Introduction
Social Media Attention Span Statistics: The current time presents an introduction to a world where people establish connections through multiple channels, which makes their ability to pay attention to things more important than their financial resources. The average consumer today demonstrates the ability to handle multiple tasks while watching social media content because they lose interest at an even faster rate than before.
The year 2025 shows a fundamental change in social media usage because people now use multiple devices to watch content, which results in brands and creators competing for brief periods of user attention while advertisers spend billions on quick-moving online advertisements.
This article presents a comprehensive analysis of 2025 social media attention span statistics, which include research data, usage statistics, and data about industry advertising expenditures.
Editor’s Choice
- Social media addiction affects 40% of users aged 18 to 22 because they struggle to maintain their focus on tasks.
- Millennials (23–38) follow closely with a 37% addiction rate, driven by habitual and work-related usage.
- Users aged 55 to 64 show a 21% social media addiction rate, which shows they have learned to manage their time better.
- Gen Z averages just 6.5 seconds of attention per social media post.
- Pre-teens demonstrate the shortest digital focus at 4.2 seconds on fast-scroll platforms.
- The attention span of people who reach their 25th birthday decreases by 19% because they develop better skills to filter out unnecessary content.
- Influencer reels under 20 seconds generate 3.7× higher engagement, but only 12% brand recall.
- TikTok users spend 69 minutes daily, the highest across platforms.
- YouTube users watch content for 59 minutes per day, which helps them maintain their focus on longer videos.
- People who check their phones 96 times per day face interruptions that break their focus multiple times throughout the day.
- People who use their devices for more than five hours every day have a 33% greater chance of developing attention problems.
- Users who primarily use mobile devices demonstrate 20% lower ability to maintain focus compared to users who primarily use desktop computers.
Social Media Addiction Levels Across Different Age Groups
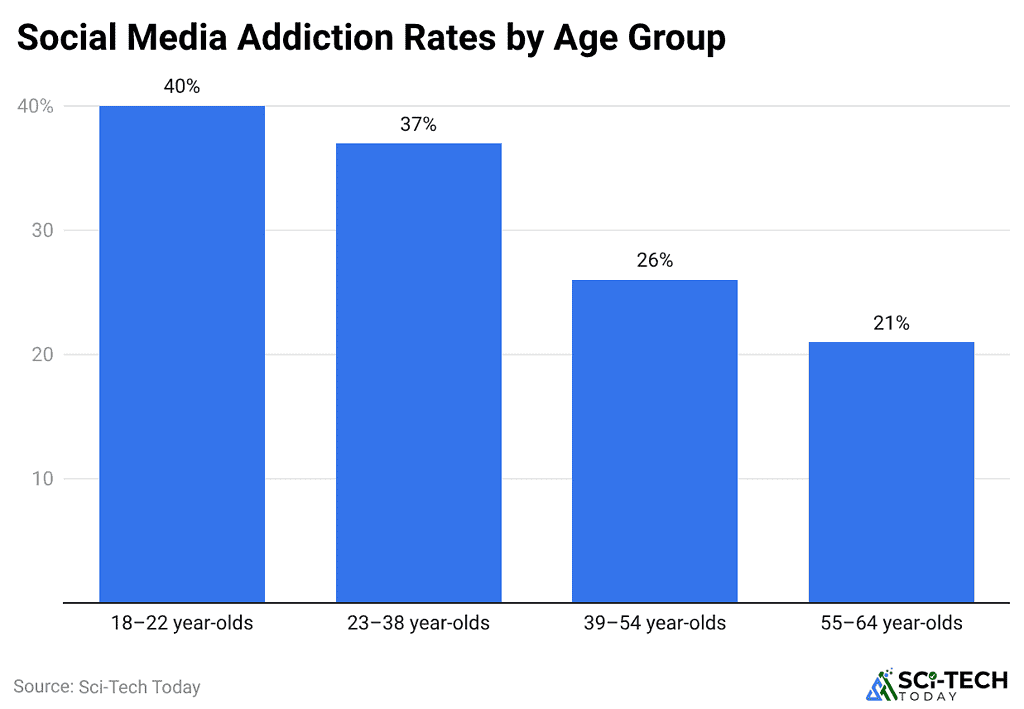
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- According to SQ Magazine, the above data shows that digital dependency decreases as people get older, which connects to changing social media attention span patterns that different generations experience.
- Young adults aged 18–22 show the highest addiction rate at 40%, which reflects their constant exposure to platforms, their consumption of short-form content, and their ability to switch between different activities.
- Reels, stories, and algorithm-based feeds that promote extended viewing drive the social media attention span of this group.
