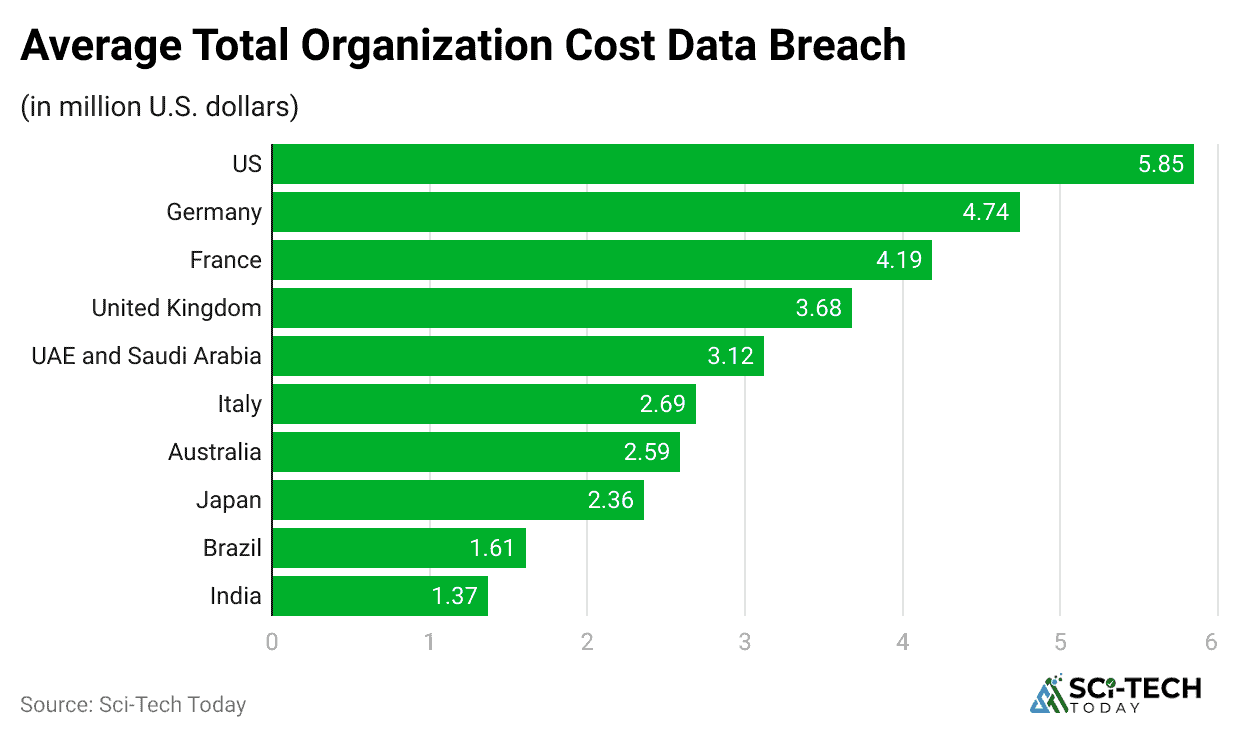
- The global average cost of a data breach has reached an all-time high of $4.44 million in 2025.
- The United States is officially the most expensive country for data breaches, where the average cost can be dramatically higher, often exceeding $9 million for major incidents among larger organizations due to complex legal and notification requirements.
- The Healthcare Industry consistently faces the highest data breach costs of any sector, with an average figure soaring past $10.93 million.
- The median loss amount for cyber incidents involving ransomware or other extortion techniques in 2025 sits at approximately $46,000 per breach.
- A major component of financial loss is Business Interruption (BI), where the inability to operate normally following an attack can be crippling; the total global cost of cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion USD in 2025, with BI being a substantial percentage of this massive figure.
- The average time it takes for an organization to identify and contain a data breach has extended to approximately 280 days, nearly ten months of operational and investigatory costs that Cyber Insurance policies are designed to cover.
| Cost of Attack | Statistical Value |
| Global Average Cost of a Data Breach | $4.44 Million |
| Average Healthcare Breach Cost | $10.93 Million |
| Median Loss per Extortion Breach | $46,000 |
| Total Global Cybercrime Damage | $10.5 Trillion USD |
The Ransomware Epidemic and Its Impact on Cyber Insurance
 (Reference: statista.com)
(Reference: statista.com)
- In the first half of 2025, ransomware attacks were overwhelmingly responsible for the massive spike in claim severity, with the average loss amount for ransomware incidents increasing by a frightening 68% compared to the previous period.
