Introduction
Satellite Launch Statistics: Satellites serve critical functions, including technology development, Earth observation, communications, space science, and navigation. These artificial objects are launched into space aboard rockets and positioned in various orbits—low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary orbit—depending on their intended applications.
As of June 2024, approximately 11,780 satellites were orbiting Earth. The number of satellites launched annually has surged, with 2,664 objects sent into space in 2023, breaking the previous year’s record. This increase is largely driven by the deployment of large constellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink, which alone accounted for around 3,500 satellites between 2020 and 2022. The proliferation of satellites underscores their growing importance in advancing global technological capabilities.
General Satellite Launch Statistics
- As of 2024, a total of 8,135 satellites are active in low Earth orbit (LEO).
- 552 satellites are operating in geostationary orbits, while 200 satellites are in medium Earth orbit (MEO).
- 19 satellites are in high Earth orbit (HEO) or graveyard orbits, 5 are in orbital decay, and 11 are marked for reentry.
- A total of 2,664 satellites were launched globally in 2023, indicating a 19% increase compared to 2022 (Source: BryceTech, 2024).
- Of all satellites launched in 2023, 94% were classified as small satellites (mass < 600 kg), largely driven by commercial constellation deployments.
- The United States contributed to 65% of the global satellite launches in 2023, maintaining the leading position among all countries.
- SpaceX was responsible for 57% of global satellite launches in 2023, deploying over 1,500 Starlink satellites.
- The commercial sector accounted for 85% of all satellite launches by volume in 2023, highlighting the growing role of private enterprises.
- Communications satellites made up 35% of satellite payloads, followed by Earth observation at 27%, and technology demonstration at 16%.
- Reusable launch vehicles were utilized in 39% of all orbital launches globally in 2023, improving launch efficiency and reducing costs.
- The Asia-Pacific region contributed to 21% of global satellite launches, with China executing 67 successful orbital launches and deploying over 250 satellites.
- Cubesats constituted 58% of all small satellite deployments in 2023, primarily for applications in research, imaging, and IoT.
- The average launch cost per satellite in low Earth orbit declined by 23% between 2020 and 2023 due to increased use of rideshare missions and advancements in launch vehicle efficiency.
- According to Satellite Launch Statistics 2023, a total of 615 satellites were launched into space during the year.
Top 10 Countries with the Highest Number of Satellites
According to Pixalytics, the following are the top 10 countries with the most satellites in space based on recent Satellite Launch Statistics.
| Country | Total Satellites |
| United States | 4,511 |
| China | 586 |
| United Kingdom | 561 |
| Russia | 177 |
| India | 62 |
| Canada | 56 |
| Germany | 48 |
| Luxembourg | 45 |
| Argentina | 38 |
| Israel | 27 |
(Source: pixalytics.com)
By Number of Objects Launched By Year
| Year | Object launched |
| 1957 | 2 |
| 1958 | 8 |
| 1959 | 14 |
| 1960 | 20 |
| 1961 | 38 |
| 1962 | 77 |
| 1964 | 107 |
| 1965 | 163 |
| 1966 | 145 |
| 1967 | 159 |
| 1968 | 140 |
| 1969 | 138 |
| 1970 | 130 |
| 1971 | 156 |
| 1972 | 133 |
| 1973 | 1990 |
| 1991 | 135 |
| 1992 | 130 |
| 1993 | 108 |
| 1994 | 123 |
| 1995 | 105 |
| 1996 | 100 |
| 1997 | 152 |
| 1998 | 157 |
| 1999 | 129 |
| 2000 | 121 |
| 2001 | 86 |
| 2002 | 96 |
| 2003 | 88 |
| 2004 | 74 |
| 2005 | 72 |
| 2006 | 95 |
| 2007 | 111 |
| 2008 | 109 |
| 2009 | 125 |
| 2010 | 120 |
| 2011 | 129 |
| 2012 | 134 |
| 2013 | 210 |
| 2014 | 241 |
| 2015 | 222 |
| 2016 | 221 |
| 2017 | 456 |
| 2018 | 453 |
| 2019 | 586 |
| 2020 | 1274 |
| 2021 | 1910 |
| 2022 | 2474 |
| 2023 | 1354 |
(Source: pixalytics.com)
According to Satellite Launch Statistics, more than 15,000 objects have been launched into space over the last 66 years. The year-on-year progress has significantly increased, and since lockdown, the number of such launches has reached over 1,000.