- Millennials between the ages of 23 and 38 exhibit a 37% addiction rate, which demonstrates how work-life digital overlap and habitual scrolling behavior contribute to their excessive online activity.
- People between the ages of 39 and 54 demonstrate a 26% addiction rate, which indicates they use social media with more restraint and experience longer periods of focused attention.
- Users between the ages of 55 and 64 exhibit the lowest rate at 21% because they use platforms in a limited manner while exhibiting more deliberate usage patterns.
- The statistics show that younger people face higher chances of experiencing digital overexposure, while older people display improved control over their online time because they prefer different types of content and demonstrate distinct ways of focusing.
Key Reasons Behind The Decline Of Attention On Social Media Platforms
- Social media platforms have developed shorter attention spans because of their fundamental design, which allows users interact.
- People experience information overload because they encounter between 6,000 and 10,000 ads every day, which forces them to evaluate content within two seconds.
- Platform architecture further accelerates this behavior. Platforms use features like infinite scroll, autoplay video, and algorithmic feeds, which enable users to consume content at high speeds while their content engagement time stays below two seconds for each post.
- Social media platforms receive more than 80% of their traffic from smartphones, which causes users to interact with content during brief periods of time instead of maintaining extended periods of engagement.
- The competition for user engagement has reached extreme levels because brand content must compete with personal updates, entertainment, and news, which appear in the same feed.
- The problem gets worse because frequent users now need only milliseconds to decide what content matters to them, which results in shorter engagement times.
- The combination of these forces leads to decreasing social media attention span, which requires businesses to demonstrate value through rapid communication methods in current online business environments.
Social Media Attention Span Differences Across Age Groups
- A clear generational divide in social media attention span, which analysts use to identify different content format preferences and digital consumption habits between generations.
- Gen Z averages just 6.5 seconds per post while pre-teens show an even lower digital attention span of 4.2 seconds on fast-paced platforms such as TikTok and Snapchat.
- The percentage of users who pay attention decreases by 19% between these two age groups because 25-year-olds show faster content filtering abilities than 18-year-olds.
- The retention rate for short-form video tutorials reaches 42% because millennials watch content for 8.3 seconds, which is their average viewing time.
- Gen X users spend 10.7 seconds watching content, while Baby Boomers watch content for 13.2 seconds because they prefer static posts and carousels.
- Users who belong to the 55 and above age group show 23% longer attention spans than younger user groups.
- Social media attention span shows different patterns across various age groups, which requires brands to develop specific content strategies that match the needs of each customer group.
Effects Of Short-Form Content On User Focus And Engagement
- Social media attention span across digital audiences has been significantly transformed by the fast-growing popularity of short-form video content, according to the data.
- Users who watch videos that last less than 30 seconds show a 27% decrease in their ability to sustain attention during task performance because they can only maintain cognitive focus for entertainment purposes.
- Scroll-driven platforms such as TikTok and Reels contribute to “scroll fatigue,” affecting 61% of users aged 18–34, while regular exposure to micro-content limits single-task focus to under 9 minutes on average.
- Behavioral spillover is evident: short-form consumers are 2.5 times more likely to abandon long-form educational content, and 52% of users skip videos longer than 60 seconds regardless of interest. Although influencer reels under 20 seconds generate 3.7× higher engagement, only 12% of viewers recall the featured brand, highlighting a recall gap.
- Overall, the findings suggest that while short-form formats boost immediate engagement, they erode long-term social media attention span and retention, creating trade-offs between visibility and meaningful cognitive impact.