- The average ransom demand has skyrocketed to over $1.3 million in the first half of 2025.
- The average ransom payout has similarly increased, now standing at approximately $2.73 million in 2025, which represents a jump of nearly $1 million from the prior year’s average.
- Organizations in the United States continue to be the most frequently targeted, accounting for nearly 50% of all reported ransomware attacks globally.
- In one highly publicized incident, the largest ever ransomware payout by an organization was reported to be $40 million.
- Organizations with internet-exposed login panels, such as those for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) or VPNs lacking proper enforcement, were statistically 3.1 times more likely to experience a claim in the first half of 2025.
| Ransomware Data | Statistical Value |
| Increase in Ransomware Claim Severity | 68% |
| Average Ransom Demand in 2025 | $1.3 Million |
| Frequency of US Ransomware Attacks | 50% |
| Increased Likelihood of Claim from Exposed Panels | 3.1x |
Key Drivers of Cyber Insurance Claims and Losses
 (Reference: cyberresilience.com)
(Reference: cyberresilience.com)
- Third-party risk has emerged as a major new driver of insured losses, accounting for a significant 31% of all cyber insurance claims in 2025.
- For the first time on record, third-party and vendor-related incidents were responsible for 23% of all incurred losses reported in 2025.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) remains the most frequent attack vector leading to claims, accounting for nearly one-third of all reported cyber claims in the first half of 2025.
- The frequency of BEC claims saw a 4% increase in 1H 2025, with businesses generating over $100 million in revenue seeing a dramatic 60% spike in the frequency of these attacks.
- Transfer Fraud (or Funds Transfer Fraud, FTF), where criminals trick employees into sending funds to fraudulent accounts, accounted for 18% of incurred claims in 2025.
- The frequency of the previously dominant Phishing as a primary cause of loss has thankfully decreased, now only representing around 9% of incurred claims in 2025.
| Claim Drivers | Statistical Value |
| Claims from Third-Party Risk | 31% |
| Claims from Business Email Compromise (BEC) | 33% |
| Incurred Losses from Transfer Fraud (FTF) | 18% |
| Claims from Phishing | 9% |
Underwriting Controls and the Rise of Security Mandates
- Insurers now often refuse to quote, or significantly restrict coverage, for organizations that do not have Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) deployed across all critical access points, especially for remote network access, privileged accounts, and all forms of corporate email.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions are now a baseline requirement, as insurers recognize that legacy antivirus software is inadequate to detect and stop the advanced attack techniques used by modern threat actors.
- The presence of Immutable Offsite Backups is now deemed a non-negotiable control, with underwriters demanding proof that critical data backups are ‘air-gapped’ and regularly tested to ensure a business can recover without paying a costly ransomware demand.
- The stabilization of premium rates, which saw some decreases of 50% to 60% for some policyholders after massive surges.
- Despite the increasing demand, a significant portion of the market remains underserved, with an estimated 72% of Small to Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) recognizing their high cyber risk but still lacking any form of essential Cyber Insurance coverage.
- Organizations that demonstrate a high degree of maturity in cyber resilience, including having a regularly tested Incident Response (IR) plan.
| Mandatory Controls | Statistical Value |
| MFA, EDR, and Immutable Backups | The Big Three |
| Premium Rate Stabilization | 50% to 60% |
| Uninsured SMEs | 72% |
| Risk Reduction Strategy | Risk Reduction |
Regional and Industry-Specific Insights
 (Reference: deloitte.wsj.com)
(Reference: deloitte.wsj.com)
- The Asia Pacific (APAC) region is anticipated to be the fastest-growing regional market for Cyber Insurance in the forecast period.
- The European market faces constant pressure from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), with potential fines reaching up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover.
- The Financial Services Industry faces an average data breach cost of $5.97 million, largely due to the overlapping and severe mandates of regulations like GLBA, PCI DSS, and SOX, which demand extensive and specialized Cyber Insurance coverage.