Top 10 Companies with the Most Satellites Orbiting Earth
DeweSoft listed the top 10 Companies with the most Satellites Orbiting Earth in 2023
| Companies | Number of Satellites |
| National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) | 63 |
| Iridium Communications Inc | 74 |
| The US. Air Force | 87 |
| Swarm Technologies | 120 |
| Spire Global Inc | 121 |
| Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation | 125 |
| Chinese Ministry of National Defense | 129 |
| Planet Labs Inc | 188 |
| OneWeb Satellites | 288 |
| SpaceX | 1,655 |
(Source: dewesoft.com)
By Breakdown of Satellites by Purpose
A similar report by Dewesoft explains the share of satellites orbiting in space by their missions based on Satellite Launch Statistics 2023.
| Purpose | Share of Satellites |
| Space Science | 2.3% |
| Space observation | 0.22% |
| Earth Science | 0.44% |
| Technology Demonstration | 0.77% |
| Navigation/ global positioning | 3.6% |
| Technology development | 7.8% |
| Earth Observation | 22.1% |
| Communications | 63% |
(Source: dewesoft.com)
Satellite Launch Statistics By Country
| Country | Launch Date | Satellite Name |
| Soviet Union | 4 October 1957 | Sputnik 1 |
| United States | 1 February 1958 | Explorer 1 |
| United Kingdom | 26 April 1962 | Ariel 1 |
| Canada | 29 September 1962 | Alouette 1 |
| Italy | 15 December 1964 | San Marco 1 |
| France | 26 November 1965 | Astérix |
| Australia | 29 November 1967 | WRESAT |
| 10 European Countries (Denmark, Belgium, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom, France) | 17 May 1968 | ESRO 2B |
| West Germany | 8 November 1969 | Azur |
| Japan | 11 February 1970 | Ohsumi |
| People’s Republic of China | 24 April 1970 | Dongfanghong I |
| Netherlands | 30 August 1974 | ANS |
| Spain | 15 November 1974 | Intasat |
| India | 19 April 1975 | Aryabhata |
| Indonesia | 8 July 1976 | Palapa A1 |
| Czechoslovakia | 24 October 1978 | Magion 1 |
| Bulgaria | 7 August 1981 | Bulgaria 1300 |
| Saudi Arabia | 8 February 1985 | Arabsat- 1A |
| Brazil | 8 February 1985 | Brasilsat A1 |
| Mexico | 17 June 1985 | Morelos 1 |
| Sweden | 22 February 1986 | Viking |
| Israel | 19 September 1988 | Ofek-1 |
| Luxembourg | 11 December 1988 | Astra 1A |
| Argentina | 22 January 1990 | Lusat |
| Hong Kong | 7 April 1990 | AsiaSat 1 |