Average Time Spent On Social Media By App
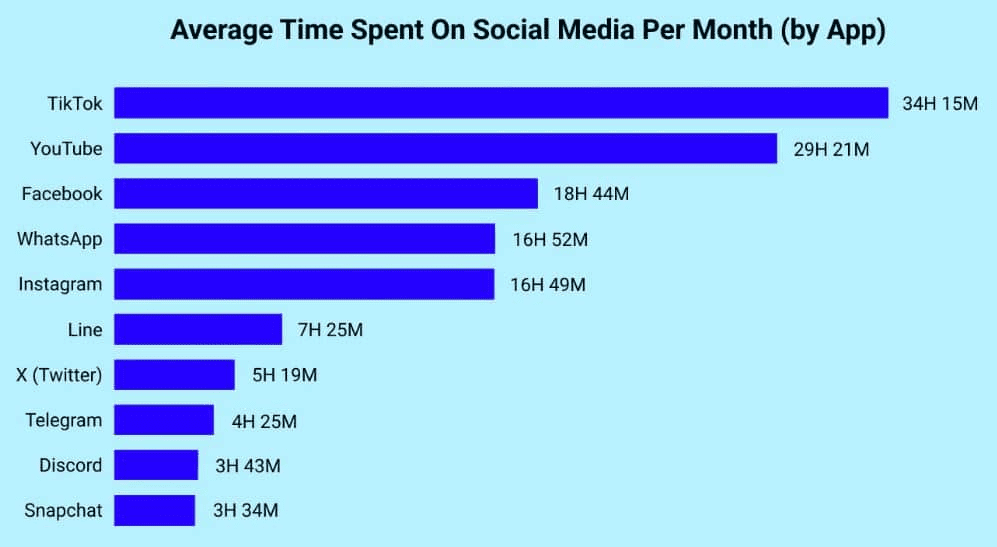
(Source: shopify.com)
- The design of scroll-based platforms like TikTok and Reels creates “scroll fatigue”, which impacts 61% of users between 18 and 34 years old. The people who watch micro-content for extended periods show a typical attention span that lasts less than 9 minutes.
- The first evidence of behavioral spillover shows that short-form content users will abandon long-form educational materials 2.5 times more than other users do.
- The users who watch videos that exceed 60 seconds skip content 52% of the time, which demonstrates their lack of interest.
- Social media platforms use short-form content to attract users, but they hurt users’ ability to think deeply about important content.
- TikTok emerges as the top platform for user engagement because users spend 34 hours and 15 minutes on the platform each month, which equals 69 minutes per day, because of its short videos that follow an algorithm-based approach.
- YouTube follows with 29 hours and 21 minutes monthly (59 minutes daily), reflecting strong demand for both short and long-form video consumption.
- Facebook establishes itself as the third platform because users spend 18 hours and 44 minutes on it each month, which shows people engage with the platform at a steady rate.
- The usage patterns of WhatsApp and Instagram show similar results, which show users spend 16 hours and 50 minutes per month on these visual platforms, resulting in 34 minutes of daily usage.
- The platforms X, Telegram, Discord, and Snapchat attract users who spend less than 12 minutes daily, which shows that these platforms serve specialized or task-oriented purposes.
Cognitive Impact Of Extended Social Media Consumption
- The prolonged period of social media usage demonstrates an analytical result because it decreases cognitive abilities while showing users’ ability to concentrate on social media content.
- Users who spend more than three hours on social media platforms face a 28% increased difficulty because they need to concentrate on their offline activities.
- Users who spend more than five hours on these platforms experience a 33% increased risk of experiencing attention interruptions.
- The process of fast content consumption leads to working memory decline because it causes an 11% decrease in mental capacity, which creates additional cognitive burden.
- Gen Z users experience scrolling fatigue because at least 40% of users need to take breaks after scrolling for more than 45 minutes.
- The average person checks their phone 96 times daily, which leads to multiple interruptions that break their focus and cause a 2.2 times increase in mistakes that happen during studying or working.
- The neurocognitive studies found that multiscreen users exhibit decreased prefrontal cortex activity and diminished function in brain regions that control their attention.
- Users who take breaks from social media platforms disclose a 42% increase in their capacity to complete tasks, which demonstrates that excessive platform usage decreases their ability to pay attention.
Most Utilized Social Media Platforms By Marketers
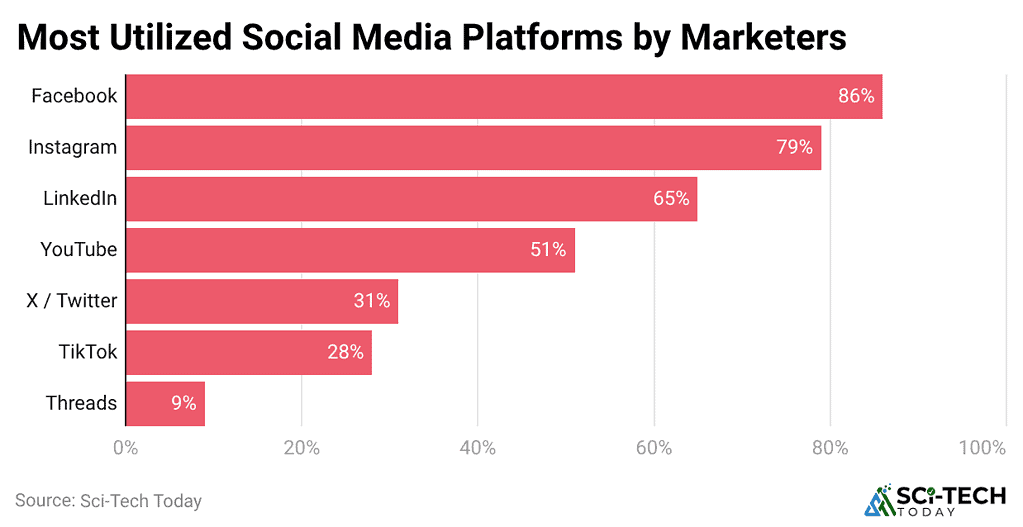
(Reference: sqmagazine.co.uk)
- Marketer adoption closely aligns with platform-level algorithm efficiency and its impact on social media attention span.