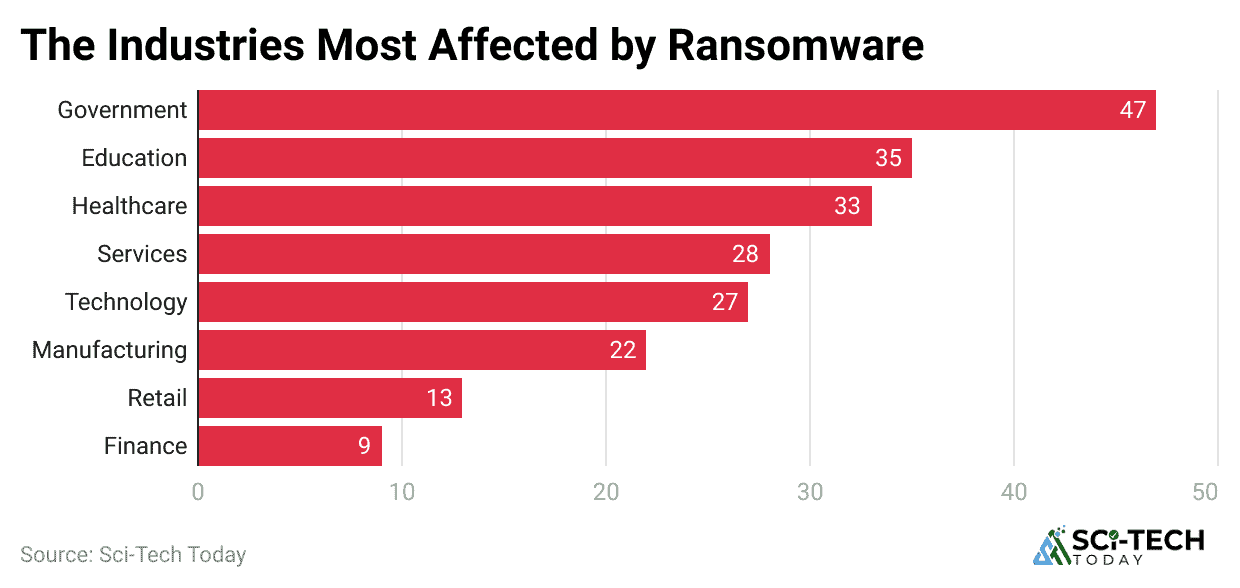
- Industries such as Transportation, Manufacturing, and Healthcare have shown the highest frequency of incurred claims in 2025.
- The sector with the highest frequency of reporting claims is often Healthcare and Finance, not because they are attacked more, but because stricter regulatory requirements mandate the reporting of even minor incidents
- The Retail sector is an increasingly frequent target, with major attacks leading to losses like $300 million in lost profits and massive market value decreases for large retailers.
| Regional/Industry | Data Point | Statistical Value |
| Fastest Growing Region | The geographical area is expected to see the highest CAGR for Cyber Insurance. | Asia Pacific |
| Maximum GDPR Fine | The potential fine for a severe data privacy violation under European law. | €20 Million / 4% Global Turnover |
| Financial Services Average Breach Cost | The high average cost of a breach within the tightly regulated financial sector. | $5.97 Million |
| Industries with the Highest Incurred Claim Frequency | The top three sectors are disproportionately affected by actual financial loss from cyber incidents. | Transportation, Manufacturing, Healthcare |
Conclusion
Overall, the statistics we’ve dissected, from the $16.3 billion market size of Cyber Insurance to the $4.44 million average cost of a breach, tell a story. The shift in the Cyber Insurance market is fundamentally changing business operations; insurers are forcing organizations to adopt the “Big Three” mandatory controls, MFA, EDR, and immutable backups, effectively using their underwriting power to raise the global cybersecurity standard.
Ransomware and third-party risk are now being big of claim severity, demanding proactive supply chain management and tested incident response plans. For any enterprise, the decision to secure a quality Cyber Insurance policy is an imperative that dictates both financial continuity and operational resilience in a world where the cyber threat economy is only projected to grow, potentially hitting a devastating $10.5 trillion USD by 2025. I hope you like this piece of content. If you have any questions, kindly let us know. Thanks for staying up till the end.