| Pakistan | 16 July 1990 | Badr-1 |
| Russia | 21 January 1992 | Kosmos 2175 |
| South Korea | 10 August 1992 | Kitsat- 1 |
| Portugal | 26 September 1993 | PoSAT-1 |
| Thailand | 18 December 1993 | Thaicom-1 |
| Turkey | 10 August 1994 | Turksat 1B |
| Czech Republic | 2 August 1995 | Magion 4 |
| Ukraine | 31 August 1995 | Sich-1 |
| Chile | 31 August 1995 | FASat-Alfa |
| Malaysia | 13 January 1996 | MEASAT-1 |
| Norway | 20 May 1997 | Thor 2 |
| Philippines | 20 March 1987 | Mabuhay (Agila 1) |
| Philippines | 19 August 1997 | Mabuhay (Agila 2) |
| Egypt | 28 April 1998 | Nilesat 101 |
| Singapore / Taiwan | 25 August 1998 | ST-1 |
| Taiwan | 27 January 1999 | Formosat-1 |
| South Africa | 23 February 1999 | SUNSAT |
| Denmark | 23 February 1999 | Ørsted |
| Georgia | 17 July 1999 | Reflektor |
| United Arab Emirates | 21 October 2000 | Thuraya 1 |
| Belgium | 22 October 2001 | PROBA-1 |
| Morocco | 10 December 2001 | Maroc- Tubsat |
| Tonga | 21 February 1981 | Esiafi 1 (previously Comstar D4) |
| Algeria | 28 November 2002 | AISAT-1 |
| Greece | 13 May 2003 | Hellas-Sat 2 |
| Nigeria | 27 September 2003 | NigeriaSat-1 |
| Iran | 27 October 2005 | Sina- 1 |
| Kazakhstan | 17 June 2006 | KazSat-1 |
| Colombia | 17 April 2007 | Libertad-1 |
| Mauritius | 21 December 2007 | Rascom-QAF 1 |
| Vietnam | 18 April 2008 | Vinasat-1 |
| Venezuela | 29 October 2008 | Venesat-1 |
| Afghanistan | 20 December 2008 | Eutelsat 48D / Afghansat 1 |
| Switzerland | 23 September 2009 | SwissCube-1 |
| Singapore | 20 April 2011 | X-Sat |
| Isle of Man | 19 October 2011 | ViaSat-1 |
| Hungary | 13 February 2012 | MaSat-1 |
| Poland | 13 February 2012 | PW-Sat |
| Romania | 13 February 2012 | Goliat |
| Belarus | 22 July 2012 | BelKA-2 |
| North Korea | 12 December 2012 | Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 |
| Azerbaijan | 7 February 2013 | Azerspace-1/Africasat-1a |
| Austria | 25 February 2013 | TUGSAT-1/UniBRITE |
| Bermuda | 14 July 2000 | Bermudasat 1 (previously EchoStar VI) |
| Ecuador | 26 April 2013 | NEE-01 Pegaso |
| Estonia | 7 May 2013 | ESTCube-1 |
| Jersey | 25 June 2013 | O3b-1/O3b-2/O3b-3/O3b-4 |
| France / Qatar | 29 August 2013 | Eutelsat 25B/ Es”hail 1 |
| Qatar | 29 August 2013 | Es” hail 1 |
| Peru | 21 November 2013 | PUCK-Sat 1 / Pocket- PUCK |
| Bolivia | 20 December 2013 | Túpac Katari 1 |