- The 86% usage rate of Facebook shows that its targeting tools and ranking systems have reached maturity, which enables businesses to achieve consistent ROI through mid-funnel campaigns.
- Instagram follows at 79% because its visual discovery features and influencer amplification enable users to maintain social media attention span during brief engagement periods.
- LinkedIn achieves 65% adoption because its algorithmic precision successfully identifies B2B segments that show professional relevance through their attentive behavior.
- YouTube usage at 51% occurs because its algorithm prioritizes watch time, which supports extended storytelling and maintains viewer engagement on social media platforms.
- Marketers show reduced adoption of X TikTok and Threads because they face three challenges, which include the changes in ranking systems, the errors in reach measurement, and the need to predict sustained audience engagement and conversion results.
Social Media Algorithm-Driven Changes In User Engagement Metrics
- The algorithmic prioritization of social media platforms creates user engagement metrics that show how social media platforms drive their users to interact with content.
- Platforms now reward creators for producing content that generates strong audience connections through their multiple interactive platforms, which include likes, comments, shares, and watch time.
- Studies show posts generating comments and shares receive up to 3× higher distribution than passive impressions, which reinforces shorter social media attention span cycles.
- Historical data from X (Twitter) shows that controversial content originally spread at twenty times slower than it does today because users tended to share emotional content after algorithms began promoting it through their emotional triggers.
- The current algorithms function as access control systems that determine whether creators and public figures can achieve quick visibility growth or visibility reduction.
- Social media platforms now see users interact with video-first content, which includes Reels and short clips at 40% to 60% higher rates because users spend less time on social media and select content based on specific formats.
Recent Advances In Attention Span Research And Digital Behavior
- Current studies from academic institutions and industry researchers demonstrate that when people consume digital content and use social media, they show distinct changes in their cognitive functions.
- A 2025 Harvard study shows mobile-first users exhibit 20% lower sustained attention than desktop users, reinforcing concerns about on-the-go usage patterns.
- 78% of Gen Z members experience phantom notification syndrome, according to MIT Media Lab research, which shows this condition takes Gen Z members out of their focused work periods.
- The analysis, which studied different times of day, found that users who scroll during the evening lost concentration at a rate that reached 32%.
- Neurotracking data from wearables displayed a 17% decrease in attention during the initial 90 seconds of using multiple applications.
- Meta research shows that users below 25 years of age now shift their attention every 39 seconds, which represents an increase from their 2020 attention span of 47 seconds.
- Stanford developed the Digital Focus Quotient in 2025 to measure digital focus changes.
- Startups and researchers create focus-first platforms that use attention cues to help people recover from cognitive fatigue while protecting their digital resource usage.
Conclusion
Social media attention span Statistics: The data from 2025 proves one truth that all people must understand because it shows how social media platforms use the scarcest resource, which they need to create their platforms. Social media attention span is shrinking because platforms use algorithms together with short video content, and their users who watch videos on mobile devices, and the current excess of available content. The platforms create better user experiences through their engagement speed improvements, yet these enhancements cause users to experience cognitive exhaustion, which leads to less focus ability and memory retention problems that will affect future generations.
Brands and creators need to achieve success through exact delivery methods, which should provide value within seconds while creating memorable experiences that deliver value to users. Digital platforms that present content through social media attention spans should use content delivery formats that pace their material and develop audience-specific methods.
FAQ
The average social media attention span ranges between 4 and 8 seconds, depending on age group and platform, with younger users showing the shortest focus duration.
Pre-teens and Gen Z have the shortest social media attention span, averaging 4.2 to 6.5 seconds per post on fast-scroll platforms.
TikTok leads with 69 minutes per day, driven by algorithmic short-form video that fragments social media attention span into frequent micro-sessions.
Mobile-first users show 20% lower sustained attention than desktop users due to fragmented, on-the-go consumption patterns.
Facebook (86%) and Instagram (79%) dominate marketer usage due to stable algorithms that efficiently capture social media attention spans.