| Lithuania | 9 January 2014 | LitSat-1 / Lituanica SAT-1 |
| Iraq | 19 June 2014 | Tigrisat |
| Uruguay | 19 June 2014 | ANTELSAT |
| Turkmenistan | 27 April 2015 | TurkmenAlem52E/MonacoSAT |
| Laos | 20 November 2015 | Laosat-1 |
| Finland | 18 April 2017 | Aalto-2 |
| Bangladesh | 3 June 2017 | BRAC ONNESHA |
| Ghana | 3 June 2017 | GhanaSat-1 |
| Mongolia | 3 June 2017 | Mazaalai (Satellite) |
| Latvia | 23 June 2017 | Venta 1 |
| Slovakia | 23 June 2017 | skCUBE |
| Angola | 26 December 2017 | AngoSat 1 |
| New Zealand | 21 January 2018 | Humanity Star |
| Costa Rica | 2 April 2018 | Proyecto Irazú |
| Kenya | 2 April 2018 | 1KUNS-PF |
| Bhutan | 29 June 2018 | Bhutan 1 |
| Jordan | 3 December 2018 | JY1-SAT |
| Nepal | 17 April 2019 | NepaliSat-1 |
| Sri Lanka | 17 April 2019 | Raavana 1 |
| Rwanda | 24 September 2019 | RWASAT-1 |
| Sudan | 3 November 2019 | Sudan Remote Sensing Satellite 1 (SRSS-1) |
| Ethiopia | 20 December 2019 | Ethiopia Remote Sensing Satellite 1 (ETRSS-1) |
| Guatemala | 7 March 2020 | Quetzal-1 |
| Slovenia | 3 September 2020 | TRISAT |
| Slovenia | 3 September 2020 | NEMO-HD |
| Monaco | 3 September 2020 | OMS-1 Cicero |
| Paraguay | 20 February 2021 | GuaraniSat-1 |
| Myanmar | 20 February 2021 | Lawkanat- 1 |
| Tunisia | 22 March 2021 | Challenge- 1 |
| Kuwait | 30 June 2021 | QMR-KWT |
| Bahrain / United Arab Emirates | 21 December 2021 | Light-1 |
| Armenia / Spain | 25 May 2022 | ARMSAT_1 |
| Moldova | 15 July 2022 | TUMnanoSAT |
| Uganda | 7 November 2022 | PearlAfricaSat-1 |
| Zimbabwe | 7 November 2022 | ZIMSAT-1 |
| Albania | 3 January 2023 | Albania – 1 & Albania – 2 |
| Vatican City / Italy | 12 June 2023 | SpeiSat |
| Oman | 11 November 2023 | AMAN-1 |
| Djibouti | 11 November 2023 | Djibouti-1A |
| Armenia | 1 December 2023 | Hayasat-1 |
| Ireland | 1 December 2023 | EIRSAT-1 |
(Source: wikipedia.org)
Number of Satellites Cataloged, Decayed, and On-Orbit
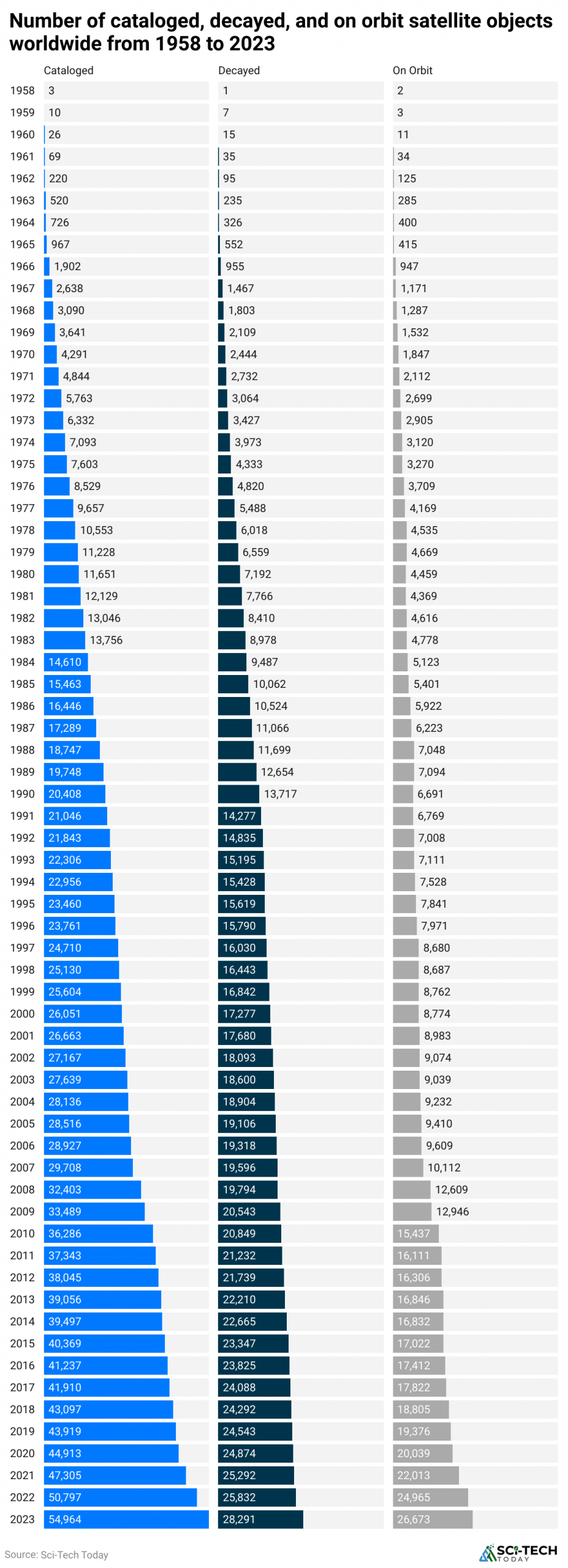
(Reference: statista.com)
According to Statista Research 2023, around 26,700 satellites orbited Earth at the beginning of the previous year, a 6.8% increase compared to 2022. Overall, segments such as cataloged, decayed, and on-orbit have shown a significant increase in the number of satellites concerning Satellite Launch Statistics.
By First Orbital Launches By Country
| Order | Country | Government | Rocket | Satellite | Date | Launch Site |
| 1 | Soviet Union | Government | Sputnik PS | Sputnik 1 | 4 October 1957 | Kazakhstan, formerly Baikonur, Soviet Union |
| 2 | United States | Government
|
Juno I | Explorer 1 | Cape Canaveral, USA | 1 February 1958 |
| 3 | France | Government
|
Diamant A | Astérix | Hamaguir, Algeria | 26 November 1965 |
| 4 | Japan | Government
|
Lambda-4S | Ohsumi | 11 February, 1970 | Uchinoura, Japan |
| 5 | China | Government
|
Long March 1 | Dong Fang Hong 1 | 24 April, 1970 | Jiuquan, China |
| 6 | United Kingdom | Government | Black Arrow | Prospero | 28 October 1971 | Woomera, Australia |
| – | European Space Agency | Government | Ariane 1 | CAT-1 (Obélix) | 24 December 1979 | Kourou, French Guiana |
| 7 | India | Government | SLV | Rohini 1 (RS1) | 18 July 1980 | Sriharikota, India |
| 8 | Israel | Government | Shavit | Ofeq 1 | 19 September 1988 | Palmachim, Israel |
| – | Ukraine | Government | Tsyklon- 3 | Strela-3 (x6, Russian) | 28 September 1991 | Russia, formerly Plesetsk, Soviet Union |
| 9 | Iran | Government | Safir- 1A | Omid | 2 February, 2009 | Semnan, Iran |
| 10 | North Korea | Government | Unha-3 | Kwangmyǒngsǒng- 3 Unit 2 | 12 December 2012 | Sohae, North Korea |
| 11 | South Korea | Government | Naro-1 | STSat-2c | 30 January 2013 | Goheung, South Korea |
(Source: wikipedia.org)
By New Geosynchronous Satellites
Based on a report, Space Activities in 2023, by Jonathan McDowell, the following chart explains the geostationary satellites launched in the mentioned year, ordered by longitude.
| Name | Piece | Operator | Mission | Location |
| Arcturus | 2023-060B | Astranis | Communications | 163.00W |
| Galaxy 37 | 2023-112A | Horizons/Intelsat SA (US) | Communications | 127.02W |
| Jupiter 3 | 2023-108A | Echostar/HNS/Echostar | Communications | 95.19W |
| Galaxy 35 | 2022-170A | Intelsat SA (US) | Communications | 93.13W |
| Intelsat IS-40e | 2023-052A | Intelsat SA (US) | Communications | 91.03W |
| Galaxy 36 | 2022-170B | Intelsat SA (US) | Communications | 88.96W |
| Viasat-3 Americas | 2023-060A | ViaSat | Communications | 88.88W |
| Amazonas Nexus | 2023-017A | Hispamar/Hispasat | Communications | 60.99W |
| Meteosat 12 | 2022-170C | EUMETSAT | Weather | 3.54W |
| Heinrich-Hertz-Satellit | 2023-093A | DLR | Communications | 0.50E |
| Luch-5Kh No. 3 | 2023-031A | FSB | Com/Sigint | 2.66E |
| EUTELSAT 10B | 2022-157A | EutelsatSA | Communications | 9.98E |
| CBAS 2 | 2023-008A | USSF SSC | Communications | 24.36E |
| Badr 8 | 2023-075A | Arabsat | Communications | 25.96E |
| Ludi Tance 4A | 2023-120A | CNSA | Radar Imaging | 89.60E |
| Zhongxing 6E | 2023-172A | China Satcom | Communications | 115.53E |
| Yaogan 41 | 2023-197A | PLA GAD/CAST | Imaging | 123.26E |
| Zhongxing 26 | 2023-023A | China Satcom | Communications | 125.13E |
| NVS-01 | 2023-076A | ISRO | Navigation | 129.36E |
| Satria | 2023-086A | SNT | Communications | 145.93E |
| Gao Fen 13-02 | 2023-036A | Yaogan Zongti | Imaging | 146.66E |
| Beidou DW 56 | 2023-066A | CNSA | Navigation | 160.07E |
| G-Space 1 | 2023-060C | Gravity Space | Communications | 165.49E |
| Elektro-L No. 4 | 2023-016A | Rosgidromet/Lavochkin | Weather | 165.81E |
| Tongxin Jishu Shiyan 10 | 2023-169A | PLA SSF | Early Warn | 173.26E |
| USA 340 | 2022-144E | USSF SSC/Millenium ES | Technology | Drift orbit |
| LINUSS1 | 2022-144G | LMSS Denver | Technology | Drift orbit |
| LINUSS2 | 2022-144H | LMSS Denver | Technology | Drift orbit |
| Shi Jian 23 | 2023-002A | PLA SSF | Communications | Drift orbit |
| LDPE 3A | 2023-008B | AFRL/RV | Technology | Drift orbit |
| Chandrayaan-3 | 2023-098A | ISRO | Planetary | Departed GEO region |
| Aditya-L1 | 2023-132A | ISRO | Astronomy | Departed GEO region |
| Syracuse 4B | 2023-093B | DGA | Communications | Orbit raising |
| Apstar 6E | 2023-005A | APT Shenzhen | Communications | Orbit raising |
(Source: planet4589.org)
India Satellite Launch Statistics
- India generated USD 143 million in foreign exchange revenue by launching 393 foreign satellites between 2015 and 2024.
- These satellites were launched for 34 countries using ISRO’s PSLV, LVM3, and SSLV launch vehicles.
- Out of the total, 232 satellites were launched for the United States, 83 for the United Kingdom, and 19 for Singapore, with others from countries including Canada, South Korea, Luxembourg, Italy, Germany, France, Japan, Israel, and the UAE.
- Additionally, 3 Indian customer satellites were commercially launched during this period.
- India has signed space cooperation agreements with 61 countries and 5 multilateral organizations.
- The major areas of international space collaboration include satellite remote sensing, navigation, communication, space science, planetary exploration, and capacity building.
- In 2023, ISRO achieved a successful soft landing on the Moon’s South Pole through the Chandrayaan-3 mission.
- Also in 2023, India launched its first solar mission, Aditya L1.
| Summary/Static | Details |
| Why in the news? | India generated $143 million by Launching Foreign Satellites Since 2015 |
| Revenue Generated | USD 143 million |
| Total Satellites Launched | 393 foreign satellites from 34 countries + 3 Indian customer satellites |
| Leading Countries | US (232), UK (83), Singapore (19), Canada (8), Korea (5), Germany (3), Japan (2), UAE (1), etc. |
| Launch Vehicles Used | PSLV, LVM3, and SSLV |
| Space Agreements | 61 countries and 5 multilateral bodies |
| Key Missions | Chandrayaan-3, Aditya L1, Gaganyaan, Bharatiya Antariksha Station (by 2035), Indian Moon Mission (by 2040)` |
| Private Sector Growth | Opened to private companies in 2020; major growth in space startups |
- The Gaganyaan Mission, India’s first manned space mission, is scheduled for 2025, with astronauts receiving training in Russia.
- India has announced plans to establish the Bharatiya Antariksha Station (Indian Space Station) by 2035.
- The country also aims to send its first astronaut to the Moon by 2040, marking another milestone in its expanding space ambitions.
Conclusion
The future of satellites is brimming with possibilities. As seen in these Satellite Launch Statistics, from revolutionizing communication networks to aiding scientific discovery and exploration, satellites will continue to play a transformative role in our lives.
As we venture further into space, responsible development and international collaboration will be key to ensuring a sustainable and peaceful future for space exploration and the benefits it brings to humanity.


